Practice the AP 9th Class Maths Bits with Answers Chapter 9 Statistics on a regular basis so that you can attempt exams with utmost confidence.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Maths Bits 9th Lesson Statistics with Answers
Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
Information collected in the form of facts, numerical figures, tables etc., is called
A) mean
B) median
C) mode
D) data
Answer:
D) data
Question 2.
Data collected from a source like registers is called
A) primary data
B) secondary data
C) pictograph
D) bar graph
Answer:
B) secondary data
Question 3.
Range of the data “18, 24, 15, 17, 33, 16, 29, 45, 12, 3, 33, 21” is
A) 33
B) 42
C) 48
D) 30
Answer:
B) 42

Question 4.
0 – 10, 11 – 20, 21 – 30, 31 – 40. The real lower limit of the class 21 – 30 is
A) 21
B) 30
C) 20.5
D) 21.5
Answer:
C) 20.5
Question 5.
In the above problem, the classes are called
A) inclusive
B) exclusive
C) continuous
D) none
Answer:
A) inclusive
Question 6.
The temperatures of a city recorded during a week are 42°, 35°, 44°, 33°, 39°, 45° and 42°. The average temperature is
A) 42°
B) 35°
C) 39°
D) 40°
Answer:
D) 40°
Question 7.

The mean of the above table is
A) 2.9
B) 3.9
C) 4.9
D) 3.7
Answer:
B) 3.9
Question 8.
In a deviation problem Σfidi = – 12 and A = 15; Σf = 20 then \(\overline{\mathbf{x}}\) =
A) 15.6
B) 14.6
C) 14.4
D) 12.4
Answer:
C) 14.4
Question 9.
Median of 3, 7, 4, 6 and 12 is
A) 7
B) 6
C) 4
D) 12
Answer:
B) 6
Question 10.
Median of the data 5,8, 9, x, 11, 13 is 9.5 (given that data is arraned in ascending order) then x is
A) 8
B) 9.5
C) 10
D) 10.5.
Answer:
C) 10

Question 11.
Formula to find mean for a grouped data is
A) A + \(\frac{\Sigma \hat{f}_{i} \mathrm{~d}_{\mathrm{i}}}{\mathrm{f}_{\mathrm{i}}}\)
B) A + \(\frac{\Sigma \mathrm{f}_{\mathrm{i}} \mathrm{d}_{\mathrm{i}}}{\mathrm{C}}\)
C) A + \(\frac{\Sigma \mathrm{f}_{\mathrm{i}} \mathrm{d}_{\mathrm{i}}}{\Sigma \mathrm{f}_{\mathrm{i}}}\) × C
D) None
Answer:
A) A + \(\frac{\Sigma \hat{f}_{i} \mathrm{~d}_{\mathrm{i}}}{\mathrm{f}_{\mathrm{i}}}\)
Question 12.
Mode of the data 3, 7,8, 8, 7,6, 8, 4, 3, 11 is
A) 3
B) 7
C) 8
D) 11
Answer:
C) 8
Question 13.
Mean of the data x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 is 15. If each observation is multiplied 3 then the mean becomes
A) 5
B) 45
C) 18
D) 12
Answer:
B) 45
Question 14.
If the mean of the data 12, 8, 6, 3, 9 is 7.6. If 5 is added to each observation then the new mean is
A) 2.6
B) 32.6
C) 12.6
D) 13.6
Answer:
C) 12.6
Question 15.
Mean of the data 8, 7, 6, 14, 12, 10, 20, 16, 15 and 14 is 12.2. If each observation is multiplied by 2 and then 3 is added, the new mean is
A) 38.6
B) 61
C) 27
D) 27.4
Answer:
D) 27.4
Question 16.
In the above problem the new median is
A) 29
B) 41
C) 40
D) 28
Answer:
A) 29
Question 17.
The median of n observations arranged in ascending order when n is even
A) \(\frac{\mathrm{n}}{2}\) observation
B) \(\frac{\mathrm{n}}{2}\) + 1 observation
C) average of \(\frac{\mathrm{n}}{2}\) and \(\frac{\mathrm{n}}{2}\) + 1 observations
D) none
Answer:
C) average of \(\frac{\mathrm{n}}{2}\) and \(\frac{\mathrm{n}}{2}\) + 1 observations

Question 18.
A data having two modes is
A) unimodal data
B) bi-modal data
C) tri modal data
D) none
Answer:
B) bi-modal data
Question 19.
The mode of the data 8,5, 3, 8,3,6, 5, 3, 7, 5 and 11 is
A) 5
B) 8
C) 3
D) 5 and 3
Answer:
D) 5 and 3
Question 20.
The difference between any two lower limits is called
A) size of the class
B) range
C) frequency
D) upper limit
Answer:
A) size of the class
Question 21.
The mean of the observations x – 1, x and x + 1 is
A) 3x
B) x
C) 2x
D) 0
Answer:
B) x
Question 22.
The median of first 10 natural numbers is
A) 11
B) 4.5
C) 6.5
D) 5.5
Answer:
D) 5.5
Question 23.
The classes 30 – 39, 40 – 49, 50 – 59, ……………… are called
A) Inclusive classes
B) Exclusive classes
C) Overlapping classes
D) Real classes
Answer:
A) Inclusive classes
Question 24.
The mode of the distribution 2, 5, 7, 5, 3, 1, 5, 8, 7, 5 is
A) 7
B) 6
C) 2
D) 4
Answer:
A) 7

Question 25.
The median value of the series 15, 12, 14, 20, 16, 10 is
A) 15
B) 14.5
C) 15
D) 14
Answer:
B) 14.5
Question 26.
The mid value of the class is used to calculate
A) Mode
B) Median
C) Arithmetic Mean
D) None of these
Answer:
C) Arithmetic Mean
Question 27.
Which of the following is not a measure of central tendency?
A) Range
B) Mean
C) Median
D) Mode
Answer:
A) Range
Question 28.
The mode of the observations 8,9,10, 11, 12, 8, 9, 12, 9, 8, 9,11, 9, 8 is
A) 8
B) 9
C) 10
D) 12
Answer:
B) 9
Question 29.
The median of the observations 6, 21, 9, 19, 15 and 13 is
A) 13
B) 19
C) 15
D) 14
Answer:
D) 14
Question 30.
The lower limit of the class 60 – 69 is
A) 9
B) 64.5
C) 60
D) 69
Answer:
C) 60
Question 31.
The upper limit of the class 30 – 40 is
A) 40
B) 30
C) 75
D) 10
Answer:
A) 40
Question 32.
The modal class of the following frequency distribution is
| Class interval |
Frequency |
| 10 – 20 |
4 |
| 20 – 30 |
9 |
| 30 – 40 |
12 |
| 40 – 50 |
15 |
| 50 – 60 |
8 |
| 60 – 70 |
2 |
A) 30 – 40
B) 40 – 50
C) 50 – 60
D) 20- 30
Answer:
B) 40 – 50

Question 33.
The mean of first ten odd natural numbers is
A) 19
B) 10
C) 20
D) 5
Answer:
B) 10
Question 34.
The width of the class interval 40 – 50 is
A) 50
B) 45
C) 10
D) 40
Answer:
C) 10
Question 35.
The value of the observation which occurs most frequently is called
A) Mean
B) Median
C) Range
D) Mode
Answer:
D) Mode
Question 36.
The average weight of 5 packets is 24 kgs and the average weight of another 10 packets is 12 kgs, then average weight of 15 packets is ……………….
A) 6 Kgs
B) 16 Kgs
C) 10 Kgs
D) 36 Kgs
Answer:
B) 16 Kgs
Question 37.
Mode of the scores 7, 8, 5, 6, 3, 6, 7, 6, 1 is ………………….
A) 7
B) 5
C) 6, 7
D) 6
Answer:
C) 6, 7
Question 38.
12.5 is the class mark of the class interval
A) 10 – 15
B) 0 – 25
C) Both A and B
D) None
Answer:
B) 0 – 25
Question 39.
Mean of three consecutive even numbers is 16. The numbers are
A) -14,-16,-18
B) 13, 15, 17
C) -13, -15, -17
D) 14, 16, 18
Answer:
D) 14, 16, 18

Question 40.
10, 12, 12, 11, 8, 15 are the marks obtained by a group of IX class students in mathematics. Even though when two students Bhanu and Roja joined with them the median doesn’t changed. The possible marks of Bhanu and Roja are
A) 13, 18
B) 6, 9
C) 17, 18
D) 9, 18
Read the following information and answer the questions from 6 – 10.
Marks of students of a class were given
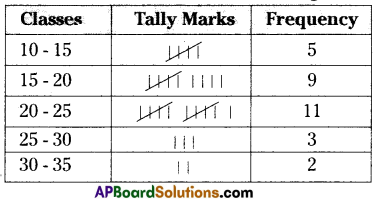
Answer:
D) 9, 18
Question 41.
From the given table the lower limit of highest frequency class
A) 30
B) 15
C) 20
D) 25
Answer:
C) 20
Question 42.
In the class no. of students more than 25 marks obtained is
A) 30
B) 5
C) 14
D) 25
Answer:
B) 5
Question 43.
If three students with marks 26, 27 and 28 were joined, which class frequency changes?
A) 30 – 35
B) 10 – 15
C) 20 – 25
D) 25 – 30
Answer:
D) 25 – 30
Question 44.
In the given data ‘ 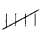 ’ represents
’ represents
A) 20
B) 10
C) 15
D) 5
Answer:
D) 5
Question 45.
While drawing a bar graph, which class bar is the smallest in it’s length?
A) 15 – 20
B) 10 – 15
C) 25 – 30
D) 30 – 35
Answer:
D) 30 – 35
Question 46.
While writing the expansion form of 5161 we use some digits. Mode of the digits used in the expansion is
A) 0
B) 6
C) 5
D) 1
Answer:
C) 5

Question 47.
Given below are the marks obtained in a Mathematics examination of Class IX:

The above data was classified as 0 – 25, 25 – 50, 50 – 75, 75 – 100.
In which class the frequency is more?
A) 75 – 100
B) 0 – 25
C) 25 – 50
D) 50 – 75
Answer:
A) 75 – 100
Question 48.
In an ungrouped data there are 10 scores. After arranging them which term is the median?
A) Average of \(\frac{n^{\text {th }}}{2}\) term and
(\(\frac{n}{2}\) + 1)th term
B) \(\frac{n^{\text {th }}}{2}\) term
C) (\(\frac{n}{2}\) + 1)th term
D) (\(\frac{n+1}{2}\))th term
Answer:
Question 49.
For an ungrouped data of 10 scores
Arithmetic mean is 12. If one more socre is joined to the previous scores the mean increases by 0.5 with this information.
Ravi: Ravi says that the new score will be 0.5 more than 12.
Harsha : Harsha says that the new score will be 5.5 more than 12.
Ritu : Ritu says that sum of 11 scores is 17.5 greater than sum of 10 scores. Now, which of these is correct?
A) All are correct.
B) Ravi and Harsha are correct.
C) Harsha and Ritu are correct.
D) Ravi and Ritu are correct.
Answer:
C) Harsha and Ritu are correct.
Question 50.
While doing a project work on weights of students in the class-room Sekhar found mean wt of the class as 28 kg, median as 29.5 kg and mode as 27 kg. While doing his project two students Eswar & Nawaz were absent in the class. If those two were attended mean, median and mode will not change. Then the possible wt’s of these two students are (in kgs)
A) 27, 29
B) 28, 28
C) 27.5, 28.5
D) 20, 36
Read the following and answer question 16 to 20 :
Data given of marks obtained by the students in an examination.
| Marks obtained |
No. of Students |
| Upto 5 |
5 |
| Upto 10 |
11 |
| Upto 15 |
19 |
| Upto 20 |
25 |
Answer:
A) 27, 29
Question 51.
No. of students who got more than 15 marks:
A) 6
B) 25
C) 19
D) 11
Answer:
B) 25
Question 52.
If 6 students were failed, then the no. of students who passed and got up to 15 marks are
A) 13
B) 5
C) 6
D) 11
Answer:
A) 13

Question 53.
No. of students who are in the class of 10 – 15 is
A) 20
B) 6
C) 8
D) 14
Answer:
A) 20
Question 54.
If 5 more students are joined with marks 12,15,8,19,6 in the class, then the no. of students who got more than 15 marks are
A) 7
B) 10
C) 9
D) 8
Answer:
D) 8
Question 55.
In 10 – 15 class 10 is called as
A) Upper boundary of 10 – 15 class
B) Lower limit of 10 – 15 class
C) Upper limit of 10 – 15 class
D) Lower boundary of 10 – 15 class
Answer:
D) Lower boundary of 10 – 15 class
Question 56.
To find mean weight of 3 types of vegetables which are 4 kg, 6 kg, 8 kg, Usha and Laxmi do like these :
Usha : Weight given = 4 kg, 6 kg, 8 kg
Mean weight = \(\overline{\mathrm{X}}\) = \(\frac{3}{18}=\frac{1}{6}\) kg
Laxmi : Weight given = 4 kg, 6 kg, 8 kg
Mean weight = \(\overline{\mathrm{X}}\) = \(\frac{4 \times 6 \times 8}{3}\) = 64kg
From the above information
A) Both are wrong.
B) Usha only wrong.
C) Laxmi only wrong.
D) Both are right.
Answer:
A) Both are wrong.
Question 57.
A paper is folded several times. When it was opened it was observed that it contained 22 triangles and 22 quadrilaterals and 12 pentagons. From the above mode is
A) Both triangles and quadrilaterals
B) Triangles
C) Quadrilaterals
D) Pentagons
Answer:
B) Triangles
Question 58.
Means of first 10 whole numbers and first 10 natural numbers is in the ratio of
A) 9: 11
B) 10 : 11
C) 11 : 10
D) 11 : 9
Answer:
A) 9: 11
Question 59.
\(\overline{\mathrm{X}}\) = A + \(\frac{\mathbf{\Sigma f}_{\mathbf{i}} \mathbf{d}_{\mathbf{i}}}{\mathbf{\Sigma} \mathbf{f}_{\mathbf{i}}}\) is the formula to find
mean for an ungrouped data. In this formula letter A represents for
A) Assumed mean
B) Arithmetic mean
C) Frequency
D) Deviation value
Answer:
A) Assumed mean

Question 60.
Mean of first five even natural numbers is
A) 6
B) 8
C) 30
D) 10
Answer:
A) 6
Question 61.
Median of 10, 15, 7, x, 27, 30 is 16, then x =
A) 15
B) 17
C) 16
D) 18
Answer:
B) 17
Question 62.
Pulse rates per minute of a patient observed by the doctor are 72, 78, 90, 102 and 73. Then the average pulse rate is
A) 76
B) 79
C) 82
D) 83
Answer:
D) 83
Question 63.
In a cricket match an over contains six balls. In a T-20 Cricket match it was already 5 balls bowled in the last over. If Sachin hits six for the last ball the mean becomes 4 runs per ball in the over. But Sachin hits four runs. Then the mean score per ball in that over is
A) 3
B) 3\(\frac{2}{3}\)
C) 4
D) 6
3
Answer:
A) 3
Question 64.
The mid value of the class 10 – 19 is
A) 14
B) 14.5
C) 15
D) 15.5
Answer:
B) 14.5
Question 65.
For the given scores \(\overline{\mathrm{X}}\) = 12 and Σx1 = 192, then n =
A) 12
B) 15.8
C) 16
D) 18
Answer:
C) 16
Question 66.
The mode of the scores 12, 11, 12, 9, 10, 9, 12 is
A) 9
B) 10
C) 11
D) 12
Answer:
D) 12

Question 67.
If the mean height of 3 boys is 142 cm. and the mean height of another 7 students is 145 cm., then the mean height of 10 students.
A) 144 cm
B) 144.1 cm
C) 144.2 cm
D) 144.4 cm
Answer:
B) 144.1 cm
Question 68.
The median of rational numbers \frac{1}{2}, \frac{2}{3}, \frac{5}{6}, \frac{1}{4} and \(\frac{3}{5}\)
A) \(\frac{1}{2}\)
B) \(\frac{3}{5}\)
C) \(\frac{2}{3}\)
D) \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Answer:
B) \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Question 69.
Mean of 2.5, \(\frac{5}{2}\), 5.2, \(\frac{2}{5}\) is ………………..
A) 0.4
B) 2.5
C) 2.65
D) 5.2
Answer:
C) 2.65
Question 70.
In the formula, \(\overline{\mathrm{X}}\) = \(\frac{\sum \mathbf{x}_{\mathbf{1}}}{\mathbf{n}}\) the letter \(\overline{\mathrm{X}}\) represents
A) No. of observations
B) Sum of observations
C) Product of observations
D) Mean of observations
Answer:
D) Mean of observations
Question 71.
a data is represented using the classes 20 – 29, 30 – 39, ………….., 120 – 129. What is the length of the class interval 90 – 99 ?
A) 90
B) 89.5
C) 10
D) 9
Answer:
C) 10
Question 72.
Two students collected two different data sets P and Q for a project.
P :A table with the weights of all students of a class. The data was collected by a student for the project.
Q: A table with lists of daywise absentees in a class. The data was collected by using the class attendance register.
Which of the following is true about P and Q?
A) P is primary data & Q is primary data
B) P is secondary data & Q is primary data
C) P is primary data & Q is secondary data
D) P is secondary data & Q is secondary data
Answer:
C) P is primary data & Q is secondary data
Question 73.
For a data, the range is
A) Maximum Value – Minimum Value
B) Maximum Value + Minimum Value
C) Maximum Value × Minimum Value
D) Maximum Value / Minimum Value
Answer:
A) Maximum Value – Minimum Value
Question 74.
A data of n observations (n is odd number) is arranged in descending order, then which observation represents median?
A) [ (\(\frac{n}{2}\))th + 1] observation
B) (\(\frac{n}{2}\))th observation
C) [latex]\frac{n+1}{2}[/latex]th observation
D) [latex]\frac{n-1}{2}[/latex]th observation
Answer:
C) [latex]\frac{n+1}{2}[/latex]th observation

Question 75.
For the data, 0, 1, – 1, 1, 2, which of the following is TRUE?
A) Mean = Median = Mode
B) Mean = Median ≠ Mode
C) Mean ≠ Median ≠ Mode
D) Mean ≠ Median = Mode
Answer:
C) Mean ≠ Median ≠ Mode
Question 76.
If each observation of the data 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 14, 15, 16, 20 is multiplied by 2, then median of new data is ……………….
A) 28
B) 26
C) 25
D) 24
Answer:
B) 26
Question 77.
Cumulative frequency is used in finding, which of the following?
A) Mean
B) Median
C) Mode
D) Range
Answer:
B) Median
Question 78.
Mode of the given data 6, 7, 8, 6, 7, 7, 9,8
A) 7
B) 8
C) 6
D) 9
Answer:
A) 7