Students get through AP Inter 2nd Year Zoology Important Questions Lesson 2(b) Excretory Products and their Elimination which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 2nd Year Zoology Important Questions Lesson 2(b) Excretory Products and their Elimination
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Name the blood vessels that enter and exit the kidney.
Answer:
- The blood vessels that enter the kidney are renal artery.
- The blood vessels that exit the kidney are renal vein.
Question 2.
What are renal pyramids and renal papillae?
Answer:
- The medulla of kidney is projected into cone shaped masses called renal pyramids.
- They contain Henle’s loops of Juxta medullayr nephrons and straight collecting ducts.
- Renal papilla is the tip of the renal pyramid opens into the pelvis.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the columns of Bertin? [AP,TS MAY-22] [TS MAR-17,19] [AP MAR-15,19]
Answer:
In the human kidney, the projections of the cortex into the medulla that separate the renal pyramids are called columns of Bertin (Renat columns).
Question 4.
Name the structural and functional units of kidney. What are the two main types of structural units in it?
Answer:
- Nephron is the structural and functional units of kidney.
- There are two types of nephrons: (i) Cortical nephrons (ii) Juxta medullary nephrons.
- Each nephron has two parts called Bowman’s capsule and renal tubule.
Question 5.
Distinguish between cortical and juxta medullary nephrons. [TS MAY-17,22] [AP MAR-17]
Answer:
- Cortical nephrons have renal corpuscle in the superficial renal cortex.
They have short loop of Henle but without vasa recta. - Juxta medullary nephrons are located near the renal medulla.
They have long loop of Henle and Vasa recta.
Question 6.
Define Glomerular filtration.
Answer:
- Glomtular filtration: The first step in the formation of urine is the ‘filtration’ of blood from glomerulus into the lumen of Bowman’s capsule.
- This passive non-energy consuming process is called glomeular filtration.
Question 7.
Define Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR).
Answer:
- GFR: The amount of filtrate formed by both the kidneys in a minute is called GFR.
- It is about 125ml/min.
Question 8.
What is meant by mandatory reabsorption? In which parts of nephron does it occur?
Answer:
- In a healthy individula the GFR is 125 ml/ 1 minute or 180 litre per day. About 85% of the filtrate is reabsorbed in a constant unregulated manner by proximal convoluted tubule and Henle’s loop, called mandatory reabsorption.
- The tubular epithelial cells of nephron reabsorb water and substances.
Question 9.
Distinguish between juxtaglomerular cells and macula densa.
Answer:
| Juxta glomerular cells | Macula densa |
| 1) Juxta glomerular cells are present on the wall of afferent renal arteriole. 2) They are modified smooth muscle cells of afferent arteriole. |
1) Macula densa are group of modified epithelia cells of distal convoluted tubule. 2) They are crowded at the place where afferent arteriole comes into contact with distal convoluted tubule. |
Question 10.
What is juxtaglomerular apparatus?
Answer:
- Macula densa with Juxta glomerular cells together form Juxta glomerular appartus.
- It regulates the kidney function.
Question 11.
Distinguish between the enzymes renin and rennin. [AP,TS MAR-16]
Answer:
- Renin is produced in kidney, where as Rennin is produced in stomach.
- Renin converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I, where as Rennin converts casein to calcium para-caseinate.
![]()
Question 12.
What is meant by the term osmoregulation?
Answer:
- Osmoregulation is the process of maintaining constant amount of water and dissolved salts in the body.
- It is the maintenance of homeostasis of an orgnasim with respect to water in the body.
Question 13.
What is the role of atrial natriuretic peptide in the regulation of urine formation?
Answer:
Atrial Natriuretic peptide (ANP) causes vasodilation and thereby decreases blood pressure. It acts as a counter check on the RAAS (Renin- Angiotensin- Aldosterone System)
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Terrestrial animals are generally either ureotelic or uricotelic and not ammonotelic. Why?
Answer:
- Ureotelism and Uricotelism are terrestrial adaptations to conserve water.
- The primary nitrogenous waste product is ammonia. Aquatic animals can easily send out ammonia into water but terrestrial animals cannot.
- In terrestrial animals which have sufficient water, excrete urea.
- Urea is formed in liver from ammonia through ornithine cycle. Urea is less toxic than ammonia. Ex: Earthworms, Cartilaginous fishes, amphibians and mammals.
They are called ureotelic animals. - The animals which live in areas where there is very less amount of water excrete uric acid. Uric acids is in the form of dry pellets or in semi solid state.
Ex: Tracheate arthropods, land snails, reptiles and birds.
They are called Uricotelic animals.
Question 2.
Differentiate vertebrates on the basis of the nitrogenous waste products they excrete giving examples.
Answer:
Animals can be grouped into three types based the excretory products they release.
- Ammonotelic animals
- Ureotelic animals
- Uricotelic
1) Ammonotelic animals: The primary nitrogenous waste product is ammonia. It is highly toxic. It is formed in liver by oxidative deamination of amino acids. Aquatic animals can excrete ammonia either through body surface by diffusion as in lower invertebrates, or through gills, as in the bony Fishes, or through kidneys, as in Fishes and higher aquatic forms.
2) Ureotelic animals: Some terrestrial animals have access to necessary amount of water but not sufficient to release ammonia. In these animals ammonia is converted to less toxic urea in liver through ornithine cycle. It is excreted through kidneys.
Ex: Earthworms, Cartilaginous fishes, Amphibians and Mammals.
3) Uricotelic animals: Terrestrial animals which have less access to water excrete uric acid. Ammonia is converted to uric acid which in the form of dry pellets or in semisolid state. This is extreme adaptation to conserve water.
Ex: Tracheate arthropods, land snails, reptiles and birds.
Question 3.
Draw a labelled diagram of the V.S of kidney.
Answer:
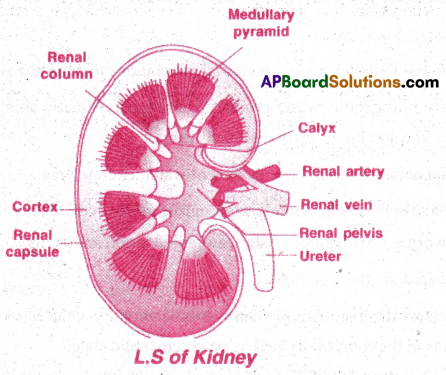
Question 4.
Describe the internal structure of kidney of man. [TS MAY-22]
Answer:
1) Kidney Structure: Kidneys are reddish brown, retroperitoneal, bean shaped organs present on either side of vertebral column at the level of anterior lumbar vertebrae.
The outer surface is convex and inner surface concave with a deep notch called hilum. Renal artery and nerves enter through hilum and renal vein and ureters come out. Each kidney is covered by a tough fibrous capsule.
2) Inner structure: There are two distinct regions, outer cortex and inner medulla. The cortex looks granular having malpighian capsules, proximal and distal convoluted tubules. The medulla is divided in cone shaped renal pyramids.
The cortex extends in between pyramids and these projections are called columns of Bertini. Tne base of the pyramid is towards cortex and apex is towards the renal pelvis. Renal pelvis is a space into which all pyramids open through Bellinis ducts. Each pyramidal apex is lodged in a cup like projection of pelvis called calyx. The pelvis is continuous with ureter.
![]()
3) Nephron: Nephrons are structural and functional units of kidney. Some nephrons are restricted to cortex and their Henle’s loops are short and touch the medulla. They are cortical nephrons.
Other Nephrons are long and their Henle’s loops extend deep into medulla. They are called Juxta medullary nephrons. The ducts of nephrons together form straight collecting ducts. They join to form Bellinis ducts which open into pelvis.
5) By the action of ADH the excess water in the filtrate is absorbed in collecting tubules so that concentrated urine is discharged into pelvis. The Nad and water are collected by vasrecta and carried out of kidney.
6) Human kidneys can produce urine which is nearly four times concentrated than glomerular filtrate.
Question 8.
Explain the autoregulatory mechanism of GFH.
Answer:
- G.F.R is glomerular filtration rate.
- It is the amount of filtrate produced by kidneys in a minute.
- In a healthy individual it is about 125ml/min, ie., 1801/day.
- But only 1 to 1.5 liters of urine is produced by a person.
- About 99% of filtrate is reabsorbed.
- When the filtration rate falls the Juxta glomerular cells release an enzyme renin (Angio tensinogenase).
- The enzyme renin converts angiotensinogen into angiotensin 1.
- Angiotensin I is converted to angiotensin TI by angiotensin converting enzyme.
- This conversion takes place in the capillaries of lungs because the converting enzyme is found in lungs.
- Angiotensin II stimulates adrenal cortex to release aldosterone.
- Aldosterone causes reabsorption ofNa+and water from DCT and CD and promotes secretion
of K+ into DCT and CD. It increases the blood pressure and GFR. This mechanism is called renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RASS). - To counter check RASS stretched wall of right artrium release atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) which cause vasodilation and reduce the blood pressure and reduce GFR and the process again begins.
Question 9.
Describe the role of liver, lungs and skin in excretion.
Answer:
Lungs, liver and skin as excretory organs:
1) Lungs: They help in CO2 elimination and also volatile compounds. It is estimated that lungs eliminate 18 L of CO2 regularly.
2) Liver: It is the largest gland located at the centre of the body carrying manifold function. It is destruction centre for aged RBC. The haemoglobin is converted to bile pigments bilirubin and biliverdin. They passout through alimentary canal. Liver also excretes cholesterol, degraded steroid hormones excess vitamins and drugs via bile.
3) Skin: It has sweat and sebaceous glands. Sweat gland eliminates salts, urea and lactic acid even though its primary function is cooling of the body. Sebaceous glands eliminates sterols, hydrocarbons and waxes through sebum, which forms protective oily coating to the skin.
Question 10.
Name the following
a) A chordate animal having protonephridial-type excretory structures.
b) Cortical portions projecting between the medullary pyrsindds in the human kidney.
c) Capillary network paralleling the loop of llcnle.
d) A non chordate animal having green glands as excretory structures.
Answer:
a) The chordate with protonephridia is Amphioxus.
b) Cortical projections in between medullary pyramids are columns of Bertini.
c) Capillary network paralleling the loop of Henle is vasa recta.
d) Green glands are excretory organs in prawn (crustacean of Arthropoda).
![]()
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Describe the excretory system of man, giving the structure of a nephron. [TS MAR-15]
Answer:
I) Human excretory system: It consists of the following
- a pair of kidneys
- a pair of ureters
- urinary bladder and
- urethra.
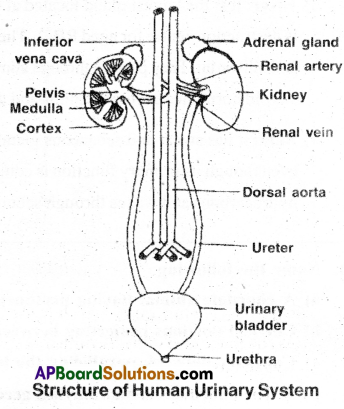
1) Kidneys:
- These are reddish brown, retroperitoneal bean shaped organs.
- These are located on either side of vertebral column at the level of anterior lumbar vertebrae.
- Right kidney is slightly lower than the left due to the presence of liver.
- Outer surface of kidney is convex.
- Inner surface is concave with a deep notch called hilum.
- The kidney is protected by a tough fibrous tissue called renal capsule.
- Internally, kidney consists of two regions, the outer cortex and inner medulla.
- The cortex contains the malpighian capsules, proximal and distal convoluted tubules of nephrons.
- The medulla is divided into multiple cone shaped masses of tissue called renal pyramids.
- The cortex extends in between pyramids as columns are called column’s of Bertini.
2) Ureters:
- There are two ureters.
- These are slender whitish tubes emerging from the pelvis of the kidneys.
- Their walls are lined by transitional epithelium. They run downwards and open into the urinary bladder.
3) Urinary bladder:
- It is a median storage sac, situated in the lower abdominal cavity.
- It has thick, muscular and distensible wall lined by transitional epithelium.
4) Urethra:
- The neck of the bladder leads into the urethra, which has an internal urethral sphincter and external urethral sphincter.
- Urethra opens into urinogenital duct in males and to outside in females.
II) Structure of Nephron: Each kidney has nearly one million nephrons which are the structural and
functional units. Each nephron has 2 parts, the (1) Bowman’s capsule and (2) the renal tubule.
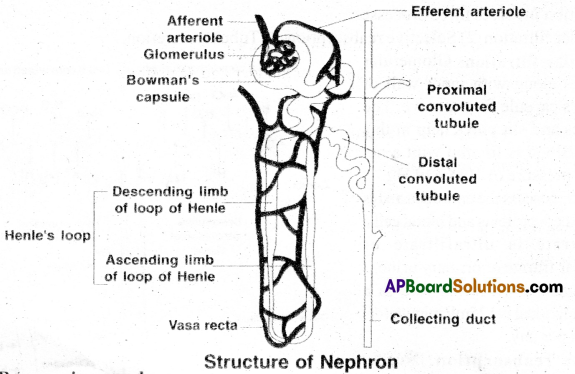
1) Bowman’s capsule:
- It is present in cortex,
- It is a double walled cup.
- The inner wall of the Bowman’s capsule has certain unique cells called podocytes which wrap around each capillary.
- The podocytes are arranged in an intricate manner so as to leave some minute spaces called filtration slits or slit pores.
- The Bowman’s capsule encloses a tuft of capillaries called glomerulus. The glomerulus and inner wall of Bowman’s capsule together form a sieve. Blood enters the glomerulus through afferent arteriole and leaves by efferent arteriole.
2) Renal tubule: It has 3 segments
(a) PCT (Proxima convoluted tubule) (b) Henle’s loop (c) DCT (Distal convoluted tubule) (a) PCT (Proxima Convoluted Tubule):
- It is present in cortex.
- It is wide and highly coiled.
- It is lined by simple cuboidal epithelium with brush border.
![]()
(b) Henle’s loop :
- It is present in medulla.
- It is hairpin shaped. It has descending and ascending limbs.
- The proximal part of the ascending limb is thin and the distal part is thick.
- The thick ascending limb continues into the DCT.
(c) Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT):
- It is present in cortex.
- The DCT present in cortex continues as the ‘initial collecting duct’ in the cortex.
- Some initial collecting ducts combine to form a straight collecting duct, which passes through the medullary pyramid.
- In the medulla, the tubes of each pyramid join and form the duct of Bellini, which finally opens on the tip of the renal papilla.
Types of Nephrons: These are two types (i) cortical nephrons and (ii) Juxta medullary nephrons. Cortical nephrons have small Henle’s loops and their entire bodies are present in cortex.
Juxta medullary nephrons have long Henle’s loops extending deep into medulla. Henle’s loops extend deep into medulla.
Question 2.
Explain the physiology of urine formation.
Answer:
Urine Formation: Kidneys are main excretory organs of human beings.
Urea along with water and other dissolved substances are collectively called urine.
Urine formation involves three processes.
- Glomerular filtration
- Selective reabsorption
- Tubular secretion.
1) Glomerular Filtration: Glomerular capillaries along with inner wall of Bowman’s capsule form a sieve. The podocytes and slit pores help in this process. Blood is filtered with a net filtration pressure of 10mm of Hg.
During this process the entire plasma is filtered except proteins and blood cells.
The filtrate is ultrafiltrate or glomerular filtrate or primary urine.
The glomerular filtration rate in a healthy individual is 125ml/ minute. (or)
180 litres per day.
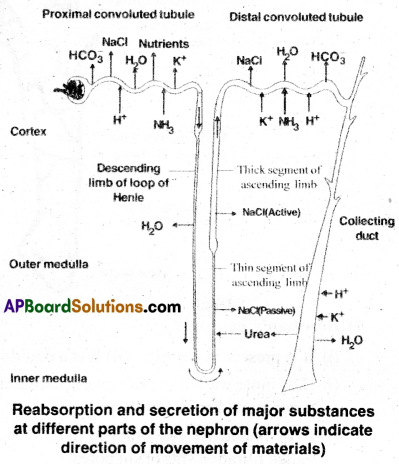
2) Selective reabsorption: Nearly 99% of primary urine and essential substances are reabsorbed by renal tubules called selective reabsorption.
About 85% of primary urine is reabsorbed in a constant unregulated manner called obligatory reabsoiption.
Reabsorption in different sections of renal tubule.
3. Tubular secretion: During the formation of urine, the tubular cells secrete substances such as H+, K+ and NH3 into the fiiterate. Tubular secretion is also an important step in the fonnation of urine, as it helps in the maintenance of ionic and acid base balance of the body fluids. Mechanism of selective reabsorption and secretion takes place in different parts of nephrons as follows:
a) Proximal convoluted tubuledt is lined by cuhoida! epithelium with brush border. About 80% electrolytes and water are reabsorbed. Water is absorbed by passive diffusion (osmosis) and Na+, glucose, aminoacids and other essential substances by active transport. H+ and NH3 are secreted. HCO3– is absorbed to maintain pH.
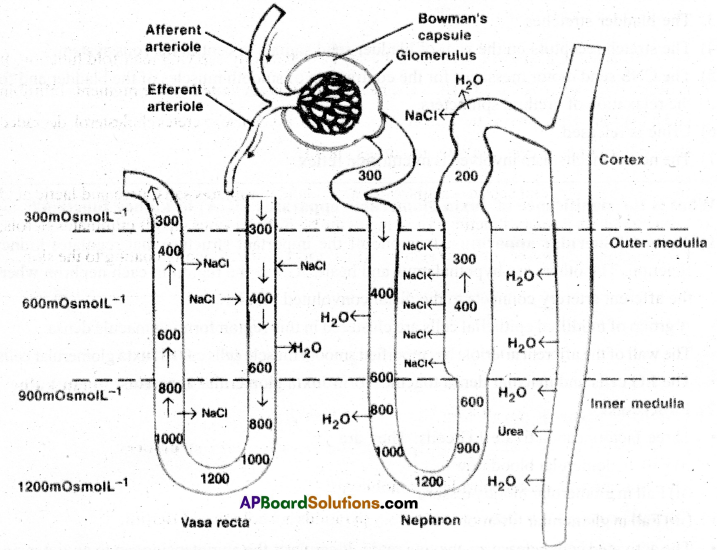
b) Henle’s loop: Water reabsorbed in descending limb by diffusion. Ascending limb has a thin segment and thick segment. NaCl is reabsorbed passively in thin part and actively in thick part.
In Henle’s loop, low osmolarity (300) is maintained towards cortex and high osmolarity (1200) at the tip in medulla.
![]()
The counter flow of blood through vasa recta removes water, NaCl and reabsorbed substances continuously.
c) Distal Convoluted Tubule(DCT): Water is reabsorbed by the action of ADH (Anti diuretic hormone). HCO3– is absorbed. H+, K+ and NH3 are secreted to maintain pH.
d) Collecting Ducts(CD): This segment allows the passage of small amount of urea to keep up its osmolarity. Concentrated urine is released into pelvis. It is hypertonic to the plasma of blood.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Accessory excretory organs in man are
1. Liver, brain and skin
2. Lungs, liver and heart
3. Skin, eyes and ears
4. Lungs, liver and skin
Answer:
4. Lungs, liver and skin
Question 2.
Activity of kidney is influenced by
1. Vasopressin and adrenaline
2. Gonadotrophins
3. Thyroxine
4. Vasopressin
Answer:
1. Vasopressin and adrenaline
Question 3.
The hormone secreted by kidney is
1. Glucose
2. Secretin
3. Erythropoietin
4. Aldosterone
Answer:
3. Erythropoietin
Question 4.
Podocytes constitute
1. Inner wall of Bowman’s capsule
2. Proximal convoluted tubule
3. Outer wall of Bowman’s capsule
4. Distal convoluted tubule
Answer:
1. Inner wall of Bowman’s capsule
Question 5.
Secretion of aldosterone from adrenal cortex is stimulated by
1. Angiotensin I
2. Angiotensinogen
3. Angiotensin II
4. Renin
Answer:
3. Angiotensin II
Question 6.
On an average, a healthy human excretes
1. 1-1.5 gms of urea per day
2. 2.5-3 gms of urea per day
3. 25-30 gms of urea per day
4. 10-15 gms of urea per day
Answer:
3. 25-30 gms of urea per day
Question 7.
Number of nephrons in each kidney in the human being is about
1. One lakh
2. One million
3. One thousand
4. One billion
Answer:
2. One million
Question 8.
The first step in the formation of urine is
1. Selective reabsorption
2. Tubular secretion
3. Glomerular filtration
4. Micturition
Answer:
3. Glomerular filtration
Question 9.
Major risk factor for renal calculi is
1. Diuresis
2. Dehydration
3. Renal failure
4. Ureaemia
Answer:
2. Dehydration
![]()
Question 10.
Secretion of ADH is regulated by
1. Stretch receptors of the urinary bladder
2. Osmoreceptors of hypothalamus
3. Chemoreceptors of medulla oblongata
4. Osmoreceptors of neurohypophysis
Answer:
2. Osmoreceptors of hypothalamus
Question 11.
Renal papillae project into cup-like cavities are called
1. Renal pyramids
2. Ducts of Bellini
3. Calyces
4. Columns of Bertini
Answer:
3. Calyces
Question 12.
JG cells release
1. Rennin
2. Angiotensinogen
3. Renin
4. Angiotensin converting enzyme
Answer:
3. Renin
Question 13.
The ultimate solution for acute renal failure is
1. Angioplasty
2. Kidney transplantation
3. Blood transfusion
4. Haemodialysis
Answer:
2. Kidney transplantation
Question 14.
In bony fishes, most of the ammonia is excreted through
1. Kidneys
2. Liver
3. Lungs
4. Gills
Answer:
4. Gills
Question 15.
Most aquatic animals arc
1. Ammonotelic
2. Uricotelic
3.Urotelic
4. Aminotelic
Answer:
1. Ammonotelic
Question 16.
The pH of urine is
1. 5.0
2. 7.4
3. 7.0
4. 6.0
Answer:
4. 6.0
Question 17.
Lungs help in the removal of
1. Cholesterol, degraded steroid hormones, certain vitamins and drugs
2. NaCl, urea and lactic acid
3. Carbon dioxide, water vapour and volatile materials
4. Sterols, hydrocarbons and waxes
Answer:
3. Carbon dioxide, water vapour and volatile materials
![]()
Question 18.
Through bile, the liver excretes
1. Cholesterol, degraded steroid hormones, certain vitamins and drugs
2. NaCl, urea and lactic acid
3. Carbon dioxide, water vapour and volatile materials
4. Sterols, hydrocarbons and waxes
Answer:
1. Cholesterol, degraded steroid hormones, certain vitamins and drugs
Question 19.
Angiotensinogen is produced by
1. Lungs
2. Macula densa
3. JG cells
4. Liver
Answer:
4. Liver
Question 20.
Excretory organs in earthworms are
1. Protonephridia
2. Malpighian tubules
3. Metanephridia
4. Antennary glands
Answer:
3. Metanephridia
Question 21.
Human kidneys can produce urine nearly
1. Ten times more concentrated than the glomerular filtrate
2. Two times more in volume than the glomerular filtrate
3. Three times less concentrated than the glomerular filtrate
4. Four times more concentrated than the glomerular filtrate
Answer:
4. Four times more concentrated than the glomerular filtrate
Question 22.
Ammonia is the excretory material in
1. Cartilaginous fish
2. Fresh water bony fish
3. Whale
4. Camel
Answer:
2. Fresh water bony fish
Question 23.
Condition in which less urine is passed is called ‘
1. Polyuria
2. Oliguria
3. Anuria
4. Dysuria
Answer:
2. Oliguria
Question 24.
Diameter of renal afferent vessel is
1. Same as that of efferent
2. Larger than that of efferent
3. Smaller than that of efferent
4. None
Answer:
2. Larger than that of efferent
![]()
Question 25.
Excretory system of a housefly is
1. Flame cells
2. Keber’s organ
3.Nephridia
4. Malpighian tubules
Answer:
4. Malpighian tubules
Question 26.
Urea is transported by
1. Blood plasma
2. Leucocytes
3. RBCs
4. Haemoglobin
Answer:
1. Blood plasma
Question 27.
The retroperitoneal kidney is
1. Kidney covered by peritoneum on ventral side
2. Kidney of fish
3. Kidney uncovered by peritoneum on dorsal side
4. Kidney covered by peritoneum on dorsal side
Answer:
1. Kidney covered by peritoneum on ventral side
Question 28.
The approximate amount of the blood Altered by both the kidneys in one minute is
1. 800mL
2. 1200mL
3. 2000 mL
4. 4250 mL
Answer:
2. 1200mL
Question 29.
Uricotelic pair is
1. Sharks and mammals
2. Reptiles and mammals
3. Birds and insects
4. Sharks and lizards
Answer:
3. Birds and insects
Question 30.
Amount of glomerular filtrate formed per day is
1. 50 L
2. 250 L
3. 500L
4. 180 L
Answer:
4. 180 L
Question 31.
Malpighian body is constituted by
1. Glomerulus, Bowman’s capsule and efferent vessel
2. Glomerulus and efferent vessel
3. Glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule
4. Glomerulus only
Answer:
3. Glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule
Question 32.
Renal pelvis, ureter and urinary, bladder are lined by
1. Columnar epithelium
2. Spamous epithelium
3. Transitional epithelium
4. Globet cells
Answer:
3. Transitional epithelium
Question 33.
Which one of the following substance is completely reabsorbed from the filtrate in the renal tubule under normal condition
1. Urea
2. Uric acid
3. Salt and water
4. Glucose
Answer:
4. Glucose
Question 34.
The yellow colour of urine is due to
1. Urea
2. Melanin
3. Uric acid
4. Urochrome
Answer:
4. Urochrome
![]()
Question 35.
The glomerular filtrate contains
1. Blood minus cells
2. Blood minus cell and proteins
3. Plasma minus cells and proteins
4. Blood minus proteins
Answer:
3. Plasma minus cells and proteins