SCERT AP Board 9th Class Social Solutions 6th Lesson Agriculture in India Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Social Studies Solutions 6th Lesson Agriculture in India
9th Class Social Studies 6th Lesson Agriculture in India Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
Name one important beverage crop and specify the geographical conditions required for its growth.
Answer:
- Tea is an important beverage crop.
- The tea plant grows well in tropical and sub-tropical climates.
- Fertile, well-drained soil, rich in humus and organic matter is essential.
- Tea bushes require warm and moist frost-free climate all through the year.
- Frequent showers are necessary.
![]()
Question 2.
The land under cultivation has got reduced day by day. Can you imagine its consequences?
Answer:
- The land under cultivation has been reducing due to the competition for land between non-agricultural uses such as housing, etc.
- As a result, the productivity of India has started showing a declining trend.
- That would lead to the scarcity of food grains in future and in turn poverty and drought situation would prevail in our country.
Question 3.
On an outline map of India show millet producing areas.
Answer:
Question 4.
What is a Minimum Support Price (MSP)? Why is a MSP needed?
Answer:
1) A Minimum Support Price is a price at which the farmers can sell their grain, if they want, to the Government.
2) The Government sets the MSP so as to cover the cost of cultivation and allow a little bit of profit to the farmer.
3) Thus the farmer, produced far markets within the country.
4) The farmers are not forced to sell their grains at cheaper prices to the traders.
Question 5.
Explain all the ways the Indian government supported the Green Revolution.
Answer:
- The Green Revolution was initially introduced in Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh, and in some parts of Andhra Pradesh and Tamilnadu.
- The Government introduced new kinds of seeds, known as High Yielding Varieties to the Indian soils.
- It was also accompanied by use of chemical fertilizers, machinery such as tractors, and others besides irrigation facilities.
- A variety of cooperative banks were set up to provide credit to farmers so that they buy raw materials such as seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides, machinery required for modern farming.
![]()
Question 6.
Do you think it is important for India to be self-sufficient in food grain production? Discuss.
Answer:
- A large portion of our population especially children and poor communities are unable to get adequate nutrition.
- Whenever there were little rains, drought situations prevailed. This led to decrease in food production and forced government to import food grains.
- To avoid these kind of situations we should be self-sufficient in food grain production.
- A large stock of food grains has built-up with the government through Food
Corporation of India that could be used in case of shortage and can avoid drought and famine situations in our country.
Question 7.
How is dry land agriculture different from agriculture in other areas?
Answer:
- 45% of the cultivable land which cannot easily be irrigated and depend solely on rainfall is known as dryland in our country.
- Unlike the cultivation of irrigated lands, dryland farming poses different challenges.
a) Conserving rainfall that the area receives is the first step. This is done through watershed development programme which includes afforestation, bunding, building check-dams, and tanks.
b) Fertility of the soil needs to be raised by adding organic manure.
c) Farmers may also need new varieties of seeds suitable for different regions, knowledge about the best ways of growing a mix of crops on the same land etc.
Hence farming in dryland is different from other areas.
Question 8.
Can you recall the incidents such as pesticides being found in soft drinks? How is this related to the use of pesticides? Discuss.
Answer:
- The use of pesticides is polluting underground water.
- The soft drink factories use this underground water for making soft drinks.
- Hence undissolved pesticides are seen in soft drink.
Question 9.
Why is chemical fertilizer used in new farming methods? How could use of fertilizers make soil less fertile ? What are the alternative ways of enriching soil?
Answer:
- The chemical fertilizers are used to increase production of crops.
- But the chemical fertilizers are basically made for petro-chemicals. And eventually remain in the soil.
- As a result, many micro organisms like earth worms are destroyed.
- These micro organisms increase the fertlity of the soil. But these are detroyed and hence this, in turn, affects the long run fertility of the soil.
- The alternative ways of enriching soil, like vermicompost, can be used to increase the fertility of the soil.
![]()
Question 10.
How has the Green Revolution in some areas resulted in short-term gains but longterm losses to farmers?
Answer:
- In Green Revoluton, the farmers are encouraged to pump ground water to water-intensive crops in low rainfall areas.
- This unsustainable pumping has reduced water storage in ground.
- Consequently, many wells and tubewells have run dry.
- More over the use of chemical fertilizers has also affected the long-term fertility of the soil. Hence we can say that Green Revolution has short-term gains and long term losses.
Question 11.
What could be the effects of foreign trade on farmers’ income?
Answer:
- Foreign trade could cause farmers’ income to fluctuate a lot.
- In certain years and for certain crops the farmers might gain from exports.
- In other years, farmers could lose because of cheap imports and fall in prices of farm products.
- Small farmers without much savings will not be able to bear this loss.
- They will be caught in debt trap and become poorer.
- Hence the government must be careful in allowing trade in farm products.
Question 12.
In earlier classes we have studied about land distribution. How does the following image reflect this idea? Write a paragraph about this in the context of Indian agriculture.

Answer:
In India more than 70% of the farmers are having only small and marginal holdings,
i. e., Less than 2 hectares and hence most of these farms are not viable. The small farmers cannot produce enough to meet even their basic requirements of their families. They can invest more in agriculture to increase production. They are unable to get financial assistances.
Caption : “A man of sixty acres :
A group of six feet”.
Question 13.
Read the para under the title ‘Fertilizer Problems’ on page 70 and comment on it.
| Fertilizer Problems : Manure and compost contain humus and living organisms that slowly release minerals as they decompose. Chemical fertilizers provide minerals (usually nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium) which dissolve in water and are immediately available to plants, but may not be retained in the soil for long. They may be leached from the soil and pollute groundwater, rivers, and lakes. Chemical fertilizers (as well as pesticides) can also kill bacteria and other organisms in the soil. This means that some time after their use, the soil will be less fertile than ever before. Without micro-organisms, the soil will be dependent on frequent addition of more and more chemical fertilizers. The variety of nutrients which are normally produced by micro-organisms may also be reduced. Thus, in many areas, the Green Revolution has actually resulted in a loss of soil fertility and ever-increasing costs to farmers. |
Answer:
- The main environmental problem associated with fertilizer use is contamination of water with nitrates and phosphates.
- Elevated nitrogen levels in drinking water.
- Environmental pollution is a significant problem. But while most of the focus is placed on polluting industries, toxins like mercury and small particle traffic pollution, a major source of environmental devastation is caused by modern food production. Far from being life sustaining, our modern chemical dependent farming methods.
– Strip soil of nutrients
– Destroy critical soil microbes.
– Contribute to desertification and global climate change, and
– Saturate form lands with toxic pesticides, herbicides and fertilizers that then migrate into ground water, rivers, lakes and oceans.
![]()
Question 14.
Observe the map given in the page 74 and locate the States where paddy is grown in the India outline map.
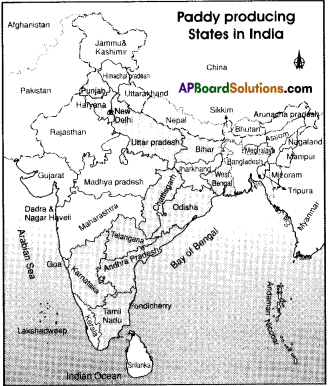
Answer:
- Punjab
- Haryana
- Uttar Pradesh
- Bihar
- West Bengal
- Chattisgarh
- Odisha
- Telangana
- Andhra Pradesh
- Karnataka
- Tamilnadu
Question 15.
Which crops are grown in your area? Which of these are grown from HYV seeds and which ones are grown from traditional seeds? Compare the HYV seeds and the traditional seeds with regard to each of the following points :
a) duration of crop
b) number of times irrigated
c) production
d) fertilisers
e) diseases
f) pesticides
Answer:
1. Paddy, sugarcane, maize, pulses are grown in our area.
2. Paddy is grown from HYV seeds and the remaining are grown from traditional seeds.
3.
| HYV Seeds | Traditional Seeds | |
| Duration of crop | Less | More |
| No. of times irrigated | Least | More |
| Production (comparatively) | More | Less |
| Fertilisers | Nominal quantity | Large quantity |
| Diseases | Least chancess | More chances |
| Pesticides | Right quantity | More quantity |
Question 16.
Conduct a Debate : Make the students two teams. One team should support chemical fertilizers and another should support organic farming.
Answer:
Teacher conducts this Debate.
Example : In agriculture it is better to be followed organic fertilizers.
Reasons :
Pesticides can enter the human body.
There is a chance of groundwater damage.
The use of fertilizers can reduce the natural nutrients on the soil surface, etc.
9th Class Social Studies 6th Lesson Agriculture in India InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Name some of the states of India where such farming is practised? (Text Book Page No. 59)
Answer:
Punjab, Haryana, Odisha, Karnataka, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar
Pradesh and some parts of Rajasthan.
Question 2.
Give some more examples of crops which may be commercial in one region and may provide subsistence in another region. (Text Book Page No. 60)
Answer:
1) In Haryana and Punjab, rice is a commercial crop whereas in Odisha it is a subsistence crop.
2) In Punjab, maize is a commercial crop whereas in Jharkhand it is a subsistence crop.
![]()
Question 3.
Distinguish which of these pulses are grown in the kharif season and which are grown in the rabi season? (Text Book Page No. 62)
Answer:
Pulses grown in the Kharif season :
Red gram, Black gram and Green gram.
Pulses grown in Rabi season :
Peas, Bean, Chickling vetch and Lentil.
Question 4.
Complete the bar diagram given on P.65 in Textbook and find out the percentage of cultivators and agricultural labourers in 1971 and 2001 respectively. (Text Book Page No. 65)
Answer:
- Student’s activity.
- Percentage of cultivators in 1971 = 62
- Percentage of agricultural labourers in 2001 = 46
Question 5.
In which decades the food grains yields grow fast? What could be probable reasons for this? (Text Book Page No. 69)
Answer:
The food grains yields grew fast between 1980 – 1990, 2000 – 2010.
The green revolution helped farmers to produce higher level of food grains.
Question 6.
Can organic farming produce enough food for all? (Text Book Page No. 72)
Answer:
If some measures are taken, I think, organic farming can produce food for all.
![]()
Question 7.
How is organic farming especially suited for small and marginal farmers? Discuss. (Text Book Page No. 72)
Answer:
Large sections of farmers in India and their land holdings are small and marginal.
Their access to external inputs is limited and their ability to improve production is low. Globalisation and the opening up of the trade barriers among the nations have resulted in the decline of agricultural prices in the local markets to the detriment of the interests of these small and marginal farmers. Thus organic farming especially is suited for small and marginal farmers.
Question 8.
Read the following table. (Text Book Page No. 66)
Number of farmers and land they possess in India (2010 – 2011)
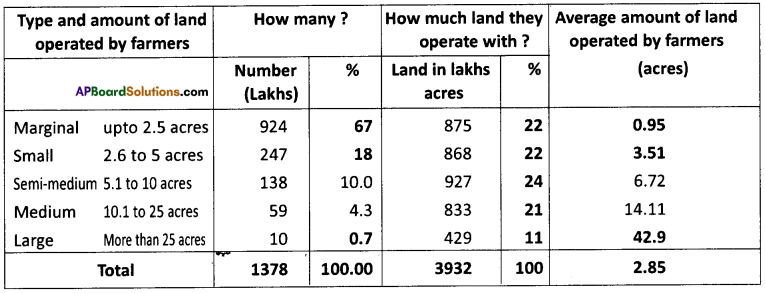
Complete the data in the table and the explanation in the following passage below.
Majority of farmers operate only small plots of lands. A typical Indian marginal farmer has only aboutacres to cultivate. There are 924 lakh farmers so that ..(2)..% of all farmers are marginal. If we add up the number of small and marginal farmers they form …(3)..% of all farmers. However, even though in percentage terms medium and large farmers is small, the number in absolute terms is large. ..(4)…lakh farmers can be together considered to be in this group. They have a powerful voice in rural areas. This group of large and medium farmers together operate …(5)…% of the land. Each large farmer for example on an average operates ..(6)..acres of land. Compare this with each marginal farmer who operates on an average ..(7)..acres of land. This inequality in distribution of land explains the inequalities in opportunities that they experience, the pov¬erty or growth opportunity that they face.
Answer:
- 2.5
- 67%
- 85%
- 69
- 32%
- 42.9 acres
- 0.95 acres.
Question 9.
Discuss the differences between self employment and looking for work using examples from your region. (Text Book Page No. 65)
Answer:
1. In self employment, people create their own employment and earn their livelihood. They do not depend either on government or an any other persons for their livelihood.
e.g.: Working in their own farms, opening a shop or public telephone booth or establishing a small organization like manufacturing of candles, matchboxes, etc.
2. On the other hand, some people cannot create their own employment. They generally depend either on government or on any other organization or a person for earning their livelihood.
e.g.: Working in the fields or others, or in a shop or working as government servant, etc.
Question 10.
Do you think that some families who were earlier cultivators are becoming agricultural labourers now? Discuss. (Text Book Page No. 65)
Answer:
Reasons:
- Small land holdings
- Dependency on seasons for rainfall
- High rate of interests on loans
- Very low minimum support price
- Lack of technology
- Big families and
- Some rituals.
All these changed the cultivators as agricultural labourers.
Question 11.
In which areas were the new methods of agriculture first tried? Why was the whole country not covered? (Text Book Page No. 68)
Answer:
1. The new methods were initially implemented in Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh and in some districts of Telangana, Andhra Pradesh and Tamilnadu.
2. The HYV seeds required a lot of water and these areas were already irrigated.
Hence the new methods were introduced in these areas.
![]()
Question 12.
Why are different methods necessary for dry land areas? (Text Book Page No. 68)
Answer:
- 45% of the land which cannot be irrigated are known as dry lands.
- It would be very difficult and expensive to irrigate these dry lands.
- These areas must depend solely on rainfall.
Hence different methods are necessary for dry land areas.
Question 13.
How increase in buffer stock would help to avoid situations of drought and famines? (Text Book Page No. 69)
Answer:
- A large stock of food grains should be maintained with the government.
- That buffer stock could be used in case of shortage of food grains and can also be used to supply foodgrains to inaccessible areas.
- We can also avoid drought and famine like situations in our country.
Question 14.
How farmers were able to raise higher amount of food grains on the same plot of land over the years? (Text Book Page No. 69)
Answer:
The use of High Yielding Varieties of seeds, chemical fertilizers, machinery, etc. made the farmers to raise higher amount of food grains on the same plot of land over the years.
Question 15.
Why did not the Indian government allow farmers to export foodgrains during the Green Revolution years? (Text Book Page No. 71)
Answer:
There would be a shortage of food grains if the government allows farmers to export food grains. So the government did not allow farmers to export food grains.
![]()
Question 16.
Why should government ban exports /import ? How does this policy help Indian farmers? (Text Book Page No. 71)
Answer:
Foreign trade could cause farmers income to fluctuate a lot. In some years farmers could lose because of cheap imports and fall in prices of farm products. So the exports ad imports should be banned.
Small farmers will not be able to bear this loss. They will get caught in debt trap and become poorer. So this ban helps the Indian farmers in preventing them from debts and heavy losses.
Question 17.
Use an atlas of India to find the locations of the below mentioned dams and mark them on a map of India. Also label the names of the major rivers on which these dams were built. (Text Book Page No. 67)
Answer:
- Bhakra-Nangal Project (Punjab)
- Nagarjuna Sagar Project (Telangana & Andhra Pradesh)
- Hirakund Project (Odisha)
- Damodar Valley (West Bengal)
- Gandhi Sagar (Madhya Pradesh)
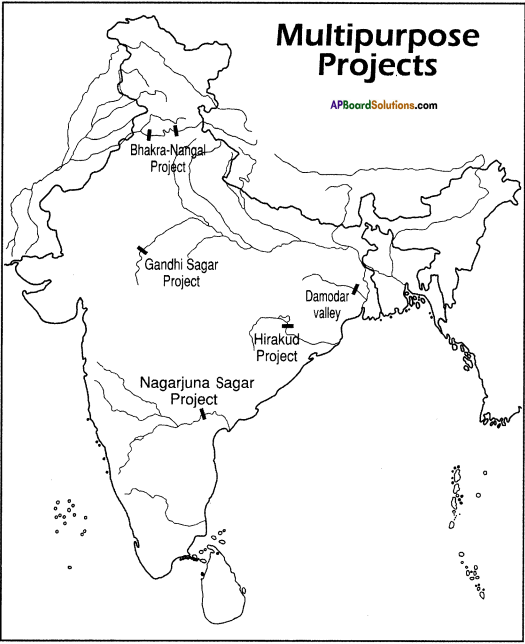
Question 18.
In your opinion, what would be the minimum amount of land required to do viable farming which would give a farmer a decent earning. How many farmers in the table Page No. 66 are doing viable farming? (Text Book Page No. 66)
Answer:
The minimum amount of land required to do viable farming may be 2 acres in my opinion. There are 67% of farmers do not have this minimum required land for viable farming.
![]()
Question 19.
Why only a small section of farmers have a powerful voice? (Text Book Page No. 66)
Percentage of large and medium farmers is 5% but they hold 32% of total cultivable land. Their average land holding is also high. Hence they have a powerful voice.