AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class English Textbook Solutions Chapter 2B The Dear Departed Part 2 Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class English Solutions Chapter 2B The Dear Departed Part 2
10th Class English Chapter 2B The Dear Departed Part 2 Textbook Questions and Answers
Comprehension
I. Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
Justify the view that the husbands of Mrs. Slater and Mrs. Jordan are men with no individuality.
Answer:
Henry and Ben are men with no individuality. They simply follow their wives’ instructions. When Mrs. Slater asks Henry to wear the old man’s slippers, he wears them even they are smaller in size. When she asks him to shift the bureau from her father’s room, he obeys her and does as she likes. He doesn’t say even a word against her will. In the same way, Ben too is a man with no individuality. Both Henry and Ben try to stop the quarrel between their wives but fail. Though they have concern for their father-in-law, they can’t express it.

Question 2.
Discuss the irony in the title ‘The Dear Departed’.
Answer:
Irony is the use of words to express something other than what is said or meant and especially the opposite of the literal meaning. The title “The Dear Departed” conveys just the opposite as the main character of the play (Abel Merry weather) does not seem to be “dear” to his own daughters. The old man is not dear to anyone. They only want his property.
Question 3.
List the arguments the two sisters gave to keep their father in their care.
Answer:
Mrs. Slater tells her father that it is quite time he comes to live with them again and they will make him very comfortable if he comes. But Mrs. Slater argues that he has not been with them as long as he was with the Jordans. Mrs. Jordan replies that she does not think their father will fancy living on with the Slaters after their stealing his things. They even say sorry for what they have done. Thus, both the sisters argue to keep their father in their care.
Question 4.
How does the spat between the old man’s daughters lead to father discovering the truth?
Answer:
The spat happens between the two sisters when their father Abel asks Mrs. Slater why his bureau and clock are brought downstairs. Mrs. Jordan understands that her sister tries to steal those things before their arrival. This leads to a quarrel between the two sisters. Mrs. Jordan tells her father that Mr. and Mrs. Slater have shifted the bureau and the clock from his room to the sitting room because they think he is dead. They have shifted the things so as Mrs. Jordan can’t lay a claim on them. After discovering the truth, Abel becomes angry because he feels that his daughters don’t even wait till his funeral and have tried to divide things between them.
Question 5.
List the comic elements in the play ‘The Dear Departed’.
Answer:
There are certain elements that make the play a comedy. The title itself is a comic one. A single person doesn’t make a comedy. It requires several who are in action and counter action. The main characters of the play, Abel Merry weather, Mrs. Slater, Mrs. Jordan, Henry and Ben all cause the comedy. The main comic thing is that both the sisters think that their father is dead. The other comic scenes in the play are :
- Following his wife’s instructions, Henry wears the old man’s new slippers.
- The Slaters hurry to steal the old man’s bureau and clock, thinking that the Jordans will arrive.
- The Slaters and the Jordans are shocked to see Abel coming into the room.
- Ben skips back and retreats with Mrs. Jordan to a safe distance when Abel thrusts his hand at Ben.
- Abel announces that he will change his will and marry John Shorrocks.
- Both the sisters argue that Abel should stay with them. (They want to own his property).
A termination must be made which springs necessarily from the preceding elements and this gives the comic solution. The arrival of Abel into the sitting room and his announcement of changing his will and marrying^ woman etc. produce such a comedy.

Question 6.
In what way is the play ‘The Dear Departed’ a commentary on the hollowness of human relationships?
Answer:
Stanley Houghton, in his one act play, tries to bring out the qualities of the two daughters, Mrs. Slater and Mrs. Jordan towards their father. The author tries to show how the sisters are interested in the property of their father rather than their care and affection towards him. When the two sisters think that their father is dead they are complaining of what a burden he is to them. The moment Abel announces about his new will in which he will leave everything to the person he is living with when he dies, they both fight for him to live with them. Thus, this play shows us the hollowness of human relationships. This is a social play on the condition of the old people who are being neglected and abandoned by their own children. Here we see the degradation of moral values in respect and care within the members of the family itself.
Question 7.
What are the three things that the father plans to do on Monday next? What effect does it have on his daughters?
Answer:
The three things that the father plans to do on Monday next are:
- At first, he wants to go to the lawyer and alter his will.
- Then he wants to go to the insurance office and pay his premium.
- Finally he wants to go to St. Philip’s Church and get married.
If Mr. Abel does all these three things, the daughters will lose the chance of getting their share in their father’s assets.
II. Arrange the following sentences in sequence so that a continuous narrative of the story of ‘The Dear Departed’ could be made.
1. One day Mrs. Slater felt that Abel Merryweather had died.
2. Suddenly Victoria came into the room telling that grandfather was moving.
3. The Slaters and the Jordans wanted to ascertain if Abel Merryweather had paid his insurance premium.
4. Abel Merryweather found fault with the two daughters and wanted to change his will.
5. Before the arrival of the Jordans, the Slaters had pinched Abel’s bureau and clock.
6. Victoria was sent to Abel Merryweather’s room to bring the key bunch of the bureau.
7. Abel Merryweather informed that he was going to marry Mrs. John Shorrocks.
8. The Slaters sent a telegram to the Jordans about the death of Abel Merryweather.
Answer:
The sequential order is:
1. One day Mrs. Slater felt that Abel Merry weather had died.
8. The Slaters sent a telegram to the Jordans about the death of Abel Merry weather.
5. Before the arrival of the Jordans, the Slaters had pinched Abel’s bureau and clock.
3. The Slaters and the Jordans wanted to ascertain if Abel Merry weather had paid his insurance premium.
6. Victoria was sent to Abel Merry weather’s room to bring the key bunch of the bureau.
2. Suddenly Victoria came into the room telling that grandfather was moving.
4. Abel Merry weather found fault with the two daughters and wanted to change his will.
7. Abel Merry weather informed that he was going to marry Mrs. John Shorrocks.
The narrative: One day Mrs. Slater felt that Abel Merry weather had died. The Slaters sent a telegram to the Jordans about the death of Abel Merry weather. The Slaters wanted to steal the old man’s things before the arrival of the Jordans. So, they had pinched Abel’s bureau and wall clock before their arrival. The Jordans arrived soon and they all thought about the announcement of the old man’s death in the papers. Then the Slaters and the Jordans wanted to ascertain if Abel Merry weather had paid his insurance premium. Victoria was sent to Abel Merry weathers room to bring the key bunch of the bureau. Victoria went into’the old man’s room and saw him moving and getting up. Being frightened, Victoria came into the room telling that grandfather was moving. Abel Merry weather came into the sitting room and both the sisters and their husbands were shocked. He found fault with the two daughters and wanted to change his will. He informed them that he was going to change his will leaving all bits of his things to whoever he was living with when he would die. He also declared that he was going to marry Mrs. John Shorrocks.

III. Here is a list of traits of a personality. Tick (✓) the traits that describe Mrs. Slater’s character.
a) Greedy
b) Overpowering
c) Honest
d) Sensitive
e) Dominating
f) Blunt
g) Straight talking
h) Humble
i) Impolite
j) Insensitive
Answer:
a) Greedy (✓)
b) Overpowering (✓)
c) Honest
d) Sensitive
e) Dominating (✓)
f) Blunt (✓)
g) Straight talking (✓)
h) Humble
i) Impolite (✓)
j) Insensitive (✓)
The traits that describe Mrs. Slater’s character are:
Greedy: Mrs. Slater’s pinching her father’s bureau and clock before the arrival of her sister Elizabeth Jordan and her husband; her asking Henry to wear her father’s slippers.
Overpowering: Mrs. Slater’s asking Victoria to close the door if her aunt Elizabeth and uncle Ben come.
Dominating: Her dominating attitude towards her husband Henry.
Blunt: Her saying to her sister, “Be quiet, Elizabeth”; her asking Victoria to change her dress.
Straight talking: When Victoria says that perhaps grandpa didn’t go to pay his insurance premium, Mrs. Slater snubs her saying “He went out”.
Impolite:
i) Mrs. Slater’s talking to Henry, “Henry, why shouldn’t we bring that bureau down here now ? We can do it before they come,
ii) When Henry says to her, “I wouldn’t care to,” she says to him, “Don’t look so daft. Why not ?”
Insensitive:
i) When Victoria says to her, “That’s grandpa’s clock,” she replies, “Be quiet! It’s ours now.”
ii) When Mrs. Jordan says to her, “I’ll tell you what’s been going on in this house, father. Nothing short of robbery,” she says, “Be quiet, Elizabeth”.

IV. The following are the features of a one act play. Which of the following characteristics does the play ‘The Dear Departed’ have? Justify.
a) Minimal characters
b) Single setting or unity of place
c) One act with one or more scenes
d) Focus on one incident
e) Limited time
f) Twist ending
Answer:
“The Dear Departed” is a one act play; so it naturally has all the above mentioned characteristics.
a) Minimal characters: The total number of characters we see in this play is only six. They are Mrs. Amelia Slater, Mrs. Elizabeth Jordan, Henry Slater, Ben Jordan, Victoria Slater and Abel Merry weather. Hence, the play has the feature of “Minimal characters.”
b) Single setting or unity of place: All the story takes place in the house of Mrs. Slater particularly in the sitting room and Abel’s bedroom. Hence, the play has the characteristic of “Single setting.”
c) One act with one or more scenes: All the story happens in one act and only one scene. Hence, it has this feature.
d) Focus on one incident: All the story moves around the death of Abel Merry weather. Hence, the play’s focus is on one incident only.
e) Limited time: The story lasts for only one or two hours. Hence, it has the feature of “limited time.”
f) Twist ending: In the end of the play, Abel announces that he will change his will and marry Mrs. John Shorrocks. This announcement was a real shock for the two sisters and their husbands. It is really an unexpected thing for them. Hence, it has the feature of “Twist ending”. Audience too can t guess this twist.
Vocabulary
I. Irregular Plurals
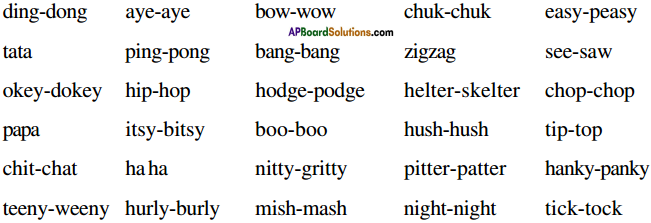
Now write the plural forms of the following nouns given in the table and say whether each of them is ‘Latin’ or ‘Greek’ word.
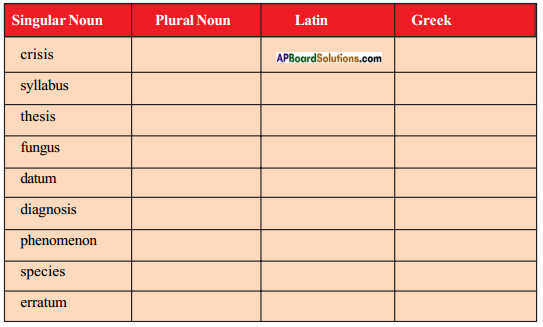
Answer:
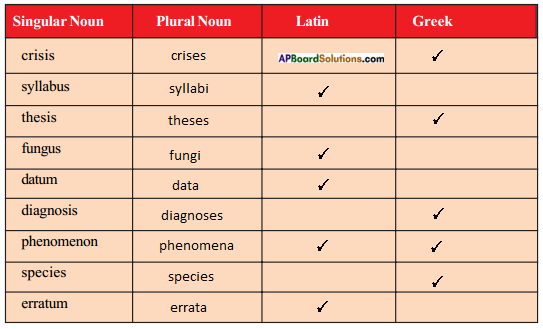
* Phenomenon – It is borrowed from Greek and ended in a’ in the plural in Latin.

II. Exclamations/Interjections
Now observe the sentences and decide which emotion is ex¬pressed in each context. Put a tick (✓) in the appropriate box. The first one has been done for you.
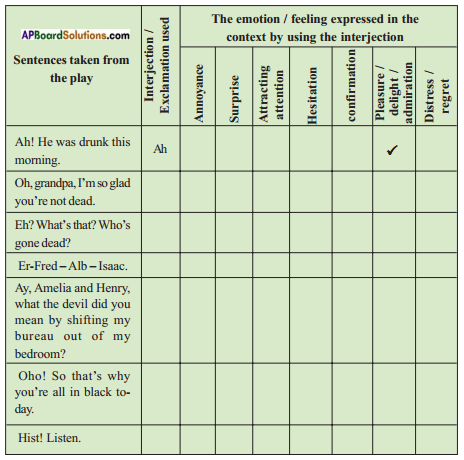
Answer:
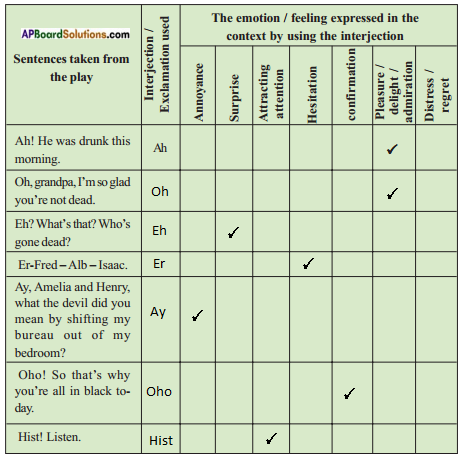
III. Compound Adjectives
Make compound adjectives choosing one word from list ‘A’ and another word from list ‘B’ and fill in the blanks with them.
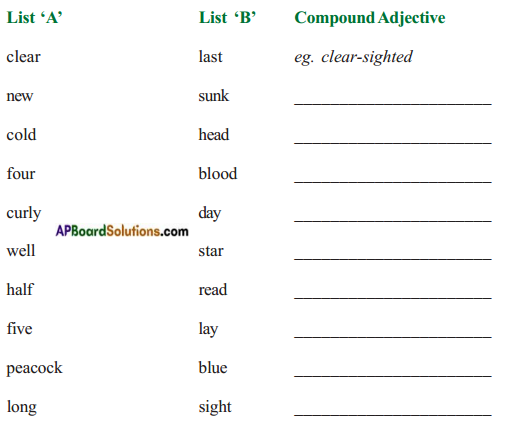
Answer:
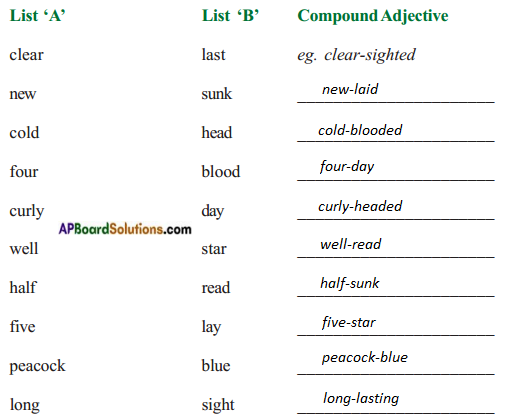
1. Sindhu is very clear-sighted about her choice.
2. The headmaster suggested a ______________________ trip to Hyderabad.
3. The _______________________________ girl who is under the tree is my sister.
4. All the people were shocked at the sight of this _______________ murder.
5. After the terrible tempest, the _____________________ sailing boat was unusable.
6. Prasad booked a room in a ____________________ hotel for Srikanth.
7. Every week, ____________________ eggs are used by my mother to make some wonderful cakes.
8. This ______________________ coat is too large for me.
9. It was a _______________________ war between the English and the French.
10. I like to correspond with this ____________________ teacher. She speaks about interesting topics.
Answer:
2. four-day
3. curly-headed
4. cold-blooded
5. half-sunk
6. five-star
7. new-laid
8. peacock-blue
9. long-lasting
10. well-read

IV. Words Often Confused
A. Write words that are likely to be confused with the words given. Find their mean¬ings and use them in sentences of your own to show the difference in meaning.
1. alter-
2. principal-
3. gait –
4. canvas –
5. check –
6. ceiling –
7. complement –
8. stationary –
9. all read –
10. advice –
Answer:
1. alter (v) – altar (n)
alter (v) : to change, or to make someone or something change e.g.: No one can alter the rules and regulations of this society, altar (n) : a holy table or surface used in religious ceremonies e.g.: The priest reached the altar to perform a religious ceremony.
2. principal (n) – principle (n)
principal (n) : someone who is incharge of a university/college e.g.: Mr. Chaitanya is the principal of St. John’s College, principle (n) : a moral rule or belief e.g.: Vinoba is a man of high principles.
3. gait (n) – gate (n)
gait (n) : the way someone walks e.g.: She has an awkward gait.
gate (n) : the part of a fence or outside wall that you can open and close so that you can enter or leave a place
e.g.: They locked the front gate and went out.
4. canvas (n) – canvass (v)
canvas (n) : strong cloth used to make bags, tents, shoes etc. e.g.: I bought a bag made of canvas.
canvass (v) : to try to persuade people to support a political party, politician etc. e.g.: Mr. Varun is very busy canvassing for votes.
5. check (v) – cheque (n)
check (v) : to do something in order to find out whether something really is correct, true or in good condition
e.g.: The guards had checked him thoroughly before he came out.
cheque (n) : a printed piece of paper that you write an amount of money on, sign and
use instead of money to pay for things
e.g.: He issued me a cheque for Rs. 25,000.
6. ceiling (n) – sealing (n)
ceiling (n) : the inner surface of the top part of a room e.g.: All the rooms in our house are built with high ceilings, sealing (n) : the activity of hunting or catching seals e.g.: Sealing is his hobby.
7. complement (n) – compliment (v)
complement (n) : someone or something that emphasizes the good qualities of an¬other person or thing
e.g.: The cashew nuts were an excellent complement for the sweets, compliment (v) : to say something nice to someone in order to praise them e.g.: Our headmaster complimented me when I saved the little girl.
8. stationary (adj) – stationery (n)
stationary (adj) : standing still instead of moving
e.g.: The teacher ordered his students to remain stationary.
stationery (n) : materials that we use for writing, such as paper, pens, pencils etc.
e.g.: I went into the shop to buy stationery.
9. all ready (phrase) – already (adv)
all ready (phrase) : completely ready e.g.: We are all ready for the test.
already (adv) : used to say something has happened before the expected time e.g.: Is it 6 o’ clock already?
10. advice (n) – advise (v)
advice (n) : an opinion about what could or should be done about a situation or problem
e.g.: He gave me a good piece of advice.
advise (v) : to give advice
e.g.: My aunt advised me to join navy.

B. Read the following paragraph. It contains errors in words often confused. Correct them and rewrite the paragraph replacing them with the right words.
It was one of those October daze when it was a pleasure to be alive. The sky was blew and the heir was cold and sharp with a cent of wet earth as the mourning sun warmed the chilled countryside. And then I caught site of a lonely be struggling to find the pollen of a final flour. Wear had he bean, this sad worker , doomed so soon to dye? I marvelled at his energy as he climbed along so many bear stalks. Finding nothing, he flue on and disappeared from cite. I continued my walk to a country in where, sitting outside, I contentedly sipped my beer, musing all the wile on the mixed fortunes of life.
Answer:
It was one of those October days when it was a pleasure to be alive. The sky was blue and the air was cold and sharp with a scent of wet earth as the morning sun warmed the chilled countryside. And then I caught the sight of a lonely bee struggling to find the pollen of a final flower. Where had he been, this sad worker, doomed so soon to die? I marvelled at his energy as he climbed along so many bare stalks. Finding nothing, he flew on and disappeared from sight. I continued my walk to a country inn where, sitting outside, I contentedly sipped my beer, musing all the while on the mixed fortunes of life.
V. Idiomatic Expressions
Here is a list of idioms and idiomatic expressions used in the play, ‘The Dear Departed’. Guess their meanings. Then look them up in a dictionary, note down their meanings and use them in your sentences.
1. get one’s own way
2. for ages
3. set foot
4. drive a hard bargain
5. get rid of
6. give way
7. at length
8. on purpose
9. took by surprise
10. at a loss
Answer:
1. get one’s own way: persuade other people to allow you to do what you want e.g.: Parents want to get their children into their own way.
2. for ages: for a long time
e.g.: I haven’t seen you for ages.
3. set foot: to enter some place
e.g.: I would not like to set foot in your house.
4. drive a hard bargain : work hard to negotiate agreements in one’s own favour e.g.: Although he has driven a hard bargain, he couldn’t get what he wants.
5. get rid of: to throw away or destroy something you do not want any more e.g.: Finally, Sekhar got rid of his old shoes.
6. give way: to stop agreeing or fighting against someone or something ; to abandon oneself.
e.g.: Don’t give way to your fears.
7. at length: in detail
e.g.: At length, they have discussed the matter.
8. on purpose: intentionally
e.g.: He entered the sitting room on purpose.
9. took by surprise: to surprise someone (took someone by surprise)- e.g.: I took my friend by surprise presenting a gold watch to him.
10. at a loss: unable to speak, unable to know how to act or what to do. e.g.: When Rahul faced the interviewers, he felt totally at a loss.

Grammar
I. Read the following sentences from the play and notice the underlined words.
Let us read the following sentences.
- She’ll come fast enough after her share of what our father has left.
- Mrs. Slater doesn’t have enough money to buy the bureau.
In both the sentences ‘enough’ is underlined. ‘Enough’ means ‘sufficient’.
In a sentence, ‘enough’ is used after adjectives, adverbs or verbs as an adverb, and before nouns as a determiner.
A. Now decide whether ‘enough’ in the following sentences is used as an ‘adjective’ or an ‘adverb’.
1. This house is not big enough for me.
2. We didn’t leave early enough.
3. I was not trained enough for the game.
4. Is there enough room for me?
5. I do not have enough clothes for my journey.
Answer:
1) This house is not big enough for me.
‘enough’ is used as an adverb.
2) We didn’t leave early enough.
‘enough’ is used as an adverb.
3) I was not trained enough for the game.
‘enough’ is used as an adverb.
4) Is there enough room for me?
’enough’ is used as an adjective.
5) I do not have enough clothes for my journey.
’enough’ is used as an adjective.

B. Complete the following sentences using ‘enough’ / ‘not enough’ and one of the words given in the list below.

1. Harish wants to be a great wrestler but he is ____________________.
2. I want to sit and watch TV but I just don’t have ____________________.
3. He tried to win the race but he came third as he was not ____________________.
4. This bath is freezing. The water is ____________________.
5. We had to sleep on the floor as there were ____________________.
6. There is ____________________ to make a cup of tea! What is wrong with the pipes?
7. If Sujatha does not have ____________________ , I can lend her.
8. Vasavi is not ____________________ to become a member of this club. She must be at least 18 years of age to join.
9. Is this coffee ____________________ for you? Would you like some more sugar?
10. Do you think he has studied ____________________ to pass the entrance exam?
Answer:
1. not strong enough
2. enough time
3. fast enough
4. not warm enough
5. not enough beds
6. not enough water
7. enough money
8. old enough
9. sweet enough
10. hard enough
II. We generally use articles (a, an and the) before common nouns. But in some cases articles are not used before them. Read the following sentences from the play ‘The . Dear Departed’ and notice the underlined common nouns.
1. He went out soon after breakfast to pay his insurance.
2. And when we’d finished dinner I thought I’d take up a bit of something on a tray.
In the above sentences the underlined common nouns ‘breakfast and dinner’ refer to the names of meals and food. In primary and general sense we don’t use articles before the words that refer to the names of meals and food i.e. breakfast, dinner, lunch, supper, pizza, fish fry and omelette.
Write the following paragraphs, inserting a, an, and the where needed.
A. Horse knows when he is going to race. How does he know? His breakfast is scanty. (He is angry about that.) He does not have saddle on his back. He is being led, not ridden, to grandstand. He is led under grandstand into unusual, special stall. Horse is nervous. Sometimes he does not know what to do when starting gate flies open and track is before him. If he does not begin to run instantly, other horses are already ahead of him. During race, when he sees another horse just ahead of him, he will try to pass him. Sometimes jockey holds him back to save his energy for last stretch. Eventu¬ally horse gets to run as fast as he can. Exercise boy, watching owner’s favourite jockey riding horse he has exercised day after day, says nothing. Secretly, he is planning for day when he.will be jockey himself, and his horse will be first to cross finish line.
B. I have horse of my own. I call her Pretty Girl. She is intelligent animal, but she is not thoroughbred horse. I could never enter her in race, even if I wanted to. But I do not want to. She is companion, for my own pleasure. I took her swimming day or two ago.

Answer:
A. A/The horse knows when he is going to race. How does he know? His breakfast was scanty. (He is angry about that.) He does not have a saddle on his back. He is being led, not ridden, to the grandstand. He is led under the grandstand into an unusual, special stall. The horse is nervous. Sometimes he does not know what to do when the starting gate flies open and the track is before him. If he does not begin to run instantly, the other horses are already ahead of him. During the race, when he sees another horse just ahead of him, he will try to pass him. Sometimes the jockey holds him back to save his energy for the last stretch. Eventually the horse gets to run as fast as he can. The exercise boy, watching the owner’s favourite jockey riding the horse he has exercised day after day, says nothing. Secretly, he is planning for the day when he will be a jockey himself, and his horse will be the first to cross the finish line.
B) I have a horse of my own. I call her Pretty Girl. She is an intelligent animal, but she is not a thoroughbred horse. I could never enter her in a race, even if I wanted to. But I do not want to. She is a companion, for my own pleasure. I took her swimming a day or two ago.
III. Compound Prepositional Phrases
Read the following sentences from the play ‘The Dear Departed’ and notice the underlined words.
1. Victoria dressed according to her mother’s instructions.
2. You both say that because of what 1 have told you about leaving my money.
3. It was here instead of in his room.
The underlined phrases are compound prepositional phrases. The following are some more important compound prepositional phrases. Their meanings are given in brackets.
along with (together with)
on account of (because of)
by means of (through the agency of)
apart from (separate from)
ahead of (earlier than somebody/something)
in front of (located before)
in place of (as a substitute for)
in spite of (disregarding the difficulty)
in case of (in the event of)
by way of (via)
due to (on account of)
for the sake of (for the good of)
in addition to (added to)
in accordance with (in agreement with)

A. Use the above compound prepositional phrases in sentences of your own.
Answer:
1. along with:
a) Ramu went along with Somu.
b) I put scale along with books in my bag.
c) Mr. Nagesh bought a TV along with a computer.
2. on account of:
a) She visited the doctor on account of her illness.
b) They cancelled their programme on account of rain.
c) On account of Prabhu’s late-coming, he was beaten severely.
3. by means of:
a) He will succeed by means of sheer determination.
b) 1 was able to buy a flat by means of a bank loan.
c) The blocks are raised by means of pulleys.
4. apart from:
a) Apart from minor injuries, he was safe after an accident.
b) We have a Maruthi car apart from our Ford car.
c) We don’t see anyone in the theatre apart from two women.
5. ahead of:
a) Mr. Rao arrived there ahead of his boss.
b) The results show that Aam Admi’ party is ahead of other parties.
c) He had got ahead of me.
6. in front of:
a) There is a pole in front of our house.
b) The fountain is in front of the building.
c) We sit in front of the TV and watch programmes.
7. in place of:
a) Mr. John came to teach in place of Mr. Robert, who was transferred.
b) She bought a red car in place of the blue car, her old one.
c) Mr. Vasan was appointed as chairman in place of Mrs. Sharma, the former chairman.
8. in spite of:
a) In spite of heavy rain, the football match was continued.
b) In spite of the pain in his leg, he played and won the match.
c) In spite of the fact that he had worked hard, he didn’t get through his exam.
9. in case of:
a) In case of heavy rains, you should postpone your trip.
b) Break the glass in case of fire.
c) In case of floods, take the help from helpline.
10. by way of:
a) We go to school by wav of market.
b) My father came home by way of Rampura.
c) They reached the place by wav of the canal.
11. due to:
a) Due to illness, she didn’t go to school.
b) The game was cancelled due to heavy rain.
c) There was a heavy loss due to improper management.
12. for the sake of:
a) The government implemented a new programme for the sake of women.
b) She had done it for the sake of you.
c) The king acquitted the criminal for the sake of justice.
13. in addition to:
a) Mr. Suraj learnt Karate in addition to Kungfu.
b) She used to teach English in addition to Social Studies.
c) You have to add sugar to the dish in addition to ghee.
14. in accordance with:
a) The boss did this in accordance with his request.
b) I designed this plan in accordance with our discussion.
c) They have tried to root out corruption in accordance with rules that have been framed recently.

B. Fill in each blank with the correct compound prepositional phrase from the options given under each sentence.
1. I finished my project work several days ________________ the deadline.
a) instead of
b) ahead of
c) in spite of
Answer:
b) ahead of
2. Sravani goes to school ______________________ Yamuna daily.
a) according to
b) in spite of
c) along with
Answer:
c) along with
3. My house stands _______________ all the other houses in the street as it is big in size.
a) apart from
b) in accordance with
c) in addition to
Answer:
a) apart from
4. Madhu got a good job ____________________ his own abilities and skills.
a) in addition to
b) instead of
c) by means of
Answer:
c) by means of
5. She was unable to attend the party ______________ her marriage engagement.
a) in spite of
b) in addition to
c) due to
Answer:
c) due to
6. ______________ fire, ring the alarm bell.
a) In spite of
b) In case of
c) In addition to
Answer:
b) In case of
7. Sriram continued his batting carefully ________________ his team though he was hungry.
a) for the sake of
b) in addition to
c) in front of
Answer:
a) for the sake of
8. You should complete your B.Ed. _____________________ your B.Sc to get a teacher job.
a) in addition to
b) according to
c) in spite of
Answer:
a) in addition to
9. The physical director of our school selected me ____________________ my friend, Ganesh for tomorrow’s match.
a) in spite of
b) in place of
c) ahead of
Answer:
b) in place of
10. ________________ his poverty, he completed his Ph.D. in English.
a) In place of
b) For the sake of
c) In spite of
Answer:
c) In spite of

IV. Language Function (It’s time + Simple Past Verb …)
Read the following contexts and express them using expressions it’s quite time’, it’s high time’, it’s time’ or it’s about time’.
1. Bhavani usually wakes up at 6 a.m. daily. It is 6.15 a.m. now. Bhavani has not woken up yet. You feel it is already late. Express your idea using it’s high time’.
Answer:
It’s high time Bhavani woke up.
2. You and your friend have spent more time than you spend daily in the playground. You feel it is late and better to go home. What would you say to your friend? Use the expression ‘It’s time’.
Answer:
It’s time we went home as it is already late.
3. You to your friend: ‘You have not thought seriously about what you want to do in your life.’ How would you express this idea using ‘It’s high time’.
Answer:
It’s high time you thought about your life seriously.
4. Your friend promised you to make a phone call at 7 a.m. But you haven’t received any phone call from him yet. Now it is 7.30 a.m. How would you express this idea using ‘It’s time’?
Answer:
It’s time my friend made me a call.
5. Your friend has been working on a project for 5 months. But he has not completed it yet. You feel that your friend should take your help to complete the project fast. Give him/her advice using ‘It’s time.’
Answer:
It’s time you took my help in order to complete the project fast.
V. The following passage has ten errors of grammar. Identify and rewrite them with necessary corrections.
Varanasi is locate on the north eastern part of India. Hindu pilgrims go to there to purify their souls. To the Hindus Varanasi is a holiest pilgrimage center to all.
Thousands of pilgrims visit this wholly city every year.
As early as four o’clock at the morning the pilgrims are seen make their way to the famous bathing steps knowed as Gatz. From there they board row boats to the holy river ganges to take bath. In doing this the pilgrims believe that their sins would be wash away.
Answer:
Varanasi is located in the north eastern part of India. The Hindu pilgrims go there to purify their souls. To the Hindus Varanasi is the holiest pilgrimage centre of all.
Thousands of pilgrims visit this holy city every year.
As early as four o’clock in the morning the pilgrims are seen making their way to the famous bathing steps known as Ghats. From there they board row boats to the holy river Ganges to take a bath. By doing this the pilgrims believe that their sins would be washed away.

Read the following sentences. Complete the conversations with the appropriate forms of the verbs. Then say why you chose simple past/present perfect forms.
1. “Is your brother in?”
“No, he isn’t. He __________________(go) to Chennai.”
“When _________ he ________________________(go) to Chennai?”
“Yesterday.”
Answer:
“Is your brother in ?”
“No, he isn’t. He has gone to Chennai”.
“When did he go to Chennai ?”
“Yesterday”.
2. “I ________ (lose) my pencil. __________you ________________________(see) it anywhere?”
“No, I________ . When ___________ you last _________(use) the pencil?”
“I ________________________(use) it when I was in the class.”
“Perhaps you ________________________(leave) it in the class.”
Answer:
“I lost my pencil. Have you seen it anywhere ?”
“No, I haven’t. When did you last use the pencil?”
“I used it when I was in the class.”
“Perhaps you have left (must have left) it in the class.”
3. A: _____________ Madhu ________________________( not arrive) yet ?
B: No, he ________________________ .
C: But he ________________already ________________________(arrive).
B: _______________ you ________________________(talk) to him?
C: No, I ____________ . I merely _______________(see) him.
B: That cannot be Madhu. He may have been somebody else.
Answer:
A : Hasn’t Madhu arrived yet?
B : No. He hasn’t.
C : But he has already arrived.
B : Have you talked to him ?
C : No, I haven’t. I merely saw him.
B : That cannot be Madhu. He may be somebody else.
4. A: ________________ you _______________(call) me, mother?
B: Yes, I_______________. ________ you _______________(see) my diary today?
I _______________(put) it on the table last night. I _______________(look) all over the house for it. But I _______________( not, find) it anywhere.
A: I _______________(see) it on the table this morning, if I remember right. Maybe father _______________(take) it with him by mistake.
Answer:
A: Have you called me. mother ?
B : Yes, I have. Have you seen my diary today ?
I put it on the table last night. I have looked all over the house for it. But I have not found it anywhere.
A : I have seen it on the table this morning, if I remember right. May be father has taken it with him by mistake.
5. “Do you know Mrs.Geetha ?”
“Yes, I do. I _______________(know) her for nearly four years. It ______________(be) at a high school that I first _______________(see) her in 2009. I ___________(work) with her for several years. Recently we _______________(meet) at the wedding of a mutual friend of us.”
Answer:
“Do you know Mrs. Geetha ?
“Yes. I do. I have known her for nearly four years. It was at a high school that I first saw her in 2009. I have worked with her for several years. Recently we have met at the wedding of a mutual friend of us.”

Writing
I. Imagine that you are the grandfather in the play. Write a letter to your Mend, Mr. Tattersall inviting him to your marriage at ‘Ring-o-Bells with Mrs. John Shorrocks. Don’t forget to say why you are going to get married at this age.
You can include the following :
a) Time of wedding
b) Place of wedding
c) Details of the bride
d) Behaviour of the daughters
e) Reason for-marrying at this age
f) Cordial invitation.
Answer:
22-222-A45,
Trafalgar Square,
Manchester City.
28th March, 20xx.
My dear Tattersall,
How are you? I am keeping quite well and hope to hear the same from you. It is a long time since I received a letter from you. What are the things with you ? Here is a surprising news for you. I am glad to write to you that I am going to get married to Mrs. John Shorrocks at twelve o’ clock at St. Philip’s Church on Monday, 7th April, 20xx. Mrs. John Shorrocks is a good woman and is the owner of ‘Ring-o-Bells’. We know each other very well. She is a famous business person in the city. Hence, I cordially invite you to attend our marriage ceremony without fail.
Now, I think that you are very much surprised to hear the news of my marriage at this age. I had to take this decision because of the the evil intentions of both my daughters Amelia and Elizabeth. You know that I have been with Amelia’s family for the last few months. A few days ago, Amelia thought me ‘dead’ and her foolish husband sent this message to my second daughter Elizabeth. Before Elizabeth and her husband’s arrival, Amelia shifted my bureau to the sitting room. She also tried to steal my clock and my slippers for her husband. After the arrival of the Jordans, both my daughters concentrated on grabbing my things. No one bothered about me. They don’t deserve to be called ‘daughters’ at all. When I understood their nature, I wanted to teach them a lesson. I announced that I would change my will the next Monday, pay my insurance premium and get married. I think that this decision is a slap on the faces of my greedy and deceitful daughters.
I hope that you will understand my feelings. I shall be very glad to see you at the ceremony on Monday. I am awaiting your arrival. Convey my best wishes to your wife.
Your loving friend,
Abel Merryweather
Address on the envelope :
To
Mr. K. Tattersall,
5-262-6/A, Joseph Towers,
Dovinci Street, Liverpool,
England.

II. Convert the play, ‘The Dear Departed’ into a story.
To adapt the story to your culture, you may make changes in the following:
a) The names of the characters
b) Description of costumes
c) Things stolen by the daughter
d) The names of the villages/towns the daughters lived in
Answer:
Mr. Rao is a seventy-two-year old man. He is living with his daughter Mrs. Sarojini and her husband Prakash. Their daughter is Sushma, who loves her grandpa very much. Mr. Rao’s another daughter is Mrs. Aruna and her husband Rajesh.
One day Mrs. Sarojini thinks that her father is dead. She tells her daughter to change her dress before her aunt Aruna and her husband come. Mrs. Sarojini’s husband Prakash has sent them the message to come home. When Prakash wonders if they will come at all, Mrs. Sarojini replies that Aruna will come at once for her share of the old man s things. Mrs. Sarojini asks her husband to wear the new shoes of her father. She also wants to pinch the old man’s TV set, computer and his bracelet too. She wants to do it before her sister’s arrival. When she tells the same, her husband agrees after some hesitation.
Mrs. Sarojini fastens the door and she and her husband shift the TV set and com¬puter and put the radio in their place. Their daughter Sushma understands that they are pinching the grandpa’s TV set and computer and asks them if they are pinching them. Mr. Prakash replies that her grandpa has given them those things before his death. Mrs. Sarojini and her husband carry them downstairs and put them in the parlour.
She asks her husband to wear her father’s bracelet round his wrist and he obeys. At the same time Mrs. Aruna and her husband come. Mrs. Sarojini tells them that the old man is found dead that morning when she takes up a bit of something for him on tray.
Mrs. Aruna and Mr. Rajesh don’t want to look at the old man. They prefer to have tea. Then they talk about how to announce the old man’s death in the papers. Then Mrs. Sarojini and Mrs. Aruna come to talk about dividing their father’s belongings. Mrs. Aruna tells that the old man has promised his gold ring for Srikar. This news amazes Mrs. Sarojini. Mr. Rajesh calls the old man “The drunken old beggar” when Sushma tells that grandpa hasn’t paid his insurance. Both the sisters complain that they have to put up with their father for all those years. Then Mrs. Sarojini asks Sushma to go and bring the bunch of keys from grandpa’s room. After some time, Sushma gets back scared and tells them that grandpa is getting up. All are amazed as they all think he is dead. Mr. Rao enters their room after a few minutes and is surprised to see Mrs. Aruna and her husband. He asks them why they are in mourning dress. Sushma tells her grandpa that she is very happy that he is not dead. Grandpa asks them who is dead. Mrs. Sarojini lies that Rajesh’s brother is dead. Mrs. Rao sees his shoes being worn by Prakash and says it is not good. Then he looks at the gold bracelet and understands that they have stolen it. He also understands that Mrs. Sarojini and her husband have stolen his TV set and computer.
Mr. Rao doesn’t want to stay with either of his daughters anymore. He declares that he is going to change his will leaving all his property to whoever he is living with when he dies. Mrs. Sarojini and Mrs. Aruna fight with each other to keep their father in their care. Both the sisters try to persuade him to keep him with them but he refuses to stay with them. Then the old man shocks them with his announcement. He announces that he has got to do three things the next Monday. He has got to go to the lawyer and change his will, to pay the insurance premium and to go to Tirumala to get married to Mrs. Laxmi, the owner of ’Komala Vilas’. He invites them all to the marriage ceremony. He thanks Mrs. Sarojini for bringing the TV set and computer downstairs as it will be easier to carry them across to his house after his marriage.

Study skills
Health is a major concern during old age. Maintaining health is very important for the elderly, particularly in rural areas, who must continue to work for a living even when they become aged. Good health is central to their ability to work, and support themselves and families. However, many poor rural elderly people have severe problems of health
Here is the data collected in January 2013 by ‘Help Age India’, a research and development journal on common health problems of the rural elderly in Andhra Pradesh. The data is collected from 150 male and 150 female rural elderly people of above 60 years old.
Common Health Problems of the Rural Elderly in Andhra Pradesh
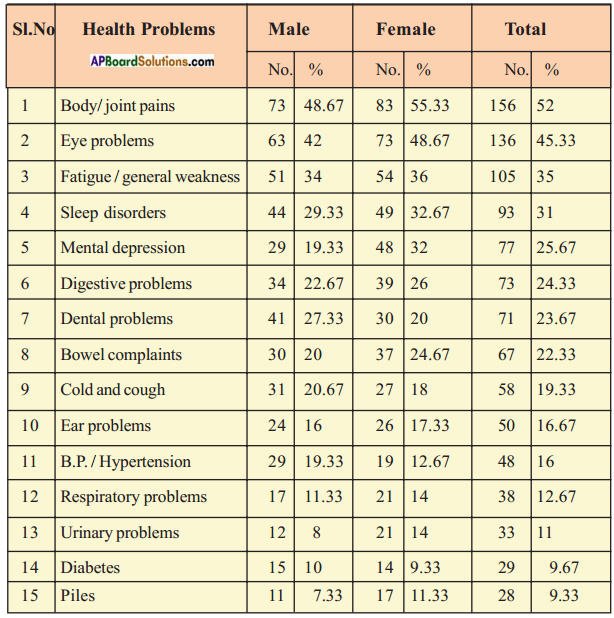
Read, understand and analyse the data given in the above table and write a report on it to present on the World Grandparents’ Day.
You should include the following points in your report:
- Introduction
- The type of diseases old people suffer from below 10%, between 10-20, 21-30, 31- 40 and 41-50.
- Which diseases have more or less effect on the health of the old people.
Answer:
This is a report based on the data collected in January 2013 by ’Help Age India’, a research and development journal on common health problems of the rural elderly in Andhra Pradesh. The data is collected from 150 male and 150 female rural elderly of above 60 years old. Health is a major concern of old age all over the world. Maintaining health is very important for the elderly who must continue to work for a living even when they become aged particularly in rural areas. However, many poor rural elderly have severe problems of health. Now, we have a look at the health problems being faced by the elderly of rural areas.
At first we see the health problems being faced by the males and the females of rural areas separately. Below 10% of males are suffering from urinary problems and piles. Between 10% and 20% of males are suffering from bowel complaints, ear problems, B.P./hypertension, mental depression, respiratory problems and diabetes. Between 21% and 30% of males are suffering from sleep disorders, digestive problems, dental problems and cold and cough. Between 31% and 40% of males are suffering from fatigue/general weakness. Between 41% and 50% of males are suffering from body/joint pains, and eye problems.

As far as women are concerned, below 10% of them are suffering from diabetes. Between 10% and 20% of females are suffering from dental problems, cold and cough, ear problems, B.P./hypertension, respiratory problems, urinary problems and piles. Between 21% and 30% of females are suffering from digestive problems and bowel complaints. Between 31% and 40% of females are suffering from fatigue/general weakness, sleep disorders and mental depression. Between 41% and 50% of females are suffering from eye problems. 55.33% of females are suffering from body/joint pains.
When we consider both males and females, below 10% of elderly people are suffering from diabetes and piles. Between 10% and 20% of them are suffering from cold and cough, ear problems, B.P./hypertension, respiratory problems and urinary problems. Between 21% and 30% of elderly people are suffering from mental depression, digestive problems, dental problems and bowel complaints. Between 31% and 40% of elderly people are suffering from fatigue/general weakness and sleep disorders. 45.33% of elderly people are suffering from eye problems and 52% of them are suffering from body/joint pains.
When we observe the data, we can understand that the health problems such as body/joint pains, eye problems, fatigue, sleep disorders, mental depression, digestive problems, dental problems and bowel complaints have more effect on the health of the old. When we compare with the above problems, the problems such as cough and cold, ear problems, B.P./hypertension, respiratory problems, urinary problems, diabetes and piles have less effect on their health. Good health is essential to their ability to work, to support themselves and families. They must get rid of their health problems to lead an active and happy life.

Listening
Listen to an interesting anecdote and say whether the following statements are true or false.
1. The woman was a stranger to Hyderabad.
2. In the beginning of the incident, the woman was at the Charminar.
3. The woman in this event might be a villager.
4. The woman knows that the buses in city have numbers.
5. The woman misunderstood the direction given by the police officer.
6. The police officer gave a wrong direction.
Answer:
1. True
2. False
3. True
4. False
5. True
6. False
Oral Activity
Work in groups. Tell your group any funny incident you may have witnessed/listened to.
Answer:
My friend Rahul told me this funny incident which he himself experienced. One evening he was returning home after watching a movie. It was very dark. He was all alone and very scared. The wind was blowing very hard. He even heard the cry of an owl.
On his way, he had to pass by a burial ground. When he was nearing it, he remem-bered horror serials he had watched on television. His mind was full of horror scenes. There was a thorny bush on the side of the road. It was so dark that nothing was visible to the naked eye. He was at his wit s end. He thought that there was something in the bush. He plucked up courage and took a step forward. He heard the sound again. There was something greyish in that bush. There were two glowing spots in the bush. He stood rooted to the spot, staring at them. He could neither go forward nor back. He thought that the glowing spots were the eyes of a skull. Suddenly, there was a ear¬splitting cry, and a huge grey form jumped out of the bush and ran away. “Aaaaaah….”
It was a donkey! He could breathe again, a donkey after all He laughed aloud for a long time. He reached his home and narrated the incident to the members of his family. They too laughed aloud.

The Dear Departed Part 2 Summary in English
When Abel Merryweather enters their room, he is surprised to see his daughter and son-in-law, Mrs. and Mr. Jordan. The two sisters and their husbands can’t believe their eyes. Abel comes forward to shake hand with his son-in-law, Mr. Ben Jordan. Ben retreats with Mrs. Jordan to a safe distance. Mrs. Slater pokes Abel with her hand to see if he is solid. Abel reveals that he is well enough but has a bit of a headache. Then Abel asks for his new slippers. When he observes Henry wearing his slippers, Mrs. Slater snatches them from Henry and gives them to Abel. He puts them on and sits in an armchair.
Abel asks them why they all are in mourning. Mrs. Jordan makes up some story to pacify him. She tells that Ben’s brother has died. Abel tells them to sit down and take tea. He suggests that they all should be jolly. Then he notices his bureau there in that room. He asks Mrs. Slater and Henry what they have been doing with his bureau. At the same time he hears a clock striking six. He looks at it and questions them why it is there. He grumbles and scolds for her deceitful acts. Mrs. Jordan blames her sister of robbing their father. The two sisters start quarrelling. Abel understands his daughters’ dishonesty. He comes to know about the reality.
Abel doesn’t want to stay with either of his daughters anymore. He addresses his daughters directly and declares that he is going to change his will leaving all his property to whoever he is living with when he dies. Mrs. Slater and Mrs. Jordan fight with each other to keep their father in their care. Both the sisters try to persuade him to make him live with them but he refuses to stay with them. Then Abel makes an announcement which shocks everyone. He announces that he has got to do three things the next Monday He has got to go to the lawyer and change his will and he has got to go to the insurance office to pay the premium and then he has got to go to St. Philip’s Church and get married. Everyone is shocked. Abel reveals that he has at last found someone who is happy to keep him. When he leaves the room, he invites them all to his marriage with Mrs. John Shorrocks who keeps the ‘Ring-o-Bells’. He thanks Mrs. Slater for bringing the bureau downstairs as it will be easier to carry it across to the Ring-o-Bells.’
The Dear Departed Part 2 About the Author
William Stanley Houghton (1881 – 1913) was a famous English dramatist. He was one of the best of a group of realistic playwrights often called the Manchester School. In every play he sought to present an idea. He had a remarkable gift for dialogue that is evident in ‘The Dear Departed’. The Dear Departed was first produced in Manchester in 1908. Here Houghton satirizes the degradation of moral values in the British middle-class.

The Dear Departed Part 2 Glossary
thrust (v): to push something somewhere quickly
skip (v): move with quick steps and jumps
smartly (adj): elegantly / stylishly
retreat (v): move back
approach (v): come near to somebody
gingerly (adv): in a careful way
poke (v): push
solid (adj): firm
what the devil (phrase): old fashioned way of showing annoyance or displeasure; (This phrase is always used in questions.)
tomfoolery (n): foolish or silly behaviour
took by surprise (idiom): happened unexpectedly so that somebody was slightly shocked
eh? (Intj): a request for repetition or confirmation of what was just said.
what the dickens (idiom): (old-fashioned and informal) used in questions instead of ‘devil’ to show that you are annoyed or surprised
hearth (n): the area of floor around a fireplace in a house
snatch (v): to take away something from someone with a quick, often violent movement
‘em (pro): them
put on (phr.v): wear
haste (n): speed in doing something, especially because you do not have enough time
Oh (Inter): used to express surprise, fear, joy, etc.
vindictive whisper (n.phr.) : talking about someone in a harsh, hasty manner
ab (Interject): used to express pleasure, admiration or sympathy hold your tongue (phrase): to tell someone to stop talking
chuckle (v): to laugh quietly

at a loss (Idiom): puzzled
er (intj): used to express hesitation or uncertainty
prompting (v): reminding the dialogue or words
ay (interjection): used to express distress or regret
drat (interjection): a fairly mild expression of slight annoyance nothing short of (Idiom): as bad as
double-faced (adj): hypocritical/deceitful/dishonest
damn it (Intellect.): an expression of displeasure annoyance
sneak: to go somewhere secretly and quietly in order to avoid being seen or heard
resume : to start doing something again alter stopping or being interrupted
thumping (v): hitting hard
gaze: look fixedly
oho (interject): used for showing that you are surprised in a happy way
sobbing (v): crying noisily. taking sudden sharp breaths
bits of things (phr): property
will (n): legal document that says what is to happen to somebody’s property alter his/her death
strike (v): come into somebodys mind suddenly
It’s quite time you came: it Is the right time to come
fancy (v): want/feel like
put up with (phr.v): bear / look after
out of senses (phr.): silly and senseless
consternation (n): a worried. sad feeling
Ring-o-Bells (n): the name of a restaurant
a good while (Idm): for quite sometime
handier (adj): easier
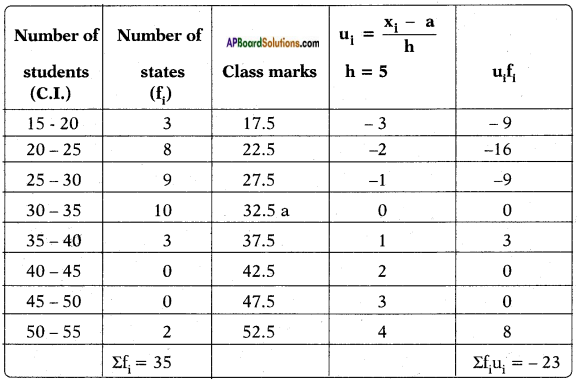
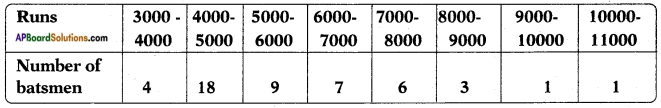
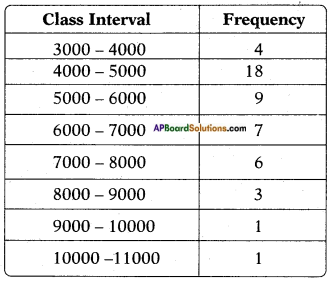
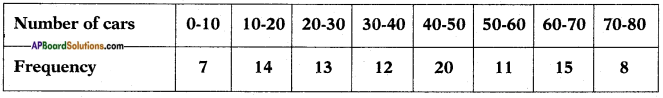
 Let the height of the tower = h m
Let the height of the tower = h m![]()
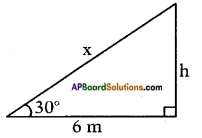 Distance between the foot of tree and the point of contact of the top of the tree on the ground = 6 cm.
Distance between the foot of tree and the point of contact of the top of the tree on the ground = 6 cm.![]()
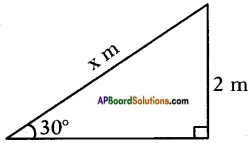 Height of slide = 2 m
Height of slide = 2 m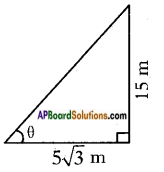 Height of the pole = 15 m
Height of the pole = 15 m![]()
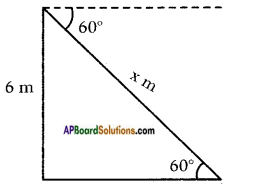 Height of the building = 6 m
Height of the building = 6 m![]()
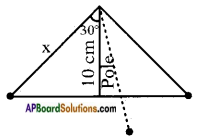
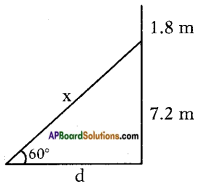 Height of the pole = 9m
Height of the pole = 9m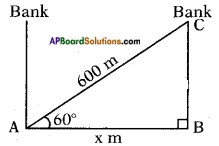 Let the width of the river = AB = x m
Let the width of the river = AB = x m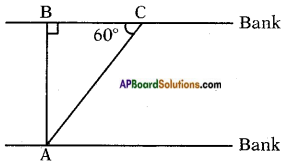 In the figure
In the figure![]()
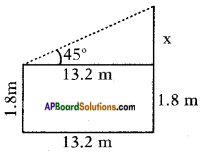 From the figure
From the figure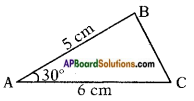 Answer:
Answer: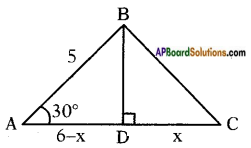 Draw a perpendicular BD to AC
Draw a perpendicular BD to AC

 Answer:
Answer:
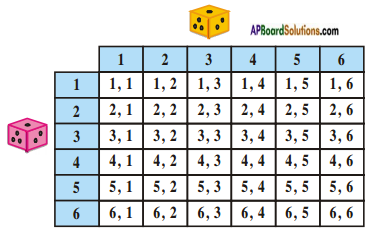 (i)
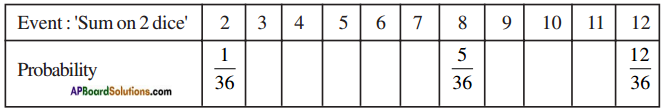
(i)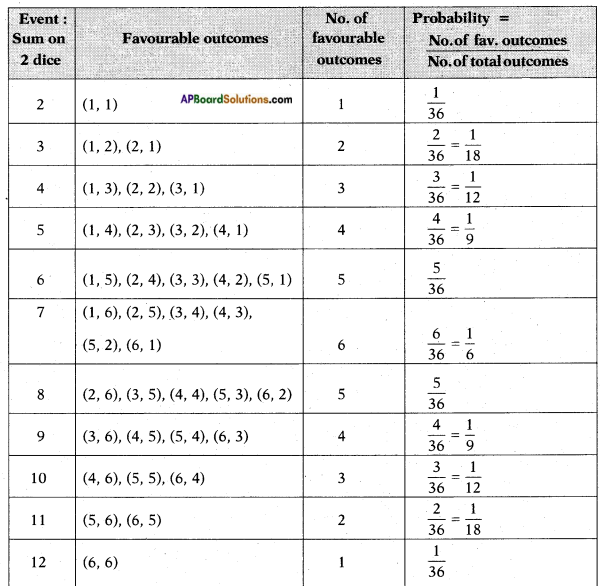 (ii) The above (given) argument is wrong [from the above table].
(ii) The above (given) argument is wrong [from the above table]. ∴ P(E) = \(\frac{\text { No. of favourable outcomes }}{\text { No. of total outcomes }}\)
∴ P(E) = \(\frac{\text { No. of favourable outcomes }}{\text { No. of total outcomes }}\)