AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class Biology Solutions Chapter 1 Nutrition – Food Supplying System Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Biology Solutions 1st Lesson Nutrition – Food Supplying System
10th Class Biology 1st Lesson Nutrition – Food Supplying System Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve your learning
Question 1.
Write differences between
(a) Autotrophic nutrition – Heterotrophic nutrition:
Answer:
| Autotrophic nutrition | Heterotrophic nutrition |
| 1. Organism makes its own food. | 1. Organism can not makes its own food. |
| 2. Food is prepared from C02, water and sunlight. | 2) Food is prepared from other organism. |
| 3. Chlorophyll is required. | 3. Chlorophyll is not required. |
| 4. It takes place during day time. | 4. It takes place throughout the day. |
| 5. Examples are all green plants and photosynthetic bacteria. | 5. All animals, Fungi and some bacteria. |
![]()
(b) Ingestion – Digestion :
Answer:
| Ingestion | Digestion |
| 1. Taking in of food into the body through mouth is called ingestion. | 1. Breaking up of complex molecules of food into simple and small molecules is called digestion. |
| 2. Ingestion does not change the chemical and mechanical structure of food. | 2. Digestion changes the chemical and mechanical structure of food. |
(c) Light reaction – Dark reaction :
(OR)
Differentiate the reactions that take place in presence of light and the reactions which do not require light in photosynthesis.
Answer:
| Light reaction | Dark reaction |
| 1. It occurs in the grana of the chloroplast. | 1. It occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast. |
| 2. It occurs only in the presence of light. | 2. It occurs in the presence or absence of light. |
| 3. It occurs in the grana of the chloroplast. | 3. It occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast. |
| 4. Light reaction absorbs oxygen and light energy. | 4. Dark reaction absorbs only CO2 |
| 5. End products are O2, ATP and NADPH. | 5. End product is Glucose. |
| 6. Photolysis of water occurs. | 6. Carbon fixation occurs. |
| 7. First stage of photosynthesis. | 7. Second stage o: photosynthesis. |
(d) Chlorophyll – Chloroplast:
Answer:
| Chlorophyll | Chloroplast |
| 1. Chlorophyll is the green coloured pigment present in the chloroplast. | 1. It is the green coloured plastid enclosed by membranes. |
| 2. It contains one atom of magnesium. | 2. It consists of 3 membranes. |
| 3. It harvests solar energy and convert into chemical energy. | 3. It is responsible for enzymatic reactions leading to the synthesis of glucose. |
![]()
Question 2.
Give reasons.
a) Why photosynthesis is considered as the basic energy source for most of living world?
(OR)
Why can we say that photosynthesis is the basic energy source for the living world?
Answer:
- All living organisms constantly need energy to be alive.
- They get energy from the food they eat.
- The food directly or indirectly comes from the green plants through photosynthesis.
- Hence photosynthesis can be considered as the basic energy source for most of living world.
b) Why is it better to call the dark phase of photosynthesis as a light independent phase?
Answer:
- The term dark reaction or light independent does not mean that they occur when it is dark at night.
- It only means that the reactions are not depend on light.
- Hence we call the dark phase of photosynthesis as a light independent phase.
c) Why is it necessary to destarch a plant before performing any experiment on photosynthesis?
Answer:
1) To get better results, it is necessary to destarch a plant before performing any experiment on photosynthesis.
2) Because if starch is present it may interfere with the result of the experiment.
d) Why is it not possible to demonstrate respiration in green plants kept in sunlight?
Answer:
- We cannot demonstrate an experiment of respiration in green plants kept in sunlight.
- Because if sunlight is present, the C02 produced in respiration will be used in photosynthesis.
- So we must conduct an experiment on respiration in green plants in a dark room.
![]()
Question 3.
Give examples.
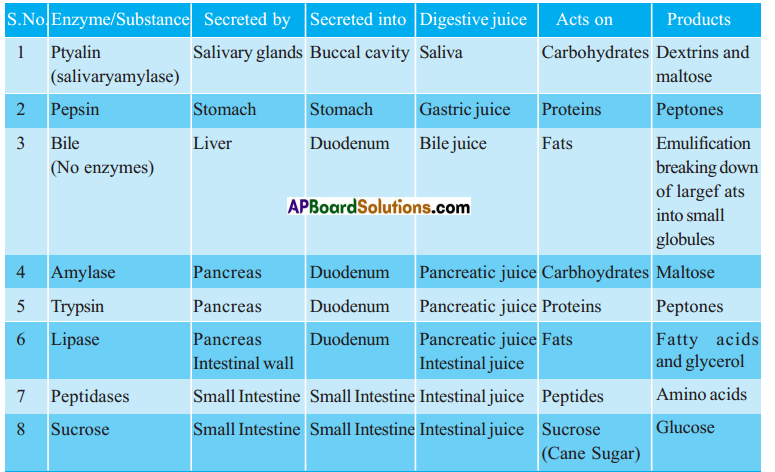
a) Digestive enzymes
Answer:
The digestive enzymes are:
- Salivary Amylase (Ptyalin),
- Pepsin,
- Trypsin,
- Lipase,
- Peptidases,
- Sucrase,
- Amylase (Pancreatic juice)
b) Organisms having heterotrophic nutrition is seen in organisms like:
Answer:
Heterotrophic nutrition is seen in organisms like:
- All animals and human beings.
- Some protozoans Ex: Amoeba.
- Some parasitic plants Ex: Cuscuta
- Saprophytes Ex: Bread moulds, yeast, mushrooms, etc.
c) Vitamins
Answer:
Water soluble vitamins:
B complex (B1) Thiamine, (B2) Riboflavin, (B3) Niacin, (B6) Pyridoxine,
(B12) Cyanocobalamine, Folic acid, Pantothenic acid, Biotin, (C) Ascorbic Acid.
Fat soluble: (A) Retinol, (D) Calciferol, (E) Tocoferol, (K) Phylloquinine.
d) Nutritional deficiency diseases
Answer:
Eg: Kwashiorkor, Marasmus etc.
![]()
Question 4.
Where do plants get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis?
Answer:
| Raw materials | Sources |
| External factors: 1. Carbondioxide |
Atmosphere |
| 2. Sunlight | Sun |
| Internal factors: 3. Water |
Ground water |
| 4. Chlorophyll and enzymes | Present in leaf. |
Question 5.
Explain the necessary conditions for autotrophic nutrition and what are its by products.
Answer:
A. Necessary conditions:
- Autotrophic nutrition takes place through the process of photosynthesis.
- Carbon dioxide, water, chlorophyll pigment and sunlight are the necessary conditions required for autotrophic nutrition.
- The rate of photosynthesis depends on availability of sunlight.
B. By products:
- Photosynthesis is the main process for autotrophic nutrition.
- Carbohydrates and oxygen are the by products of photosynthesis.
Question 6.
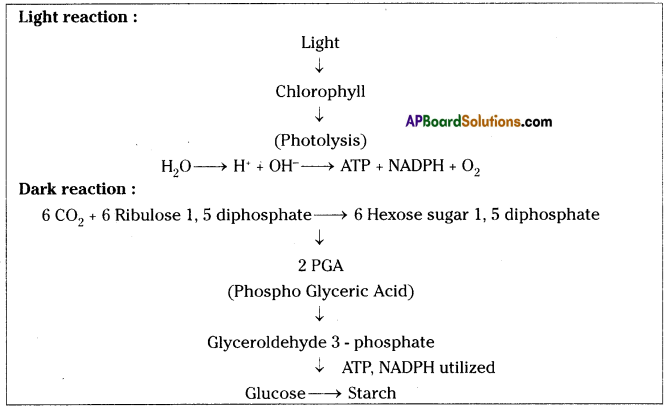
With the help of chemical equation explain the process of photosynthesis In detail with the help of a flow chart.
Answer:
Process of photosynthesis:
- The chemical equation representing the process of photosynthesis is

- Definition: Photosynthesis is a photochemical reaction during carbohydrates are formed using carbon dioxide and water in the chloroplasts of the green plants in the presence of sunlight.
- CO2 water, sunlight and chlorophyll are the requirements of photosynthesis.
- Glucose, O and water are the end products of the reaction.
- Photosynthesis have two phases.
1) Light reaction 2) Dark reaction - Light reaction have three steps, i) Oxidation of chlorophyll ii) Photolysis iii) Formation of ATP, NADPH and O2
- In dark reaction CO2 is utilized and finally glucose is formed which is converted and stored as starch.
FLOW CHART:
Question 7.
Name the three end products of photosynthesis.
Answer:
Glucose, oxygen and water are the three end products of photosynthesis.
![]()
Question 8.
What is the connecting substance between light reaction and dark reaction?
Answer:
The hydrogen of NADPH present in the stroma is the connecting substance between light reaction and dark reaction.
Question 9.
Most leaves have the upper surface is more green and shiny than the lower ones. Why?
(OR)
In most of leaves the upper surface will be more green and shiny than the lower surface. Why?
Answer:
- The upper surface comprising of the palisade parenchyma.
- The lower surface comprising of the spongy parenchyma.
- Palisade parenchyma contains more number of chloroplasts than the spongy parenchyma.
- Thus the upper surface is more green and shiny than the lower ones.
Question 10.
Explain the structure of chloroplast with a neatly labelled sketch.
(OR)
Explain the structure of a chloroplast with the help of a rough diagram.
Answer:
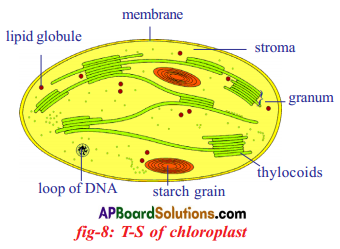
- Chloroplast is a membranous structure consisting of 3 membranes.
- The third layer forms stacked sac like structures called granum.
- The intermediatery fluid filled colourless portion is called stroma.
- It is responsible for enzymatic reaction leading to the synthesis of glucose in plants.
- Substances found in chloroplast, capture sunlight are called photosynthetic pigments.
- Chlorophyll pigment contain one atom of magnesium.
- Two major kinds of chlorophylls are associated with thyakoid membranes.
- Chlorophyll-a is blue-green in colour and chlorophyll-b is yellow-green colour.
- Around 250-400 pigments molecules are grouped as light harvesting complex units in granum.
- Some of the events occur in chloroplast are :
a) Conversion of light energy to chemical energy.
b) Splitting of water molecule.
c) Reduction of carbondioxide to carbohydrates.
![]()
Question 11.
What is the role of acid in stomach?
Answer:
- The internal walls of stomach has number of gastric glands. They secret gastric juice.
- It contains HCl and enzymes.
- HCl kills the bacteria present in the food and protects us from their harmful effects.
- And also denatures the proteins so that enzymes can act easily on them.
Question 12.
What is the function of digestive enzyme?
Answer:
- The function of digestive enzyme is to increase the process of breaking up of complex molecules into simpler and absorb molecules.
- This makes easy for the body to absorb food.
Question 13.
How is the small intestine designed to absorb digested food? Explain.
(OR)
How is food absorbed by villi in small intestine?
Answer:
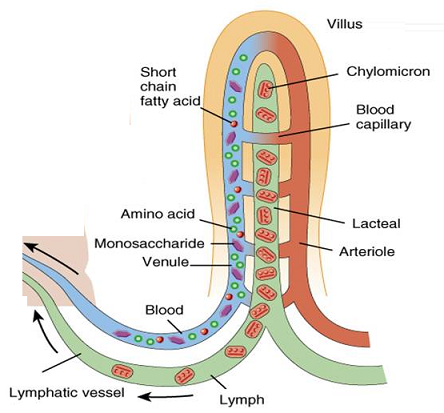
- Small intestine is the largest part in digestive system.
- Absorption is its main function including last stage of digestion.
- The inner surface of small intestine has millions of tiny finger-like projections called villi.
- Due to the presence of villi, the absorbing surface area of small intestine increases.
- And the large surface area of small intestine helps in the rapid absorption of digested food.
- The digested food which is absorbed through the walls of the small intestine goes into our blood.
- Long and folding structure increase the ability of small intestine.
![]()
Question 14.
How are fats digested in our bodies? Where does this process take place?
What is emulsification? How it helps in digestion of fats? (OR)
How are fats digested? Where do they get digested?
Answer:
- Bile juice and lipase enzymes helps in fat digestion.
- Bile juice is secreted by liver.
- Fats are digested by converting them into small globules like forms by the help of the bile juice.
- This process is called emulsification.
- Lipase enzyme is secreted by pancreas.
- It converts emulsified fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
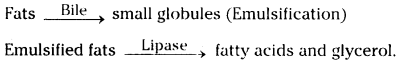
- This process takes place in duodenum and small intestine.
Question 15.
What is the role of saliva in the digestion of food ?
(OR)
How does saliva digest food ?
Answer:
- Saliva is secreted by three pairs of salivary glands present in the mouth.
- Human saliva contains an enzyme called amylase (ptyalin).
- It converts starch into maltose (a sugar).
- The food is mixed thoroughly with saliva and becomes wet and slippery.
- Saliva helps in the smooth passage of food in the food pipe.
Question 16.
What will happen to protein digestion as the medium of intestine is gradually rendered alkaline ?
Answer:
- The food coming from the stomach to intestine is acidic in nature.
- Bile and pancreatic juices render the internal condition of the intestine gradually to a basic or alkaline one.
- Protein digestion continues even if the medium of intestine is gradually changed to alkaline.
- In the alkaline medium pancreatic enzyme trypsin can act on the food and digests the proteins.
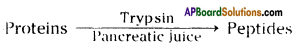
- The enzymes present in the intestinal juice like peptidases complete the digestion of proteins into amino acids.
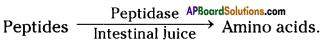
![]()
Question 17.
What is the role of roughages in the alimentary tract?
Answer:
- Roughages are the fibres of either carbohydrates or proteins.
- Plenty of roughages in the diet avoid constipation.
- Roughages help in the easy movement of faeces in the large intestine.
- They help in the easy digestion of food and keep the alimentary canal clean and healthy.
Question 18.
What is malnutrition? Explain some nutrition deficiency diseases.
Answer:
Malnutrition: Eating of food that does not have one or more than one nutrients in required amount is known as malnutrition.
Malnutrition is of three types:
- Calorie malnutrition,
- Protein malnutrition,
- Protein calorie malnutrition.
Nutrition deficiency diseases:
- Kwashiorkor disease: This is due to protein deficiency in diet.
Symptoms:
i) Body parts becomes swollen due to accumulation of water in the intercellular spaces,
ii) Very poor muscle development,
iii) Swollen legs,
iv) Fluffy face,
v) difficult to eat,
vi) diarrhoea,
vii) Dry skin. - Marasmus: This is due to deficiency of both protein and calories. Generally this disease occurs when there is an immediate pregnancy or repeated child births.
Symptoms:
i) Lean and weak,
ii) Swelling in joints of limbs,
iii) Less developed muscles,
iv) Dry skin,
v) diarrhoea.
![]()
Question 19.
How do non-green plants such as fungi and bacteria obtain their nourishment?
Answer:
- Bacteria and fungi are non-green plants. So they cannot prepare their own food materials.
- They are saprophytes which feed on dead and decaying plant and animal bodies.
- The fungi and bacteria breakdown the complex organic molecules present in dead and decaying matter by releasing chemical substances into simple substances out¬side the body.
- These simpler substances are then absorbed by fungi and bacteria as their food.
Question 20.
If we keep on increasing CO2 concentration in the air, what will be the rate of photosynthesis?
Answer:
- If the CO2 concentration in the air increases, the rate of photosynthesis also increases.
- If the CO2 concentration raises above 5% then the rate of photosynthesis reduces.
- At certain CO2 concentration the rate of photosynthesis is constant.
- Here a rise in CO2 levels has no affect on the rate of photosynthesis as the other factors such as light intensity become limited.
Question 21.
What happens to plant if the rate of respiration becomes more than the rate of photosynthesis ?
Answer:
- Respiration is a catabolic (destructive) process and photosynthesis is an anabolic (constructive) process.
- If the rate of respiration becomes more than the rate of photosynthesis, the amount of food oxidised will be more than the food produced.
- This affects the growth and development of plants and may even results in the death of the plant.
![]()
Question 22.
Why do you think that carbohydrates are not digested in the stomach?
(OR)
Where are carbohydrates digested in alimentary canal?
Answer:
- For the digestion of carbohydrates enzyme ptyalin or amylase are required.
- The gastric juice produced by stomach do not contain the enzyme ptyalin or amylase, it contains only pepsin which digests proteins.
- Hence carbohydrates are not digested in the stomach.
- Carbohydrates are partially digested in the mouth and completely in small intestine.
Question 23.
What process do you follow in your laboratory to study the presence of starch in leaves?
(OR)
(Activity – 1)
How do you test the presence of starch in leaves ? (OR)
Mention the materials required and explain the experiment to prove the presence of starch in leaves. What inference do you draw from this experiment?
Answer:
Aim: To study the presence of starch in leaves.
Apparatus: Beaker, test tube, bunsen burner, tripod stand, asbestos gauze, ethanol, leaf, petridish, iodine solution.
Procedure:
- Select a leaf of a potted plant with soft thin leaves.
- Boil the leaf in methylated spirit over a water bath till it becomes pale white due to the removal of chlorophyll.
- Observe the leaf.

- Spread the leaf in a dish and add a few drops of tincture iodine / betadine solution on it. Again observe the leaf.
Observation: The presence of starch will be indicated by a blue-black colour in leaf. Result: The experiment proves that starch is present in leaves. It is formed by Photo-synthesis.
Precautions:
- Do not boil the methylated spirit test tube directly on flame.
- Boil the water bath with low flame.
![]()
Question 24.
How would you demonstrate that green plants release oxygen when exposed to light? (OR) (Lab Activity)
Write the experimental procedure to prove that oxygen is produced during photosynthesis in the presence of light. (OR)
What materials are required to prove that oxygen is produced during photosynthesis in the presence of light? What procedure we need to follow to perform the above experiment?
We have conducted experiment that prove the release of oxygen when photosynthesis happens?
i) What are the plants used for this experiment? Where do they grow?
ii) How did you conduct the above experiment? In which context large number of air bubbles released? Do you noticed?
Answer:
i) Hydrilla plants are used for this experiment they grow in water.
ii) Experiment to demonstrate the release of oxygen during photosynthesis.
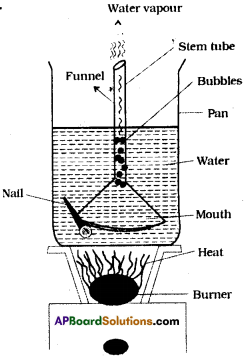
Aim: To prove that oxygen is produced during photosynthesis by hydrilla funnel experiment.
Apparatus: Beaker with water, test tube, funnel, hydrilla twigs, glowing splinter.
Procedure:
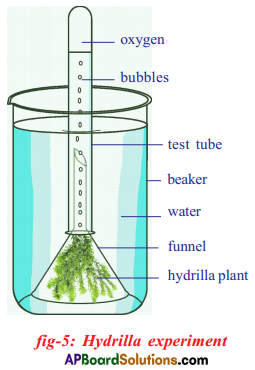
- Arrange the apparatus as shown in the figure.
- Place some water plant hydrilla in a beaker containing pond water, and cover these by a short stemmed funnel.
- Invert a test – tube full of water over the stem of the funnel.
- Ensure that the level of water in the beaker is above the level of stem of the inverted funnel.
- Place the apparatus in the sun for at least 2 or 3 hours.
- After sometime it is observed that gas bubbles come from the hydrilla plant. These bubbles are collected at the end of the test tube pushing the water into the beaker.
- After sufficient gas is collected test – tube is taken out of the beaker carefully by closing it with thumb.
Observation: Test the gas in the test – tube by inserting a glowing incense stick which would burst into flames. This shows the presence of oxygen.
Result: This shows that oxygen is produced during photosynthesis.
Precautions:
- Funnel should be smaller than the beaker.
- Necessary care is to be taken while removing the test tube from the stem of the funnel.
![]()
Question 25.
Collect information from your primary health centre of malnutrition child at various ages and make a table your own and display in the classroom.
 Answer:
Answer:
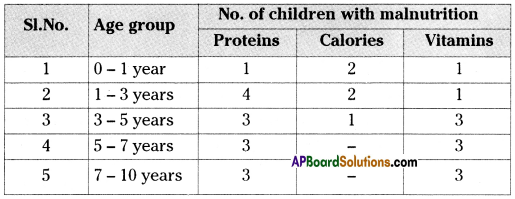
Question 26.
If there were no green plants, all life on the earth would come to an end ! Comment.
(OR)
The survival of organisms would become difficult, if there are no green plants on the earth. How do you support?
Answer:
- Plants play the most important part in the cycle of nature.
- Without plants there could be no life on earth.
- Plants are the only organisms that can make their own food and all other living beings directly or indirectly depend on plants for their food.
- Moreover plants release oxygen into the atmosphere through photosynthesis.
- Oxygen is essential for the organisms to respire.
- Hence without green plants, all life on the earth would come to an end.
Question 27.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of chloroplast found in leaf, and its role in photosynthesis.
Answer:
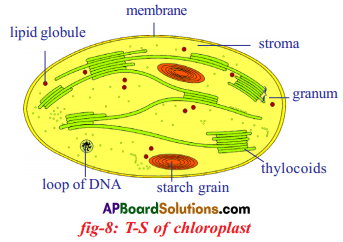 Role of Chloroplast in photosynthesis:
Role of Chloroplast in photosynthesis:
- Chloroplasts trap solar energy.
- They convert that solar energy into chemical energy.
- They help in the formation of glucose.
![]()
Question 28.
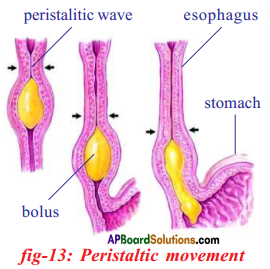
Draw the label diagram of human digestive system. List out the parts where peristalsis takes place.
Answer:
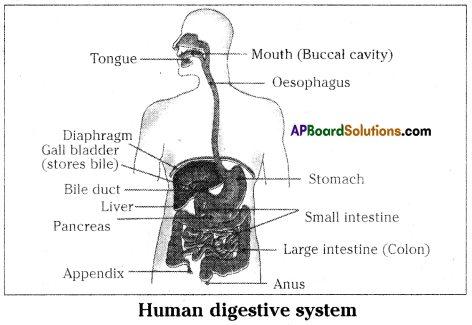 Parts where peristalsis takes place: Oesophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine.
Parts where peristalsis takes place: Oesophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine.
Question 29.
Raheem prepared a model showing the passage of the food through different parts of the alimentary canal. Observe this and label its parts.
 Answer:
Answer:
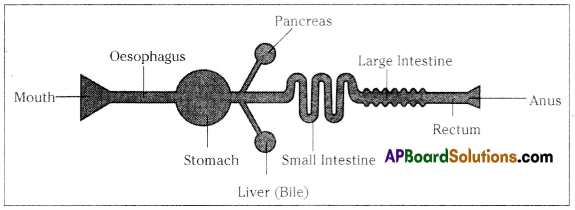
![]()
Question 30.
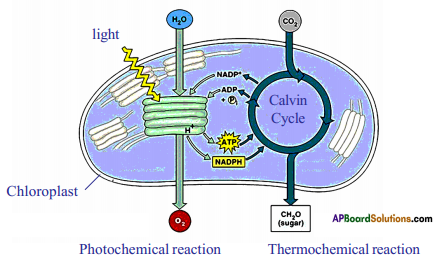
Observe the following diagram and write a note on light dependent, light independent reactions.
 Answer:
Answer:
Note on light dependent reactions:
- Light dependent reactions are also called as photochemical phase.
- The light dependent reaction takes place in chlorophyll containing thylakoids called grana of chloroplasts.
- Several steps occur in the light dependent reaction.
- Step – 1: The chlorophyll on exposure to light energy becomes activated by absorbing photons.
- Step – II: The energy is used in splitting the water molecule into two component ions named hydrogen (H+), hydroxyl ion (OH–). This reaction is known as photolysis.
- Step – III: OH– ions through a series of steps produce water (H2O) and O2.
- The end products of light reaction are ATP, NADPH and O2.
Note on dark reaction or light independent reaction:
- In light independent phase the hydrogen of the NADPH is used to combine it with CO2, by utilizing ATP energy and to produce glucose.
- This synthesis occurs in a number of steps using certain special intermediate compounds (mainly RUBP – Ribulose hi phosphate) and enzymes. Finally glucose is converted to starch.
- All these reactions occur in the stroma region of the chloroplast.
Question 31.
Almost all the living world depends on plants for food material. How do you appreciate the process of making food by the green plants?
(OR)
What facts about the green plants do you appreciate?
Answer:
Leaf is a wonderful machine to synthesize food:
- The leaf is the important site of photosynthesis and is called as food factory of the plant.
- This plant organ can be treated as a wonderful natural machine which converts solar energy into useful chemical energy.
- With all his scientific knowledge and technical skills, man has not produced anything similar leaf for utilization of solar energy without polluting the atmosphere.
- This machine provides food and supports the life by providing oxygen for all the organisms including man on this planet.
- Nature has given us such a wonderful machine free !!
![]()
Question 32.
Even a hard solid food also becomes smooth slurry in the digestive system by the enzymes released at a particular time. This mechanism is an amazing fact. Prepare a cartoon on it.
Answer:
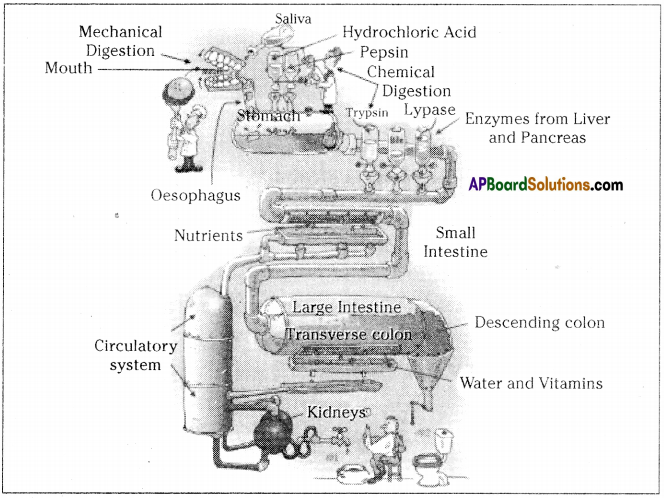
Question 33.
What are good food habits?
Answer:
The food habits I am going to follow after reading this chapter are:
- I take balanced diet which contains proper amounts of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals.
- I avoid taking food containing high proportion of fat.
- I eat food as much required by my body. I do not over eat.
- I will not eat rich meals over several days.
- I eat simple balanced meals, eat it leisurely and thoroughly masticating the food.
- I avoid doing violent exercise soon after eating food.
- I empty the bowels regularly avoiding constipation.
- I will see to have plenty of roughages in the diet.
(OR)
After reading the chapter nutrition, I would like to follow the following food habits.
- Having simple, well balanced meals.
- Eating them in a leisurely manner.
- Thoroughly masticating the food.
- Avoiding strenuous exercise soon after eating food.
- Drinking plenty of water and having regular bowel movement.
- Decreasing consumption of coffee or tea per day.
- Taking leafy vegetables at least 3 times a week and taking of fruits and vegetables plenty.
- Maintaining regular timings for daily food consumption.
![]()
Fill in the blanks.
- The food synthesized by the plant is stored as ———–.
- ———– are the sites of photosynthesis.
- Pancreatic juice contains enzymes for carrying the process of digestion of ———– and ———–.
- The finger-like projections which increases the surface area in small intestine are called ———–.
- The gastric juice contains ———– acid.
- ———– vitamin is synthesized by bacteria present in intestine.
Answer:
- carbohydrates
- Chloroplasts
- proteins, fats
- Villi
- HCl
- Cyanocobalamin
Choose the correct answer.
- Which of the following plant take the food by parasitic nutrition? [ ]
A) Yeast
B) Mushrooms
C) Cuscuta
D) Leeches
Answer: C & D - The rate of photosynthesis is not affected by [ ]
A) Light intensity
B) Humidity
C) Temperature
D) Carbon dioxide concentration
Answer: B - A plant is kept in dark cupboard for about forty eight hours before conducting any experiment on photosynthesis in order to [ ]
A) Remove chlorophyll from leaves
B) Remove starch from leaves
C) Ensure that no photosynthesis occurred
D) Ensure that leaves are free from the starch
Answer: B - The digestive juice without enzyme is [ ]
A) Bile
B) Gastric juice
C) Pancreatic juice
D) Saliva
Answer: A - In single-celled animals, the food is taken by [ ]
A) the entire body surface
B) mouth
C) teeth
D) vacuoles
Answer: A - Which part of the plant takes in carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis? [ ]
A) Root hair
B) Stomata
C) Leaf veins
D) Sepals
Answer: B
10th Class Biology 1st Lesson Nutrition – Food Supplying System Activities
Activity – 1
How do you prove experimentally that carbon dioxide is necessary for photosynthesis by Mohl’s half leaf experiment?
(OR)
List out the materials required and the procedure to be followed to prove that ‘carbon dioxide’ is essential for photosynthesis.
(OR)
You know that the factors like CO2, Light and Chlorophyll are essential for photosynthesis. Write any one of experiment related to the factors essential for photosynthesis.
Answer:
Aim:
To prove-that carbon dioxide is essential for photosynthesis by Mohl’s half leaf experiment.
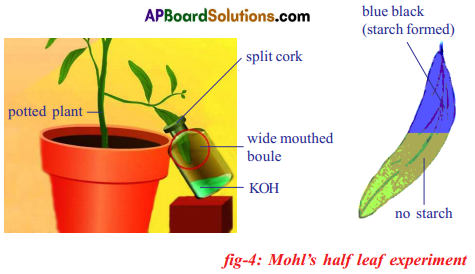 Apparatus:
Apparatus:
Wide mouthed transparent bottle, KOH solution, potted plant, vertically split cork, Iodine solution.
Procedure:
Arrange the apparatus as shown in the figure.
- Take a healthy potted plant and keep it in the dark for nearly a week for the removal of starch from the leaves.
- A wide mouthed transparent bottle is taken.
- Put potassium hydroxide pellets or potassium hydroxide solution (KOH) in the bottle.
- This KOH absorbs CO2 present in the bottle.
- Insert splitted cork in the mouth of the bottle.
- Insert one of the leaves of destarched plant through a split cork into transparent bottle.
- Arrange half of the leaf is inside bottle and the remaining half outside.
- Leave the plant in the sunlight for 2-3 hours.
- After a few hours, test this leaf and other leaf of this plant for starch.
![]()
Observation :
- The part of the leaf outside the bottle turns blue-black because starch is formed in this part due to photosynthesis.
- The part of the leaf inside the bottle does not turn blue-black because the carbon dioxide present inside the bottle is absorbed by potassium hydroxide solution.
- All the other factors water, sunlight and chlorophyll are available but not CO2. Hence starch is not formed in the leaf part which is inside the bottle.
Result: This experiment proves that CO2 is necessary for photosynthesis. Precautions:
- The part of the leaf kept inside the bottle should not touch potassium hydroxide solution.
- The apparatus should be kept air tight by applying grease or vaseline.
Activity – 2
Sunlight is necessary to form starch in green leaves.
(OR)
Write the materials required and the procedure to prove that light is essential for Photosynthesis.
(OR)
Write the procedure, precautions and observations in the lab activity, “Sunlight is necessary for photosynthesis”.
Answer:
Aim:
To prove that light is necessary for photosynthesis to form starch.
Apparatus:
Potted plant, light screen, iodine solution.
- Keep potted plant in dark for one week to remove starch.
- Take one black paper and cut it with your own design.
- Keep design paper properly on the both sides with the help of clips.
- Ensure that light does not pass through the covered area with black paper.
- Keep the arranged apparatus at sunlight available area.
- After few hours of exposure to bright sunlight detach the leaf.
- Boil the leaf in methylated spirit over water bath. It becomes pale white due to the removal of chlorophyll. Take the leaf from test tube and spread the leaf in a petridish.
- Add few drops of Iodine on leaf. The parts of the leaf, which could get light through the cut out design, turns blue-black colour.
- The parts of the leaf which could not get light are not turned into blue – black colour.

Observation:
It is observed that only the parts of the leaf, which could get light through the cut out design, turn blue black, showing the presence of starch.
Result:
This experiment proves that light is necessary to form starch in the process of photosynthesis.
![]()
Activity – 3
Demonstrate litmus paper test on salivary amylase in the mouth.
Answer:
- Before taking food into the mouth, take a litmus indicator paper and touch it to the tongue.
- We observe no colour change in litmus paper.
- Perform the litmus test again after chewing the food and swallowing it.
- The red litmus paper turns to blue colour.
- The blue litmus paper do not turns to red colour.
- This demonstrates that amylase converts complex carbohydrates to simple sugar.
- Amylase is alkaline in nature. This turns litmus paper blue when touches glucose at the second time.
Activity – 4
Observe different digestive enzymes and their role in digesting food in a tabular form.
Answer:
10th Class Biology 1st Lesson Nutrition – Food Supplying System InText Questions and Answers
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 2
![]()
Question 1.
Can you think of some raw materials needed for photosynthesis?
Answer:
Yes. Photosynthesis needs the following raw materials.
- Sunlight, CO2 water are external factors.
- Chlorophyll and enzymes are internal factors.
Question 2.
What could be the end products of the process of photosynthesis?
Answer:
Glucose, water and oxygen are the end products of photosynthesis.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 4
Question 3.
Do you think solar energy transforms into chemical energy by the process of photosynthesis?
Answer:
Yes, solar energy transforms into chemical energy by the process of photosynthesis.
Question 4.
What are the materials that you think would be essential for the synthesis of carbohydrates in the process of photosynthesis?
Answer:
The materials essential for the synthesis of carbohydrates in the process of photosynthesis are carbon dioxide, water, sunlight and chlorophyll.
Question 5.
Do you think the equation tells us about all the materials involved?
Answer:
Yes, the materials which are essential for photosynthesis and the products formed are involved in the equation.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 5
![]()
Question 6.
What had Priestly done to introduce the mint plant without disturbing the experimental setup?
Answer:
 Priestly should have tilted the bell jar to one side and introduced the mint plant without disturbing the experimental set up.
Priestly should have tilted the bell jar to one side and introduced the mint plant without disturbing the experimental set up.
Question 7.
How did Priestly light the candle from outside?
Answer:
Priestly might have used convex lens through which beam of sun rays can light the candle from outside or he might have used long burning stick, to light the candle by lifting the jar partially.
Question 8.
Do you find any relationship between candle, rat, mint plant? Discuss.
Answer:
Priestly’s experiment confirmed that gaseous exchange was going on and plants were giving out a gas that supported burning and was essential for the survival of animals.
By combustion process candle releases carbondioxide. By respiration process rat also releases carbondioxide. During photosynthesis process mint plant uses this carbondioxide and releases oxygen. This oxygen will be used by rat to stay alive and for the candle to burn.
So there is a relationship between respiration and photosynthesis by candle, rat and mint plant.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 6
Question 9.
Why was the plant kept in dark and then in sunlight?
Answer:
- The plant is kept in the dark for nearly a week to remove the starch from the leaves.
- Then only we can understand that the starch is formed in the leaves or not after the experiment when the plant is kept in the sunlight.
![]()
Question 10.
Why did we study two leaves in the Mohl’s half leaf experiment?
Answer:
- To test CO2 is essential or not for photosynthesis, two leaves are used in the experiment.
- One leaf with the plant and another one used in the experiment.
- The leaf which is exposed to the atmospheric air becomes bluish-black. It proves that starch is prepared in the leaf by using CO2 from atmosphere.
- The leaf inside the flask containing potassium hydroxide, which absorbs CO2 present in the bottle does not become bluish black. It shows that CO2 is necessary for photosynthesis.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 7
Question 11.
What precautions do you need while removing test tube from the beaker? Discuss with your teacher.
Answer:
- When sufficient gas is collected lift the test tube carefully from the beaker by closing its mouth with the thumb.
- Because of that the gas present in the test tube cannot escape into the atmosphere.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 8
Question 12.
Which part of leaf turns blue black? What about the remaining part?
Answer:
- The part of the leaf, which could get light through the cut design turns to blue black showing the presence of starch.
- The remaining part of the leaf which did not get light, do not turn blue, indicating that starch is not prepared.
Question 13.
Observe the colour of the leaf stained with iodine. Can you tell why it is stained differently?
Answer:
- Some parts of the leaf prepared starch.
- Some parts of the leaf does not prepared starch.
- So it is stained differently.
![]()
Question 14.
What about plants having coloured leaves?
Answer:
Plants having coloured leaves also carry out photosynthesis. The coloured leaves containing pigments pass on the energy of sunlight trapped by them to chlorophyll.
Question 15.
How is that new leaves which look dark red in colour in several plants turn green?
Answer:
- The new leaves which look dark red in colour contain coloured chromoplasts.
- As the leaf grows the chromoplasts turns to chloroplasts and the leaf appears green in colour.
Question 16.
Do plants having reddish or yellowish leaves also carry out photosynthesis?
Answer:
- Yes. Plants having reddish or yellowish leaves also carry out photosynthesis.
- The pigments present in reddish or yellowish leaves pass on the energy of sunlight trapped by them to chlorophyll.
Question 17.
What made plants carry out photosynthesis while even green coloured animals (like some birds) could not?
Answer:
- Chlorophyll and other pigment molecules trap (harvest) solar energy, convert it into chemical energy in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast.
- But animals having green colour on their body cannot trap solar energy and cannot perform photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is possible only in plants but not in animals.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 9
![]()
Question 18.
Where is chlorophyll and other pigments present in the plant?
Answer:
Chlorophyll and other pigments are present in the grana thylakoids of chloroplast in leaf.
Question 19.
Do you think the new reddish leaves of plants also carry out photosynthesis? What could be the role of their colour?
Answer:
- Yes. New reddish leaves of plants also carry out photosynthesis.
- Chromoplasts are responsible for the reddish colour of leaves.
- They also pass on the energy of sunlight which they trap to the photosystems.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 10
Question 20.
What makes chloroplast appear completely different from other cell organelles?
Answer:
- Substances found in chloroplast, which capture sunlight are called photosynthetic pigments.
- Two major kinds of chlorophyll are associated with thylakoid membranes.
- Chlorophyll – a (blue – green in colour) and chlorophyll – b (yellow – green); around 250 to 400 pigment molecules are grouped as light harvesting units in each granum.
- Such innumerable units in chloroplasts make them appear completely different from other organelles.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 13
![]()
Question 21.
What happens to the food once it enters our body?
Answer:
- The food once enters our body it gets digested by various enzymes in different parts of alimentary canal.
- Digestion starts in the mouth and it completes in the small intestine.
- Finally it absorbed in the small intestine into the circulatory system.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 15
Question 22.
Name the enzymes which act on carbohydrates.
Answer:
Ptyalin (salivary amylase), amylase and sucrose are the enzymes that act on carbohydrates.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 16
Question 23.
What are the end products of fats?
Answer:
The end products of fats are fatty acids and glycerol.
Question 24.
What are the enzymes that act on proteins?
Answer:
Pepsin, Trypsin and Peptidases are the enzymes that act on proteins.
Question 25.
Which digestive juice contains no enzymes?
Answer:
Bile juice produced by liver contains no enzymes.
![]()
Question 26.
What do you think about the process of digestion?
Answer:
- The process of digestion occurs in the alimentary canal or digestive system.
- During the process of digestion large complex macro molecules present in the food are converted to simple and small molecules.
- Digestion provides the food material properly absorbed by the body.
Question 27.
What are the major steps of digestion?
Answer:
The major steps of digestion are
- Ingestion
- Digestion
- Absorption and
- Defecation.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 18
![]()
Question 28.
Collect information about pellagra and discuss with your teacher.
Answer:
- Pellagra is a vitamin-deficient disease.
- Niacin (Vitamin – B3) is essential for the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
- The resources for vitamin – B3 are kidney, liver, meat, egg, fish, oil seeds and legumes.
- Deficiency of niacin results in a disease called PELLAGRA.
Symptoms: Pellagra is described by 3 Ds – Diarrhoea, Dermatitis, Dementia.
A more comprehensive list of symptoms include
- Sensitivity to sunlight
- Aggression
- Dermatitis
- Alopecia (hair loss)
- Edema (swelling)
Smooth, beefy red, glossitis, red skin lesions, insomnia (sleepless), weakness, mental confusion, nerve damage are the symptoms of this pellagra.
Prevention: By taking of yeast, meat, fish, milk, eggs, green vegetables, beans and cereal grains, we can prevent this disease.




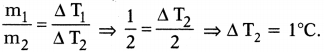
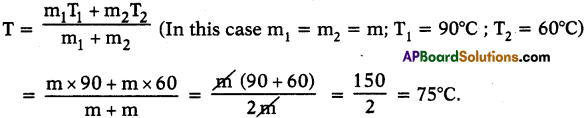
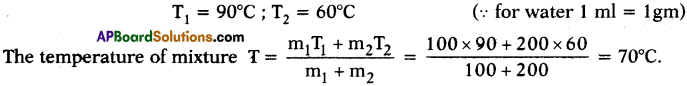


 Answer:
Answer:


 Answer:
Answer:
 Answer:
Answer:







 Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer: