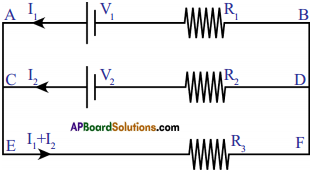
AP State Syllabus AP Board 9th Class Biology Solutions Chapter 9 Adaptations in Different Ecosystems Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Biology Solutions 9th Lesson Adaptations in Different Ecosystems
9th Class Biology 9th Lesson Adaptations in Different Ecosystems Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
What do you understand by adaptations in organisms and why do they adapt? (AS 1)
Answer:
- The ways and means that organisms adapt or develop over a certain period of time in different conditions for better survival are adaptation of organisms.
- Adaptation is a feature that is common in any population because it provides some improvement for better survival.
![]()
Question 2.
With the help of two examples, explain how these organisms have adapted themselves in the ecosystem? (AS 1)
Answer:
- Mangroves grow in a wet and salty place.
- They have evolved to have curious looking projections from their roots called pneu- matophores or knees.
- These pneumatophores develop from the lateral roots that are growing near the surface, and protrude upto 12 inches out of the soil.
- Pneumatophores aid the plants in maintaining adequate root respiration in a watery environment.
- We don’t find such structures in plants growing around us.
- Another example is in kaiabanda, the leaves are reduced to spines so that there is little transpiration loss and water is stored in the tissues of the stem (succulent stems)
- This helps the plant to live in conditions of water scarcity as we come across in deserts.
- With the above two examples, we can say that these organisms have adapted them-selves in the ecosystem.
Question 3.
Collect some aquatic plants- cut the leaves and stems. Observe them under microscope and record your observations like presence air /absence of air spaces etc. and answer the below. (AS 3)
a) Are there any other reasons for their floating?
Answer:
The bodies of aquatic plants are delicate with more than 80% of their weight consisting of water.
b) Draw a diagram of what you have observed under microscope.
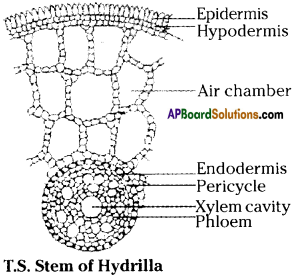
Question 4.
What special adaptations can be seen in the following organisms? (AS 1)
a) mangrove trees
b) camel
c) fish
d) dolphins
e) planktons
a) Mangrove trees :
Answer:

- Mangroves grow in a wet and salty place near the sea shore.
- From their roots arise pneumatophores or knees.
- These pneumatophores develop from the lateral roots that are growing near the surface and protrude upto 12 inches out of the soil.
- Pneumatophores. aid the plants in maintaining adequate root respiration in a watery environment.
b) Camel:
Answer:

- In camel hump stores fat fordater use.
- Long eyelashes protects eye from sand.
- Nostrils closes voluntarily to protect from blowing sand.
- Long legs keeps the body away from hot ground.
c) Fish :
Answer:’
- The body is covered by scales.
- Fishes bear specialised structures to swim like fins.
- Fishes have floaters in their body (special structures of their digestive canals) to be able to inhabit particu¬lar levels in the water body.
- Fishes respire with gills.


d) Dolphins:
Answer:
Dolphins have adapted to their environment in the following ways :
Fins shape – A dolphins tail goes up and down to help it dive up to get the air. The shape of their fins also help to propel them through the water.
To help dolphins save oxygen while they dive under water, their heart beat slower during a dive and their blood is diverted from other parts of their body to their heart, lungs and brain. They also save oxygen via muscles, which have a protein called myo-globin which in turn stores oxygen.
They have a blubber or fat which provides insulation helping the dolphin stay warmer under cold water.
They have a body covering of skin. The upper most layer of skin produces an oil which forms a film that cover the dolphin’s body.
Being mammal dolphin breathe with lungs rather than gills. So they breathe from a blow hole which closes before the dolphin goes into the water. The long nose helps the dolphin to fight sharks and their teeth help them to catch fish.
They have well developed echo location by which they locate other animals and also communicate with each other.
e) Planktons:
Answer:
Microscopic photosynthetic organisms like planktons have droplets of oil in their cells that keeps them float.
![]()
Question 5.
If an animal of euphotic zone has to survive in abyssal zone, what adaptations are required to survive there? (AS 1)
Answer:
Adaptations required to survive in abyssal zone are :
- The animals should have wide mouths and huge curved teeth which prevent escape of any prey.
- Absence of skeleton, flattened bodies are required.
- Animals should have special structures that produce light on their bellies, around their eyes, and at the sides of their bodies.
- The animals should show bioluminescence in the dark waters.
Question 6.
Marine water fishes drink more water than fresh water fishes. Do you agree? Justify.
Answer:
- Yes, marine water fishes drink more water than fresh water fishes.
- Because several marine fishes have a lower internal salt concentration than that of the water they swim in.
- So they tend to dehydrate as water is lost by osmosis.
- To compensate, they drink large amount of water and excrete the salts both via their kidneys and through highly specialised cells in the gills.
Question 7.
Visit a nearby pond or lake. Record the organisms you have observed and their adaptations. (AS 4)
Answer:
- Nearby pond or lake consists of three zones namely littoral zone, limnetic zone, and profundal zone.
- In the topmost littoral zone, the edge of a water body is home to snails, insects, several crustaceans, fishes and amphibians, and the eggs and larvae of dragonflies.
- Predators present are tortoise, snakes, and ducks.
- Adaptations : Several organisms have well developed sight, usually have dull and greyish bodies, and are fast swimmers.
- Limnetic zones contains fresh water fish, crustaceans like daphnia, cyclops, and small shrimps are present.
- Floating- plants like water hyacinth, wolfia, pistia along with algae are present.
- Adaptations seen in the plants this zone are presence of air space, leaves covered with wax, etc.
- In the profundal zone scavengers and predators for example crustaceans, crabs, fishes like eels and snails, turtles are present.
- They adapt themselves by feeding on dead animals that settle down.
Question 8.
Draw a lake showing different zones. Why are they called so? (AS 5)
Answer:
Zones of Lake :
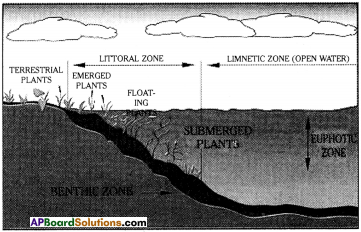
1) Littoral zone :
The zone close to shore. They reaches all the way. Plants living in this zone perform photosynthesis.
2) Limnetic zone :
Sunlit part of the lake surrounded by the littoral zone. This zone extends at a depth where sunlight penetrates.
3) Profundal zone :
It is much colder and denser than previous zones.
Question 9.
Collect information of one lake from internet and prepare a table of organisms adapted at different zones.
Answer:
Different zones in lakes and types of organisms present:
1) The littoral zone :
a) The topmost and warmest zone at the edge of a water body is home to snails, clams, insects, several crustaceans, fishes and amphibians and eggs and larvae of dragonflies.
b) Plants like mosses, water lily, vallisneria, hydrilla etc. are found along with several types of algae.
c) Predators of this zone are tortoise, snakes and ducks.
2) The limnetic zone :
a) This zone contains variety of fresh water fish with bright shiny scales.
b) Transparent or whitish bodied crustaceans like daphnia, cyclops, small shrimps are also found in this zone.
c) There are different types of floating plants like water hyacinth wolfia, pistia along with a variety of algae.
3) The profundal zone :
a) Mostly heterotrophs are present.
b) Scavengers and predators like crustaceans, crabs, fishes like eels and glossogobius (isika dondu), snails, turtles etc are present.
c) Many kinds of bacteria are also present in this zone that help in decomposition.
![]()
Question 10.
Write the effect of temperature on the organisms adapted in a lake and pond in a tabular form. (AS 1)
Answer:
- In deeper lakes during summer only the surface water is heated up while the deeper layer remain cold. During summer the ponds dry up.
- In tropical regions water gets heated up and evaporates in lakes. During average temperatures the water in the pond heated up and evaporates.
- The requirements necessary to the organisms like oxygen and nutrients gets decreased in the lake.
- The salinity of the water increases, concentration of oxygen decreases and availability of food decreases in pond during average temperatures.
- In the cold regions upper layers of the lake gets frozen during winter and lower layers does not.
- The entire pond gets frozen during winter.
- Aquatic animals in tropics undergo aestivation or hybernation to overcome extreme cold or hot seasons.
Question 11.
Amphibians are wonderful creatures on the earth. How do you appreciate their adaptation? (AS 6)
Answer:
- Amphibian body has small waist, no neck. Streamlined body shape helps in swimming.
- Skin is thin and moist allows gaseous exchange in cutaneous respiration.
- Front legs used to keep the front portion of the body off the ground.
- Hind legs able to jump great distances and change direction quickly.
- Eyes are positioned on top of head gives the frog a wide angled visual field.
- Mouth is very large and broad can able to catch and eat large prey.
- Tongue attached at front of mouth enables it stick the prey when caught.
- Frogs start their lives as aquatic tadpoles with gills to breathe. As tadpole grows into frogs lungs replace the gills and allows frog to breathe on land.
Question 12.
Some animals and plants survive only in certain conditions. Nowadays human activities cause damage to these conditions. What do you think about this? (AS 7)
Answer:
- Human activities are causing lot of damage to biodiversity.
- Human activities such as deforestation, overgrazing, conversion of forest land to agricultural land, hunting and indiscriminate killing of animals for their products, and pollution can endanger the plant and animal species.
- If proper care is not taken plants and animals may disappear totally from the surface of the earth.
Question 13.
In the chapter on ecosystem, we had studied about the mangrove ecosystems. What kind of abiotic conditions did you study in them? (AS 1)
Answer:
Kinds of abiotic conditions in mangrove ecosystems are soil, pH, oxygen, nutrients, winds and currents, light, temperature, humidity, tides, salinity.
![]()
Question 15.
Are there any rivers meeting in the Bay of Bengal in the Coringa ecosystem? Collect information and make a note on them.
Answer:
- Coringa mangrove is situated South of Kakinada Bay and is about 150 km South of Visakhapatnam.
- Coringa is named after the river Coringa.
- Coringa mangroves receive fresh water from Coringa and Gaderu rivers, distributors of Gautami, Godavari rivers, and neritic waters from Kakinada Bay.
- Numerous creeks and canal traverse this coringa ecosystem.
Question 17.
The Murrel (Korramatta) and Rohu are fishes found in rivers. Will they be able to live in the coringa ecosystem ? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer:
- Yes, Murrel and Rohu be able to live in the coringa ecosystem.
- Because coringa ecosystem gets fresh water from rivers coringa, Gaderu and distributories of Gautami, Godavari rivers.
- If the salinity of the water in the coringa ecosystem increases, the water enters the body of fresh water fishes.
- The water can be excreted in the form of urine, but to maintain a suitable salt bal¬ance fresh water fish need to reabsorb salt through the kidneys and salt collecting cells in gills.
Question 18.
How the frogs got protected themselves from cold and heat?
Answer:
- Frogs are cold blooded animals so they can’t tolerate extreme cold or heat conditions.
- They protect themselves from extreme cold conditions by a process called hibernation (winter sleep) and from extreme heat conditions by Aestivation (summer sleep)
- During these processes they burrow deep in the ground and remain motionless until the conditions are favourable.
- During this period the rate of metabolic activities slow down and the animal goes into a nearly unconscious sleepy condition.
![]()
Question 19.
How do you appreciate the processing protection pebble plants from the enemies?
Answer:
- Pebble plants are also called living stones.
- They protect themselves from their enemies by adapting themselves to their habitat.
- They survive by living partly underground.
- They avoid being eaten by blending in with surrounding rocks.
- Leaves of these plants are not green as in almost all higher plants, but various shades of cream, grey and brown, patterned with darker windowed areas, dots and red lines.
- The markings on the top surface disguise the plant in its surroundings (camouflage)
- Thus, they adopt wonderfully to their habitats and protect themselves from their enemies.
9th Class Biology 9th Lesson Adaptations in Different Ecosystems InText Questions and Answers
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 131
Question 1.
What is a habitat?
Answer:
Habitat is the immediate environment occupied by an organism or the living place of an organism.
Question 2.
Is a tree habitat only for a crow?
Answer:’
No. Tree is a habitat for variety of birds and insects.
![]()
Question 3.
In what way an ecosystem is different from habitat?
Answer:
In ecosystem biotic and abiotic components are present. Habitat is the place where organisms live in an ecosystem.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 134
Question 4.
You may know animals that live in water. Do you find in them any suitable characters adapted to live in water? Write a note on them in your notebook.
Answer:
- Structural adaptations in the bodies like presence of special air spaces.
- Such air spaces help them to swim and float in water.
- The aquatic organisms bear specialized structures to swim like flippers as in turtles and fins in fishes.
- Fishes, dolphins have floaters in their body to be able to inhabit particular levels in the water body.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 135
Question 5.
In what way flexible stem is useful to the aquatic plants?
Answer:
- In aquatic plants flexible stem contains a parenchymatous tissue known as arenchyma.
- Arenchyma consists of number of air filled spaces.
- These air spaces help the plant to float on water.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 137
Question 6.
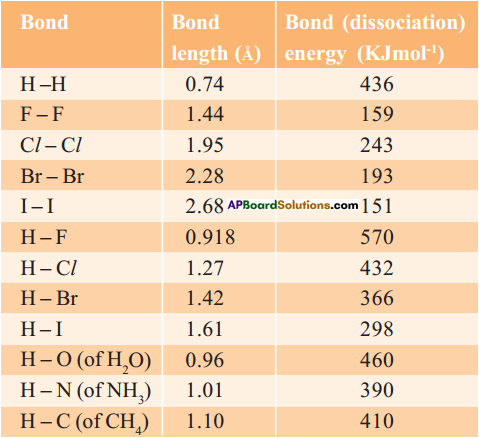
Observe the table and answer the following questions.
Answer:
a) How many zones can you see in the figure basis of light penetration? Name them.
Answer:
Three zones are present. They are eu- photic zone, bathyal zone and abyssal zone.
b) What types of abiotic conditions do you find as per the given table?
Answer:
Light, temperature and depth.
c) What will effect adaptation to marine life other than the conditions shown in the table and figure?
Answer:
Salinity, oxygen, rainfall, regular windflow, soil, pH, nutrients, humid-ity, oceanic currents effect adaptation to marine life.
d) What happens to the temperature and pressure as depth increases?
Answer:
As depth increases temperature decreases and pressure increases.
e) Which zone has more animals? Guess why.
Answer:
- Bathyal zone has more animals. Because the conditions in this zone are suitable for the organisms to grow.
- Red and brown kelps are the primary producers. They provide food to other organisms in that zone.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 139
Question 7.
Does Pulikat lake of Nellore come under fresh water ecosystem or not? Why?
Answer:
- Pulikat lake of Nellore comes under marine or salt water ecosystem.
- Because the salinity of water in the lake is 3.5%.
- Main salts present in the Pulikat lake are sodium and potassium.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 140
Question 8.
‘Think, how webbed feet helps ducks?
Answer:
- Webbed feet of birds help them to adapt conditions on land as well as in water.
- Webbed feet have enabled them to be good swimmers.
![]()
Question 9.
Why cranes have long legs and long beaks?
Answer:
- Cranes have long, thin legs wander through the mud shallows searching for insects.
- Long beak help them in searching of insects in the mud.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 141
Question 10.
How are marine ecosystems different from fresh water ones?
Answer:
- The saliny of water in marine ecosystem is 3.5% whereas it is 1.8% in fresh water.
- Marine ecosystems are huge and they make up about three-fourths of the earths surface.
- The number of organisms present in marine ecosystems are more when compared to fresh water ecosystem.
Question 11.
Write two types of adaptations you find in marine ecosystems, different from fresh water ecosystems.
Answer:
- Many marine animals have blubber fur insulation from the cold and some fish have an antifreeze like substance in their blood to keep it flowing.
- Marine animals must regulate the interaction of fresh water and salt water in their bodies.
- Specially developed kidneys, gills and body functions help to maintain salt concentrations across members through osmosis.
Question 12.
What are the similarities in adaptation on the basis of light penetration in the two aquatic ecosystems?
Answer:
- In both the aquatic ecosystems, light penetrates upto a depth of zoom only.
- The light intensity is sufficient to perform photosynthesis.
- In the low light intensities below 200 mts depth is sufficent to perform photosynthesis by some kelps.
- Due to the lack of light in abyssal and profundal zones, usually scavengers and predators exists.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 142
Question 13.
Which zone do you think, when compared to marine ecosystems, is absent in fresh water ecosystem?
Answer:
Benthic zone is absent in fresh water ecosystem when compared to marine ecosystem.
![]()
Question 14.
What would be a major factor leading to different types of adaptations in marine, fresh water ecosystems?
Answer:
Light would be a major factor leading to different types of adaptation in marine, fresh water ecosystems.
Question 15.
Do all plants shed their leaves at same time in a year throughout the world?
Answer:
- No. Some plants in temperate regions shed their leaves before the winter starts.
- In tropical regions some plants shed their leaves before the start of summer.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 143
Question 16.
Are thorny leaves also an adaptation to temperature?
Answer:
- No. They are not adaptation to temperature.
- They are adaptation to protect themselves from the animals who eat them.
Question 17.
If the trees have broad leaves at the time of snow fall season what will happen?
Answer:
If the trees have broad leaves at the time of snow fall season, the branches of tree can break due to the weight of snow gathered on each leaf and branch during snow fall.
Question 18.
Why polar bear has thick fur on its body?
Answer:
- Polar bear has thick fur coat or hair covering on their bodies.
- The fur act as insulator preventing heat loss from its body.
![]()
Question 19.
In what way thick skin helps the seal to protect from cold weather?
Answer:
- In the thick layer of skin, fat is deposited in seals.
- The thick layer of fat deposited under their act as insulators preventing heat loss from its body.
- The fat not only insulates the body but helps in producing heat and energy.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 132
Question 20.
Can you give some examples of fleshy leaf plants?
Answer:
Yes. Bryophyllum, Aloe, and Agave are the examples for fleshy leaved plants.
Question 21.
Why xerophytic plants do not have broad leaves?
Answer:
To prevent the excessive loss of water through respiration xerophytic plants do not have broad leaves.
Question 22.
You may see Kittanara, a xeric plant, grown as fence around crop fields in some areas in our state. Actually those places are not desert. How can they grow there?
Answer:
They grow there because this plant shows adaptations in that places.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 133
Question 23.
Do all animals living in desert conditions show adaptations?
Answer:
Yes, all animals living in desert conditions show adaptations.
![]()
Question 24.
Why some animals have scales on their body?
Answer:
- Scales mainly protect the animals from environment.
- In desert animals scales allow them to retain moisture by preventing the evaporation of water through the skin.
- This allows the animal to become dehydrated and animal requires small amount of water to survive.
Question 25.
Why the animals that lives in burrows usually comeout during night time only?
Answer:
To protect themselves from extreme hot conditions, animals that live in burrows usually comeout during night time only.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 139
Question 26.
Which organism among jelly fishes and decomposers present in euphotic zone?
Answer:
Jelly fishes are present in euphotic zone.
Question 27.
What kinds of adaptations can be seen in the organisms of the euphotic zone?
Answer:
- The organisms living in this zone are mostly floaten and swimmen.
- Animals in this zone usually have shiny bodies reflecting light away to merge with shiny water surface are transparent.
- These usually have sharp vision.
Question 28.
What kind of adaptations can be seen in the organisms of abyssal zone?
Answer:
- The larger animals in abyssal zone have wide mouths and huge curved teeth which prevent escape of any prey.
- Absence of skeleton, flattened bodies are some other characteristics observed.
- Some animals also have special structures that produce light on their bellies, around their eyes and at the sides of their bodies.
- Some animals shows bioluminiscence in the dark waters.
Question 29.
What differences can you find in the animals of bathyal zone when compared to animals of euphotic and abyssal zones?
Answer:
- Most of the plants found in this zone are the red and brown kelps, sponges, corals even animals with tubular bodies like squids and large animals like whales, etc.
- Some of the animals in the bathyal zone have a flat body like the ray fishes.
- Big eyes sensitive to very dimlight may present in bathyal zone animals.
![]()
Question 30.
How organisms of different zones of marine ecosystem are adapted?
Answer:
- The animals of euphotic zone are mostly floaters and swimmers.
- Animals in this zone usually have shiny bodies reflecting light away to merge with shiny water surface.
- Animals of euphotic zone have very sharp vision.
- Some of the animals in bathyal zone have a flat body like the ray fishes.
- The animals may have big eyes sensitive to very dim light in bathyal zone.
- Absence of skeleton, flattened bodies are some adaptations found in animals of abyssal zone.
- Some animals in abyssal zone may have special structures that produce light on – their bellies, around their eyes and at the sides of their bodies.
- Some animals in abyssal zone shows bioluminiscence in the dark waters.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 141
Question 31.
Organisms of the oceans have a lesser salt content in their bodies than the seawater around 3.5%. The fluid could drain out of the body of the organisms into the sea. This could be dangerous and fatal to the organism. How do they survive under such conditions?
Answer:
- Several marine species have a lower internal salt concentration than that of the water they swim in. So they tend to dehydrate as water is lost by osmosis.
- To compensate, they drink large amounts of water and excrete the salts both via their kidneys and through highly specialised cells in the gills.
Question 32.
Can fish in estuarine ecosystem survive in river as well as in sea?
Answer:
- Yes, fish in estuarine ecosystem survive in river as well as in sea.
- Two of the main challenges of estuarine life are the variability in salinity and sedimentation.
- Many species of fish living in estuarine have various methods of control to the salt shifts.
- They regulate the salt concentrations using osmoregulaters.
9th Class Biology 9th Lesson Adaptations in Different Ecosystems Activities
Activity – 1
Question 1.
i) Take a Kalabanda (Aloevera) and a Balsam plant in two separate pots.
ii) Water each of them with two tablespoons of water.
iii) Do not water them for a week.
iv) Observe the condition of the plants after a week.
Observations :
a) Which plant showed growth?
Answer:
Kalabanda plant showed growth.
b) Which plant dried first? Why?
Answer:
Balsam plant dried first. Because Balsam plants are not watered regularly. They need water to grow.
Activity – 2
Question 2.
i) Collect an aquatic plant out of a water body (e.g. Duck weed, Hydrilla, Vallisneria etc.) ii) Carry it back home and plant it in a pot and water it.
Observations :
a) From the above activity we see that some plants dry up without water very quickly, while other can grow even with very little water.
b) Each of these plants are adapted to the conditions in their surroundings on the basis of need of water.
Activity – 3
Question 3.
You know some of the animals that reside in and around lake or pond. Make a list of those animals and the characteristics of their body.
List of animals and reside in and around lake or pond :
Insects : Dragonfly, Damsefly, Mayfix, Stonefly, Dobsofly, Caddisfly, Cranefly, Water bugs, Beetles, etc.
| Crustaceans | Cray fish, Scuds, Shrimps |
| Molluscs | Snails |
| Annelids | Leeches |
| Fish | Blugill, Bass, Catfish, Sculpin, Minnow |
| Reptiles | Snakes, turtles |
| Amphibia | Frogs |
Characteristics of the body of animais living in and around lake:
| Animals | Characteristics |
| 1) Mosquito | The body is segmented and it is a carrier of diseases. |
| 2) Shrimps | ‘ These are small, bottom dwelling crustaceans with a translucent exoskeleton. |
| 3) Snails | A soft bodied animal with a hard protective shell. |
| 4) Swan | Swans are long necked water birds, webbed feet are present. |
| 5) Crayfish | Fresh water crustaceans with four pairs of walking legs. Body is segmented with head and thorax united. |
| 6) Dragonfly | it is a flying insect with a long abdomen. Body is elongated with two pairs of transparent wings. |
| 7) Earthworm | It is a little animal with a long, soft body and no legs. |
| 8) Fish | It lives in the water and breathe with gills. |
| 9) Goldfish | It is a type of crap that makes a nice pet, kept in aquariums and swims with fins. |
| 10) Toads | The skin is dry and leathery. Toads are amphibians with poison glands, short legs and snout like parotid glands. Drier skin. Webbed feet helps in walking and swimming. |
| 11) Leech | The body is segmented. It sucks blood of other animals. |