Students get through AP Inter 2nd Year Zoology Important Questions Lesson 3(a) Musculo-Skeletal System which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 2nd Year Zoology Important Questions Lesson 3(a) Musculo-Skeletal System
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is a ‘motor unit’ with reference to muscle and nerve?
Answer:
Motor unit: A motor neuron along with muscle fibres innervated by its telodendrites is called Motor unit.
Question 2.
What is triad system? [TS MAY-22] [TS MAR-15,16,17]
Answer:
- Triad System: Each T tubule is flanked on either side by several terminal cistemae of the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
- T tubule and the two terminal cistemae at its sides form the triad system.
![]()
Question 3.
Write the difference between actin and myosin.
Answer:
| Actin | Myosin |
| 1) Actin is a thin contractile protein | 1) Myosin is thick contractile protein |
| 2) Actin is present in light band called isotropic band, | 2) Myosin is present in dark bands called anisotropic band. |
| 3) Actin filaments are connected to Z line | 3) Myosin filaments are connected to M line. |
Question 4.
Distinguish between red muscle fibers and white muscle fibers. [AP MAY-22HAP MAR-15,19]
Answer:
| Red muscle fibers | White muscle fibers |
| 1) Red muscle fiber have more myoglobin and more mitochondria. | 1) White muscle fibers have less quantity of myoglobin and very few mitochondria. |
| 2) They are called aerobic muscles. | 2) They are called anaerobic muscles. |
| 3) They utilise oxygen stored in mitochondria. | 3) They depend on anaerobic process for release of energy. |
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
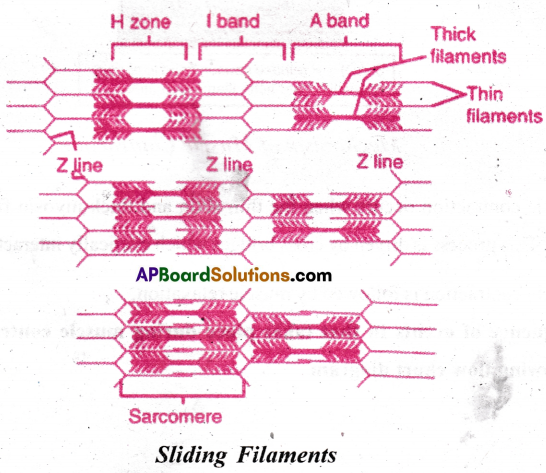
Write a short note on sliding filament theory of muscle contraction?
Answer:
- Sliding filament theory which explains the process of muscle contraction.
- Contraction of a muscle fibre takes place by sliding of thin filament over thick filament, which shortens the myofibril.
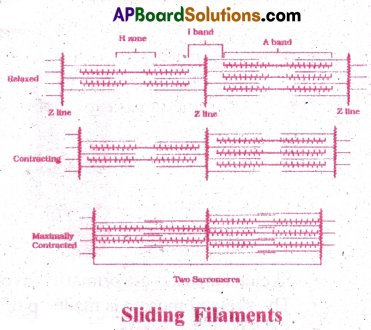
- A special contractile proteins called Actin & Myosin are present in each muscle fibre. Actin is a thin protein present in light band called ‘I’ band.
- Myosin is a thick protein, present in dark band called ‘A’ band.
- A dense and narrow elastic fibre called ‘Z line, which bisects the I-band at its mid point. Central part of the thick filament which is not overlapped by the thin filament is called ‘H’ zone.
- During muscle contraction, myosin heads, bind to the exposed active sites on the actin molecules and form ‘cross bridge .
- This cross bridge pulls the thin filaments towards the centre of the A band. The ‘Z line attached to the actin filaments is also pulled leading’to the shortening of the sarcomere ie.contraction.
- During the shortening of the muscle the I bands get reduced in length, where as the ‘A’ bands retain their length, and ‘H’ zone disappears.
Question 2.
Describe the important steps in muscle contraction. [TS MAY-22]
Answer:
Muscle contraction is explained by sliding filament mechanism. It was proposed by Hugh Huxley and Jean Hanson. It involves the following five steps.
- Excitation of muscle.
- Formation of cross bridges.
- Power stroke
- Recovery stroke
- Relaxation of muscle.
1) Excitation of muscle: On receiving the signal from CNS the neuro muscular Junction (end plate) releases acetylcholine. It generates action potential in sarcolemma which reaches sarco plasmic cistemae through T-tubuIe. Calcium ions are released from cistemae.
2) Formation bf cross bridge: Ca+ ions are connected to Tn C unit of troponin. TheTn-C tropomysin complex moves away from active sites of actin molecules. The myosin head binds to active sites forming cross bridge P1 (energy phosphate)is released.
3) Power Stroke: The myosin cross bridges pull actin filament toward ‘M’ line (Centre of A band). The I zone is reduced. A band retains its size. Z lines are brought close together. H zone disappears then the muscle contracts.
4) Recovery Stroke: ADP is released, myosin cross bridges are broken. Myosin gets connected to another ATP site and contraction cycle continues.
5) Relaxation: The motor impulses stop. Ca ions pumped back to cistemae. I band A band retain their size. Then the muscle is relaxed.
Question 3.
Describe the structure of a skeletal muscle.
Answer:
Skeletal Muscle Structure:
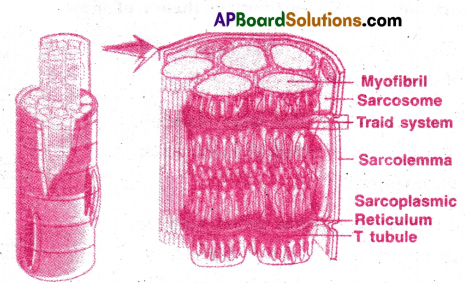
- Skeletal muscles are primarily involved in locomotion and bodily movements.
- The skeletal muscle is made up of muscle bundles or fascicles.
- Each fascicle contains cylindrical muscle fibres. The fascicles are held together by collagenous connective tissue called fascia.
- Each muscle fibre has an outer sarcolemma, enclosing sarcoplasm.
- There are many peripheral nuclei (syncytium)
- The endoplasmic reticulum is sarcoplasmic reticulum, which stores calcium ions.
- There are large number of parallel myofibrils in sarcoplasm.
Myofibril:
- Each myofibril has altemata light and dark bands light band has actin filaments and dark band has myosin filaments.
- Actin filaments are connected to Z line (Krause’s membrane)
- Myosin filaments are connected to M line.
- The part of myofibril from one Z line to the other is sarcomere (functional unit of muscle fibre) Light band is called I band and dark band is A band.
- A band has central light zone called H band or Hensen’s disc.
- The saroplasmic cistemae and T-tubules of invaginated sarcolemma form triads.
![]()
Question 4.
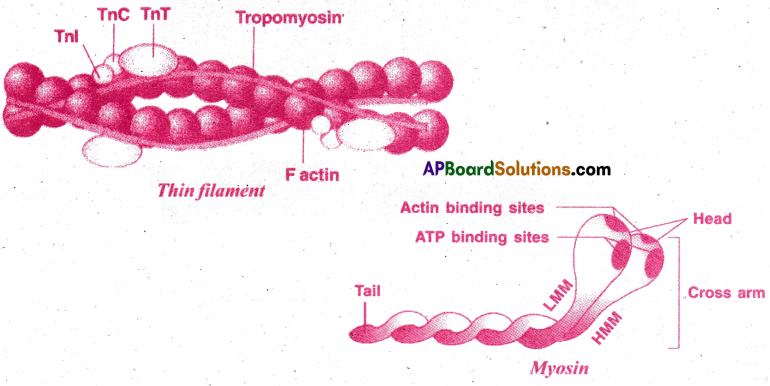
Write short notes on Contracticle proteins.
Answer:
The contractile proteins of a muscle are actin and myosin.
Actin: Each actin filament is formed of two F actin molecules twisted around each other filament. Each F actin molecule is a polymer of monomeric G actin molecules.
- Actin is associated with tropomyosin and troponin proteins.
- Tropomyosin is a filamentous protein that runs along the length of Actin filaments.
- Troponin has three units namely Tn-T, Tn-I, and Tn-C.
- Tn-T binds to tropomysin. Tn-I is an inhibitor protein.
- Tn-C combines with Ca ions.
- Troponin and tropomyosin are called regualtory proteins.
Myosin:
- It is a motor protein.
- It can covert chemical energy into mechanical energy.
- Each myosin molecule has two spirally twisted polypeptide chains.
- Each chain has many monomeric protein called meromyosin.
- Each meromyosin has a head with short arm and tail.
- The head with short arm is formed of heavy meromyosin(Hmm
- The tail is formed of light meromyosin (LMM)
- There are about 200-300 meromyosin molecules in a thick filament.
- The heads are directed towards Z line. The head and shortarm is also called Cross arm.
Question 5.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of the ultrastructure of muscle fiber.
Answer:
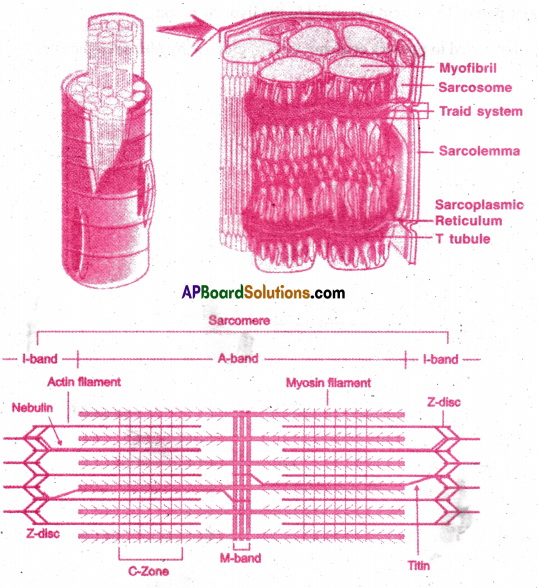
Question 6.
Draw the diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscle showing different regions.
Answer:
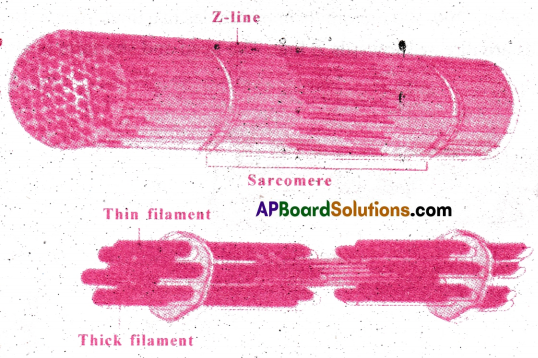
Question 7.
What is Cori’s çycle explain the process.
Answer:
Cori’s Cycle:
- Lactic acid is produced when oxygen Is not available during rapid contractions of skeletal muscles. It is partly oxidised.
- Major part of lactic acid is carried to the liver by blood.
- It is converted to pyruvic acid and then to glucose by gluconeogenesis.
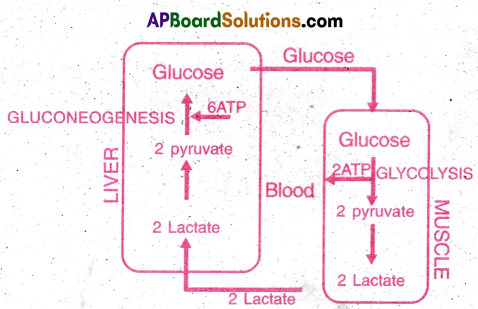
![]()
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
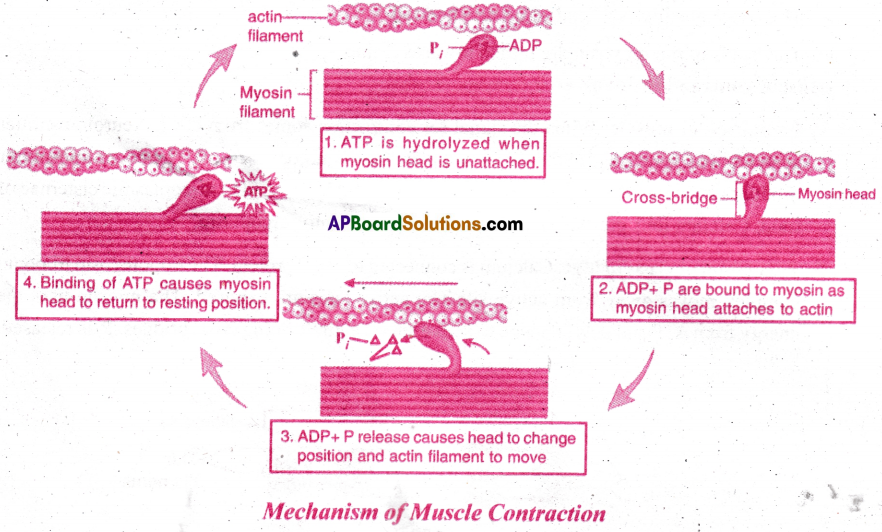
Explain the mechanism of muscle contraction.
Answer:
Mechanism of muscle contraction: Muscle contraction is best explained by sliding filament theory.
- It explains that the thin filaments slide over thick filament bringing about contraction. This theory was proposed by Hugh Huxley and Jean Hanson.
- The contractile proteins are actin and myosin
- Actin: It is present in thin filaments found in I band of sarcomere. They are attached to Z line. These actin molecules have Active sites.
- These active sites are covered by tropomyosin and troponin proteins in relaxed state.
- Myosin protein is present in thick filaments located in A band. They are connected to M line.
- Each myosin has 2 meromyosin molecule.
- The meromyosin has a head, short arm and tail.
- The heads of meromyosin are turned towards Z line.
Muscle contraction involves following stages:
1) Excitation of muscle: When the signal for contraction somes from CNS, Neurotransmitter acetylcholine is released at the motor end plate (neuromotor junction). The neuro transmitter produces action potential in sarcolemma. The potential is carried to sarcoplasmic cistemae of traid. Calcium ions present in Cistemae are released into sarcoplasm.
2) Formation of cross bridge: Calcium is connected to Tn-C protein. The tropomyosin troponin complex moves away from active site.The active sites are exposed. The myosin uses the energy from ATP and gets attached to active site of actin forming cross bridges. P1 is released.
3) Power stroke: The meromyosin contracts, pulling the actin filaments with cross bridges towards M line (centre of A band). The Z lines are pulled towards M line (centre of A band). The size of the sarcomere is reduced bringing about contraction of muscle. The H zone of A band completely disappears.
4) Recovery Stroke: ADP is released, myosin cross bridges are broken. Myosin gets connected to another ATP site and contraction cycle continues.
5) Relaxation of muscle: The motor impulse stops. Ca ions are released from Tn-C and reach the cistemae. Tropomyosin, Troponin complex covers the Active sites. The Z lines return to their normal position. The muscle is relaxed.
Question 2.
List in sequence, the events that take place during muscle contraction?
Answer:
Muscle Contraction. ‘Muscle contraction mechanism’ is explained by the ‘sliding filament theory’ proposed by Jean
- Muscle contraction occurs when the thin actin and thick myosin filaments slide over each other. This process is driven by cross bridges which cyclically interact with the actin filaments.
- Muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation.
- The sequence of events in that takes place during muscle contraction are depicted in the following flow chart diagram.
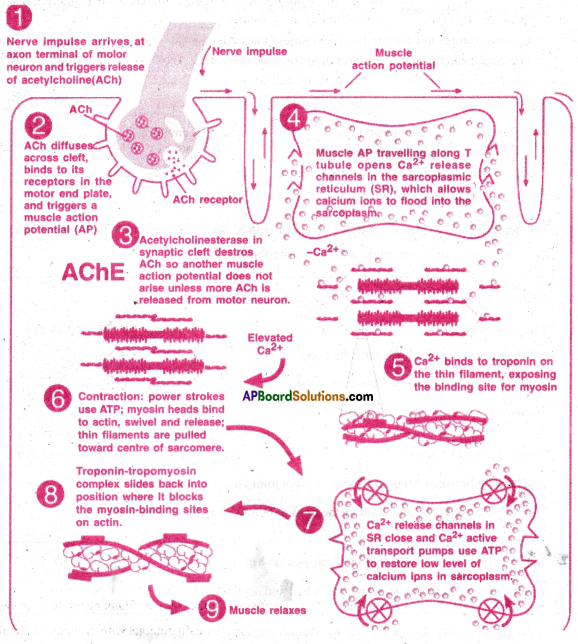
![]()
THE SKELETON
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Name two cranial sutures and their locations.
Answer:
- Coronal sutures in between frontal bone and parietals.
- Lambdoid sutures between parietals and occipital bones.
Question 2.
Name the keystone bone of the cranium. Where is it located? [ TS MAR-19]
Answer:
- Spheniod bone is the keystone bone present in the base of cranium.
- It articulates with most of cranial bones.
Question 3.
Human skull is described as dicondylic skull. Give the reason.
Answer:
The occipital bone has two condyles on either side of foramen magnum, which articulate with atlas and hence called dicondylic skull (as in amphibians).
Question 4.
Name the ear ossicles and their evolutionary origin in human beings. [AP,TS MAR-16]
Answer:
The ear ossicles:
- Malleus- modified articular bone
- Incus – modified quadrate bone
- Stapes – modified hyomandibular.
Question 5.
Name the type of joint between (a) atlas 7 axis (b) carpal/metacarpal of the human thumb.
Answer:
- The joint between Atlas and axis is a pivot joint (Atlas td Axial joint)
- The joint between carpal and metacarpal of human thumb is the saddle joint.
Question 6.
Name the type of joint between Femur and hip bone.
Answer:
The joint between femur and hip bone is ball and socket joint.
Question 7.
Name the type of joint between (a) Cranial bones (b) Inter-tarsal joint.
Answer:
- The joints between cranial bones are called sutures. They are fibrous joints or synarthroses.
- The intertarsal joint is called gliding joint.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
List out the bones of the human cranium.
Answer:
Human Cranium is formed by eight bones:
- Single frontal bone: It forms the forehead and anterior cranial floor and roof of orbits.
- Two Parietal bones: They form major part of roof and sides of the cranium.
- Two temporal bones: They cover the sides and lateral floor of the cranium.
- Single occipital bone: It forms the posterior and posterior ventral part of cranium. It has a large opening called foramen magnum through which medulla oblongata continues into spinal cord. Two condyles are present on either side of foramen magnum (dicondylic skull)
- Sphenoid (single bone) bone: It forms the base of the cranium. It is articulated with most of the cranial bones. Hence it is called as keystone bone.
- Ethmoid (single bone): It is present in the middle of anterior floor of cranium.
Question 2.
Write short notes on the ribs of human being.
Answer:
Ribs:
- Ribs form the thoracic cage present in the human chest.
- There are 12 pair of ribs.
- Dorsally the ribs articulate with vertebral column by two heads and hence called bicephalic (double headed)
- The first seven pairs are true ribs. Ventrally they are connected to the sternum by hyaline cartilages.
- 8th, 9th, 10th ribs are connected to cartilage of 7th rib. They are called vertebrochondral ribs.
- The 11th and 12 pairs are not connected to sterinum. They are called floating ribs.
- The last five pairs are false ribs (8,9,10,11 &12).
- Rib cage is formed by thoracic vertebrae, ribs and sternum.
![]()
Question 3.
List the bones of human fore limb.
Answer:
Bones of fore limb: Each forelimb has 30 bones.
- Humerus (upper arm)
- Radius and ulna (forearm)
- Carpals 8 (wrist bones)
- Metacarpals 5 (palm)
- Phalanges 14 (fingers)
Question 4.
List the hones of the human leg.
Answer:
Bones of Leg: Each leg has 30 bones .
- Femur – thigh bone and the longest bone)
- Tibia & fibula – bones of the shank (knee).
- Tarsals – Ankle bones (7)
- Metatarsals – 5 (bones of foot)
- Digital bones -14 (toes)
- Patella (knee cap) a sesamoid bone formed in tendon.
Question 5.
Draw a neat labeled diagram of pelvic girdle.
Answer:
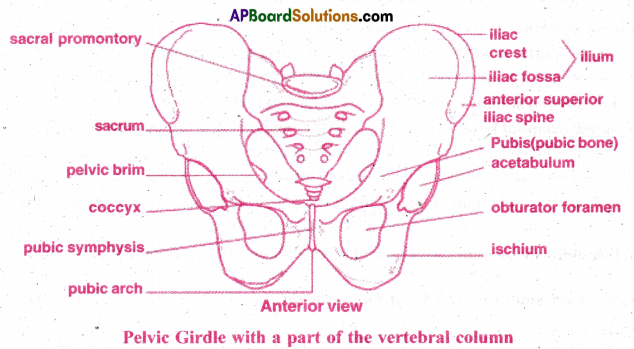
Question 6.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of the skeleton of the fore limb of man.
Answer:
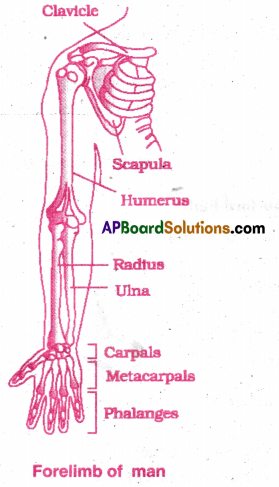
Question 7.
Describe the structure of synovial-joint with the help of a neat labelled diagram. [TS MAY-17][AP MAR-17,19][IPE-14]
Answer:
- Synovial Joint: Synovial joint is free moving joint (Diarthroses)
- This joint has a double layered synovial capsule.
- The outer is dense collagen layer which is continuous with periosteum of the bone.
- It prevents dislocation of joint.
- Inner layer is formed of areolar tissue and elastic fibres.
- It secretes a viscous synovial fluid which contains hyaluronic acid and phagocytes.
- It acts a lubricant for free movement of joint.
- Ball and socket joint, Hinge joint, Pivot joint, gliding joint, condyloidjoint, saddle joint are all synovial joints.
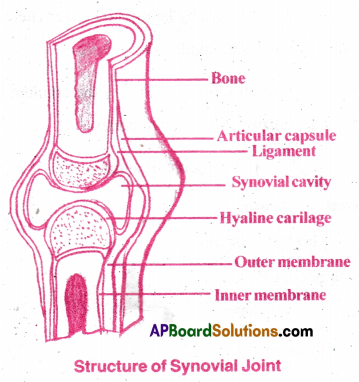
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
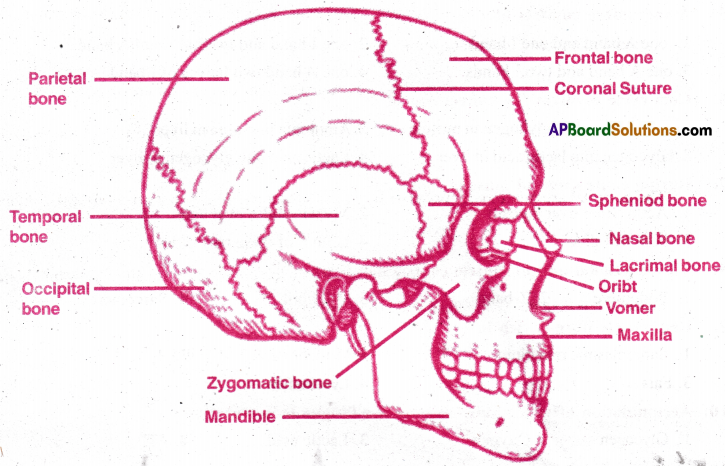
Describe (lie structure of human skull
Answer:
Structure of Skull of man: Skull is a part of axial skeleton. It is composed of cranial bones and facial bones.
Cranium: It is brain box. It is a solid box. It is formed by eight bones joined by sutures which are immovable joints.
The cranial bones are as follows:
- Single frontal bone: Which forms the fore head and anterio ventral part of cranium.
- Two parictals: Which forms major part of roof and sides of cranium. In between frontal and parietals there is coronal suture.
- Two temporal bones. They form the sides and side floor of the cranium.
- Single occipital bone: Which forms the posteior and posterio ventral portion of the skull. It has a large foramen magnum through which medulla oblongata continues into spinal cord. The occipital articulates with parietals by lambdoid suture. There are twd condyles on either side of foramen magnum. Hence the skull is dicondylic.
- Sphenoid bone (single): Which forms the base of the cranium. It is called keystone bone . because it articulates with many of the cranial bones.
- Ethmoid (single) bone It is in the middle of anterior part of cranium.
Facial bones. There are 14 bones.
- Nasal bones form the bridge of the nose.
- Maxillae form the upper jaw
- Zygomatic bones are cheek bones.
- Lacrimals are small bones near orbit.
- Palatine bones form palate along with maxillae
- Inferior nasal conchae scroll like bones in nasal cavity.
- Vomer – a triangular bone in the base of nasal cavity
- Mandible – It forms lower jaw. Longest and strongest of facial bones. It is only the movable bone of skull.
![]()
Sense capsules are as follows:
Nasal cavity: Nasal septum divides the cavity into left and right cavities.
Orbits- Bony depressions to lodge eyes.
Ear Ossicles: Malleus, Incus and Stapes are present in middle ear cavity to transfer sound vibrations form ear drum to internal ear. Malleus is modified articular, incus is modified quadrate and stapes is modified hyomandibular.
Hyoid: Hyoid is a U shaped bone at the base of the tongue between larynx and mandible. It keep the larynx open.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The smallest bone of the face Is
1. Lacrimal
2. Palatines
3. Vomer
4. Mandible
Answer:
1. Lacrimal
Question 2.
The longest bone in the body is
1. Stapes
2. Humerus
3. Tibia
4. Femur
Answer:
4. Femur
Question 3.
The longest and strongest bone of skull is
1. Hyoid
2. Maxilla
3. Zygomatic
4. Mandible
Answer:
4. Mandible
Question 4.
The hardest substance in human body is present in
1. Bone-Ossein
2. Chitin-Protein
3. Tooth-Enamel
4. Muscle-Myosin
Answer:
3. Tooth-Enamel
Question 5.
A sarcomere consists of
1. one A band and one I band
2. one I band and two halves of A band
3. one A band and two I bands
4. one A band two halves of I band
Answer:
4. one A band two halves of I band
Question 6.
Cori cycle invokes the conversion of
1. Lactic acid into glycogen in muscle
2. Ammonia into urea in liver
3. Glycogen into lactic acid in liver
4. Lactic acid into glycogen in liver
Answer:
4. Lactic acid into glycogen in liver
Question 7.
During contraction of muscle
1. Actin slides over thyosin
2. Myosin slides over actin
3. both will slide
4. neither of these two slides
Answer:
1. Actin slides over thyosin
![]()
Question 8.
The functional unit of muscle contraction is .
1. Podomere
2. Z-band
3. Myofibril
4. Sarcomere
Answer:
4. Sarcomere
Question 9.
ked muscle fibre is rich in
1. Sarcoplasmic reticulum
2. Mitochondria
3. Fats
4. Lysosomes
Answer:
2. Mitochondria
Question 10.
Accumulation of which substance causes fatigue in a muscle
1. Glycogen
2. Oxygen
3. Lactic acid
4. ATP
Answer:
3. Lactic acid
Question 11.
1-lensen’s discs are found in
1. Smooth muscles
2. Skeletal muscles
3. All muscles
4. All involuntary muscles
Answer:
2. Skeletal muscles
Question 12.
Con’s cycle is associated with
1. Formation of urea
2. Protein metabolism
3. Glycogen metabolism
4. Lipid metabolism
Answer:
3. Glycogen metabolism
Question 13.
Which of the following is a motor protein?
1. ‘F’actin
2. ‘G’ actin
3. Myosin
4. Tropomyosin
Answer:
3. Myosin
Question 14.
During recovery stroke
1. Actomyosin swings towards H-zone
2. Light meromyosin swings towards H-zone
3. Actomyosin swings away from H-zone
4. Heavy meromyosin swings towards H-zone
Answer:
3. Actomyosin swings away from H-zone
Question 15.
Number of bones in the adult human is
1. 80
2. 280
3. 156
4. 206
Answer:
4. 206
Question 16.
Key stone hone of the skull is
1. Occipital
2. Sphenoid
3. Frontal
4. Ethmoid
Answer:
2. Sphenoid
Question 17.
Coxal bone is a part of
1. Sternum
2. Pectoral girdle
3. Cranium
4. Pelvic girdle
Answer:
4. Pelvic girdle
Question 18.
The bone associated with the skull ¡s
1. Atlas
2. Vomer
3. Manubrium
4. Ischium
Answer:
2. Vomer
Question 19.
The cartilaginous joint is
1. Gomphose
2. Coronal suture
3. Sýndesmose
4. Synchrondrose
Answer:
4. Synchrondrose
Question 20.
Number of bones in human axial skeleton is
1. 120
2. 80
3. 144
4. 206
Answer:
2. 80
![]()
Question 21.
Acetabulum is a part of
1. Skull
2. Pectroal girdle
3. Manubrium
4. Pelvic girdle
Answer:
4. Pelvic girdle
Question 22.
Astragalus and calcaneum occurs ¡n
1. Shoulder
2. Hip
3. Fore limb
4. Hind limb
Answer:
4. Hind limb
Question 23.
Bone formed b ossification in a tendon ¡s called
1. Membrane bone
2. Dermal bone
3. Cartilage bone
4. Sesamoid bone
Answer:
4. Sesamoid bone
Question 24.
Contractile unit of muscle fibre is
1. H line
2. Sarcomere
3. H zone
4. H field
Answer:
2. Sarcomere
Question 25.
During contraction of muscles
1. Actin Filament slides over actin
2. Myosin filament slides over actin
3. Actin filament slides over myosin
4. Myosin filament slides over actin
Answer:
3. Actin filament slides over myosin
Question 26.
Foramen magnum is found ¡n
1. Sphenoid
2. Temporal
3. Occipital
4. Ethmoid
Answer:
3. Occipital
Question 27.
Human vertebra is an example of
1. Long bone
2. FIat bone
3. Seamoid bone
4. Irregular bone
Answer:
4. Irregular bone
Question 28.
The onl movable bone in the skull is
1. Mandible
2. Maxilla
3. Ethmoid
4. Flat bone
Answer:
1. Mandible
Question 29.
Zygomatic is a part of
1. Pelvic girdle
2. Skull
3. Pectoral girdle
4. Vertebral column
Answer:
2. Skull
Question 30.
CoricIe is relationship between
1. Muscle glycogen & liver glycogen
2. Muscles pyruvate & liver Lactic-Acid
3. Muscles glycogen & blood glucose
4. All of abbve
Answer:
1. Muscle glycogen & liver glycogen
Question 31.
Phosphogen in vertebrates is
1. Phospho creatine
2. Phospho arginine
3. ATP
4. Phosphoric acid
Answer:
1. Phospho creatine
Question 32.
Total number of bones ¡n the appendicular skeletal system is
1. 80
2. 28
3. 126
4. 206
Answer:
3. 126
Question 33.
At the central of A-bond, a comparatively less dark zone is called
1. I-band
2. H-band
3. Z-une
4. M-une
Answer:
2. H-band
Question 34.
Which myolilament slides ¡n a sarcornere during contraction in the skeletal muscle
1. Troponin
2. Tropomyosin
3. Actin
4. Calmodulin
Answer:
3. Actin
![]()
Question 35.
The last two pairs of ribs are called
1. True ribs
2. False ribs
3. Floating ribs
4. Vertebrostemal ribs
Answer:
3. Floating ribs
Question 36.
Longest muscle in the human both is
1. Sartorius
2. Serratus anterior
3. Gluteus max imus
4. Stapidius
Answer:
1. Sartorius
Question 37.
The number of bones ¡n the cranium and face are, respectively
1. 8,14
2. 14,8
3. 24,30
4. 26,30
Answer:
1. 8,14
Question 38.
Amphicoelous ‘ertebral is found ¡n
1. Eight vertebra of frog
2. Ninth vertebra of frog
3. Cartilaginous fishes
4. Both (1)& (2)
Answer:
1. Eight vertebra of frog
Question 39.
Pannus is related to
1. Gout
2. Osteoarthritis
3. Rheumatoid arthritis
4. Bursitis
Answer:
4. Bursitis
Question 40.
The body part having a single pair of bones is
1. External ear
2. Wrist
3. Pelvis
4. Nasal septum
Answer:
3. Pelvis
Question 41.
Which of the following bones does not belong to the category of visceral bones
1. OS cordis
2. OS penis
3. OS innominate
4. OS palpebrae
Answer:
3. OS innominate
Question 42.
Number of curves in our vertebral column is ……….. and the number of primary curves is
1. one, two
2. one, one
3. four, two
4. four, four
Answer:
3. four, two
Question 43.
Which of the following joints is of the pivot type?
1. Head of radius and ulna
2. Atlas and axis vertebra
3. 2 zygapophyses of vertebrae
4. Both (1) and (2)
Answer:
4. Both (1) and (2)
Question 44.
Mark the True statement
1. Biceps is an extensor muscle
2. Muscle tetanus is sustained contraction of muscle
3. Creatinine is the energy rich compound of skeletal muscles of the vertebrates
4. All of the above
Answer:
2. Muscle tetanus is sustained contraction of muscle
Question 45.
Which of the following muscle disorder occurs due to the formation of defective antibodies?
1. Duchenne muscular dystrophy
2. Myasthenia gravis
3. Denervation atrophy
4. All of the above
Answer:
2. Myasthenia gravis
Question 46.
Epiphyseal plates at the extremities of long bones help in
1. Bone moulding
2. Elongation of bone
3. Bone formation
4. Formation of haversiari canals
Answer:
2. Elongation of bone
![]()
Question 47.
White muscle fibres present
1. Eyeball muscles
2. Pectoralis major
3. Deltoids
4. All of above
Answer:
4. All of above
Question 48.
Muscles of Iris & Ciliary body originate
1. Ectoderm
2. Mesoderm
3. Endoderm
4. All of above
Answer:
1. Ectoderm
Question 49.
Cross bridge are formed during
1. Muscle contraction
2. Nervous contraction
3. Tissue regeneration
4. All the above
Answer:
1. Muscle contraction
Question 50.
Functionally cardiac muscles are similar to
1. Involuntary muscles
2. Unstriped muscles
3. Striped & Unstriped muscles
4. None
Answer:
1. Involuntary muscles