Students get through AP Inter 2nd Year Zoology Important Questions Lesson 2(a) Body Fluids and Circulation which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 2nd Year Zoology Important Questions Lesson 2(a) Body Fluids and Circulation
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write the differences between ‘open’ and ‘closed’ systems of circulation.
Answer:
- In the Open type of Circulation, blood flows through vessels and sinuses. Capillaries are absent.
Ex: Leeches, Arthropods, molluscs, Echinoderms, Ascidians. - In the Closed type of Circulation, blood flows through blood vessels. Capillaries are present. Ex: Annelida, Cephalopoda, Cephalochordata, Vertebrata.
Question 2.
The sino-atrial node is called the pacemaker of our heart. Why? [TS MAY-22]
Answer:
- Sino-atrial node (SAN) is called the pacemaker because it has the ability to generate action potentials with out any external stimuli.
- It initiates heart beat. It lies in the right upper part of right atrium.
![]()
Question 3.
What is the significance of atrio-ventricular node and atrio-vcntricular bundle in the functioning of the heart?
Answer:
- Atrioventricular node is present lower left comer of right atrium close to interatrial septum.
A.V.Node is relay point. It relays the action potentials received from SAN. - Atrio ventricular bundle or bundle of His is a bundle of nodal fibres present in inter ventricular septum. It carries the electrical impulses (action potential) from A.V.Node to purkinje fibres present in lateral walls of ventricles.
Question 4.
Name the valves that guard the left and right atrioventricular apertures in man.[TS MAR-15]
Answer:
- The left atrioventricular aperture is guarded by Bicuspid or Mitral valve.
- The right atrioventricular aperture is guarded by tricuspid valve.
Question 5.
Where is the valve of Thebesius in the heart of man?
Answer:
Valve of Thebesius is present at the opening of coronary sinus into the right atrium.
Question 6.
Name the aortic arches arising from the ventricles of the heart of man.
Answer:
- Pulmonary arch arises from left anterior side of the right ventricle. It carries venous blood to lungs.
- Sytemic arch arises from right side of the left ventricle and carries oxygenerated blood to various parts of the body
Question 7.
Name the heart sounds. When are they produced? ‘
Answer:
- The heart sounds are Tub and ’Dup’.
- First heart sound is ‘Lub’. It is produced in ventricular systole due to closure of the AV valves.
- Second heart sound is ‘Dup’.It is produced in cardiac diastole due to closure of semilunar valves.
Question 8.
Define cardiac cycle and cardiac output. [AP MAR-20]
Answer:
- Cardiac cycle: Cardiac events that occur from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next is called cardiac cycle. Its duration is about 0.8 sec.
- Cardiac output: It is the volume of blood pumped out by the ventricle per minute.
Cardiac output = stroke volume x No.of beats per minute= 5040 ml/min or approximately 5 liters.
Question 9.
What is meant by double circulation? What is the significance?
Answer:
- The blood circulation in which blood passes through the heart twice, in a complete cycle is called double circulation. It consists of pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation.
- Significance: It prevents the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated types of blood.
Question 10.
Why the arteries are more elastic than the veins?
Answer:
- Arteries are more elastic because they have to cope up with high pressure blood pumped from the heart. The pressure at the major arteries is more than in the minor arteries.
- In veins the pressure is less. So they have walls with minimum elasticity.
![]()
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Describe the evolutionary change in the structural pattern of the heart among vertebrates.
Answer:
Evolution of Vertebrate heart:
- Heart is a modified blood vessel. It is clearly evident in the developmental stages.
- In fishes there is a two-chambered heart having an atrium and ventricle. The blood is sent to gills for oxygenation. As the blood passes through it is venous blood it is also called venous heart. The circulation is single circulation.
- Amphibians have three-chambered heart with two atria and one ventricle. It is the beginning of double circulation, (incomplete double circulation)
- Reptiles also have 3 chambered heart but the ventricle is incompletely divided.
- Crocodiles, birds and mammals have four chambered heart with double circulation i.e., having a separate pulmonary and systemic circulations.
Question 2.
Describe atria of the heart of man.
Answer:
- There are two atria in the heart of man. .
- They are thin walled receiving chambers.
- Right atrium is larger than the left atrium.
- The two atria are separated by inter atrial septum.
- There is a depression in the septum called fossa ovalis. It is the remnant of an opening in foetus called foramen ovale which is important in foetal circulation.
- Right atrium receives venous blood from all over the body except lungs by two caval veins.
- Left atrium is small and receives oxygenated blood from lungs through pulmonary veins.
- The atria are connected to ventricles through atrioventricular openings guarded by bicuspid or mitral valves (left side) and tricuspid valves (right side).
Question 3.
Describe the ventricles of the heart of man.
Answer:
Ventricles: They are two thick walled posterior chambers of the heart.
- They are pumping chambers.
- The wall of the left ventricle is thicker than the right ventricle.
- The two ventricles are separated by the interventricular septum.
- Left ventricle pumps blood to various body parts except lungs through systemic aorta and other major arteries.
- Right ventricle pumps the blood only to lungs through pulmonary arch.
- Inner wall of the ventricle is raised into ridges called columnae cameae.
- Some of these ridges are conical and large called papillary muscles.
- Chorda tendinae are collagenous cords extending from papillary muscles to the flaps of tricuspid and bicuspid valves.
Question 4.
Draw a labelled diagram of the L.S. of the heart of man.
Answer:
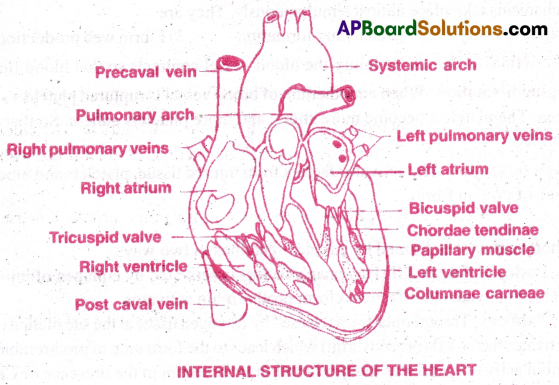
Question 5.
Describe the events in a cardiac cycle, briefly.
Answer:
1) Cardiac cycle: Cardiac cycle consists of three stages namely atrial systole, ventricular systole and cardiac diastole.
- Blood enters the atria from pulmonary veins and venacavae.
- From atria, blood flows into ventricles through atrioventricular apertures.
- The semilunar valves are closed at this stage.
2) Atrial Systole:
- The sino atrial node generates action potential (electrical impulses) which pass through atrial walls.
- The atria contract forcing blood into ventricle. It is the atrial systole.
![]()
3) Ventricular Systole:
- The action potential reaches Atrioventicular node. From AV node it is passes through bundle of His and purkinje fibres. The ventricles contract forcing the blood into pulmonary aorta and systemic aorta.
- The bicuspid and tricuspid valves close producing first heart sound ‘Lub’.
4) Ventricular diastole:
- Ventricles relax.The semilunar valves close at a time producing the second heart sound ‘Dup’.
- As the ventricular pressure decreases further, the AV valves open.
- The cycle of events begin again.
- The duration of cardiac cycle is 0.8 sec.
Question 6.
Explain the mechanism of clotting of blood.
Answer:
Clotting of Blood: Blood clotting is haemostasis. It takes place at the site of injury. Three blood clotting mechanisms take place almost simultaneously. They are
- Vasoconstriction
- Platelet plug formation
- Fibrin web production.
1) Vasoconstriction: At the site of injury the blood vessel contracts so that blood flow stops.
2) Platelet plug formation: When endothetium of blood vessel is ruptured platelets are adhered to collagen. The platelets become more sticky and more platelets adhere. So that a platelete plug is formed.
3) Fibrin web formation: The activator factors from injured tissue, platelets and blood proteins form a web of protein fibrin.
Mechanism:
1) Prothrombin activator is formed by cascade reactions in two ways.
Intrinsic Pathway:Factor XII (Hageman’s factor) is activated by collagen of injured blood vessel. Which activate other factor to form prothrombin activator.
Extrinsic Pathway: Thromboplastin is released by damaged tissue at the site of injury. Thrombo plastin activates factor VII (proconvertin) which leads to the formation of prothrombin activator.
2) Prothrombin activator activates the prothrombin to thrombin in the presence of Ca++.
3) Thrombin converts soluble fibrinogen to soluble fibrin monomers. It has weak H bonds.
- Factor XIII (fibrin stabilizing factor) stabilizes fibrin strengthening with covalent bonds replacing hydrogen bonds.
- Blood cells and platelets are entangled in fibrin mesh. The mesh work along with cells contract expelling serum. It is called clot retraction.
Question 7.
Distinguish between SAN and AVN.
Answer:
| SAN | AVN |
| 1) SAN (Sino Atrial node) is present at the right upper comer of the right atrium near the opening of superior venacava. 2) SAN has the intrinsic capacity to produce action potential (electric impulses) which passes through the walls of the heart. |
1) AVN(Atrio ventricular node) is located at the base of the inter atrial septum of the right atrium close to the opening of coronary sinus. 2) AVN is relay centre, receiving action potential from SAN and forwarding to bundle of His. |
Question 8.
Distinguish between arteries and veins.
Answer:
| Arteries | Veins |
| 1) Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood from heart to organs. 2) Arteries are bright red in colour. 3) Arteries are located deep in body 4) Arteries are thick walled with two elastic laminae and thick tunica media. 5) Arterial lumen is narrow 6) Valves are absent in arteries 7) Blood flows with high pressure in arteries 8) Arteries end in capillaries |
1) Veins are blood vessels that carry blood from different organs to the heart. 2) Veins are dark red in colour. 3) Veins are located superficial in body. 4) Veins are thin walled with one elastic laminae and thin tunica media. 5) Veinal lumen is wide. 6) Valves are present in veins. 7) Blood flows steadily with low pressure in veins. 8) Veins begin in capillaries. |
![]()
Question 1.
Describe the structure of the heart of mao with the help of neat labelled diagram. [AP,TS MAY-22] [TS MAR-17,16]
Answer:
Structure of the Human heart: Human heart is a hollow muscular, cone shaped and pulsating organ situated betweeen lungs(mediastinum). The size is about a clenched fist. It is mesodermal mongin.
1) Pericardium: Heart is covered by double walled pericardium. The outer layer is fibrous pericardium and inner layer is serous pericardium.In between these two layers, there is pericardial fluid which reduces friction and allows free movement of the heart.
2) Heart wall: It consist of three layers.
- Outer epicardium
- Middle myocardium
- Inner endocardium.
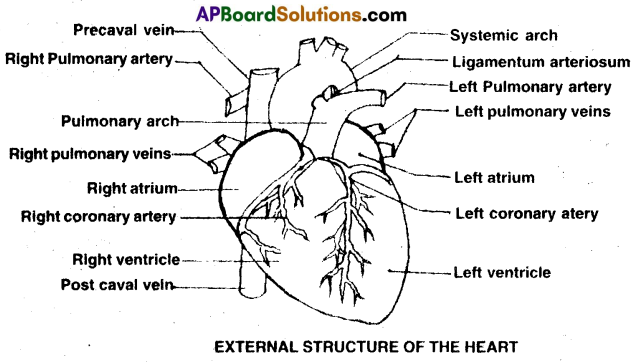
3) External Structure: Human heart has four chambers.
- Two small upper chambers are called atria.
- Two large lower chambers are called ventricles.
- Atria and ventricles are separated by a deep transverse groove called coronary sulcus.
- Each atrium has small ear lobe like projection called auricular appendix.
- The ventricles are separated by two inter ventricular grooves, in which the coronary arteries and their branches are located.
4) Internal structure:
Heart consists of (a) Atria (b) Ventricles (c) Nodal tissue (d) Aortic arches.
(a) Atria:
- Atria are thin walled blood receiving chambers. The right one is larger than the left.
- The two atria are separated by thin inter-atrial septum.
- In the foetal heart, the atrial septum has a small pore called foramen ovale.
- In adults, fossa ovalis is present in the inter atrial septum
- Right atrium receives dexoygenated blood from different pans of the body (except lungs)
- Left atrium receives oxygenated blood from each lung through two pulmonary veins.
- Atria and ventricles are separated by a membrane atrio -ventricular septum.
(b) Ventricles:
- These are thick-walled blood ‘pumping chambers’ (lower chambers)
- The two ventricles are separated by an interventricular septum.
- The wall of the left ventricle is thicker than the right ventricle
- The inner surface of the ventricles is raised into muscular ridges called columnae cameae.
- Some of these ridges are large and conical, and are called papillary muscles.
- Chordae tendineae are collagenous cords that connect papillary muscles to the tricuspid valve and the bicuspid (mitral) valve in the heart.
(c) Nodal tissue :
- It is a modified heart muscle. It consists of two nodes and fibres.
- A patch of this tissue is present in SAN(sinoatrial node). It is located in the right upper comer of right atrium close to the opening of superior venacava.
- Another mass of this tissue called AVN (atrioventricular node) is seen in the lower left comer of the right atrium.
- AVN forms AV bundle or “His” bundle, which is divided into right and left bundle branches.
(d) Aortic arches: There are two aortic arches in man.
- Pulmonary Arch: It arises from the left anterior angle of the right ventricle. Its opening is guarded by the pulmonary valve and it carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
- Systemic Arch: It arises from the left ventricle. Its opening is guarded by the aortic valve. It transports oxygenated blood to different parts of the body through its branches.

Question 2.
Write notes on the working of the heart of man. [AP MAR-19,17,16,15] [TS MAR-16]
Answer:
Working of heart:
- Generation & conduction of action potentials.
- Cardiac cycle
- Cardiac Output
- Double circulation.
1) Generation & conduction of action potentials:The contractions of heart chambers are due to the action potential generated by nodal tissue SAN. They cause the contraction of atria.
![]()
2) Cardiac cycle: The cardiac events that occur from the beginning of one heart beat to the begining of the next beat is called cardiac cycle. It lasts for about 0.8 sec.
Cardiac cycle consists of 3 phases (a) atrial systole (b) ventricular systole (c) cardiac diastole
(a) Atrial systole: The SAN generates an action potential which stimulates both the atria and to contract simultaneously causing the ‘atrial systole’.
- It lasts for about 0.1 sec.
- This increases the flow of blood into the ventricles by about 30%.
- The remaining blood flows into the ventricles before the atria/ systole.
(b) Ventricular systole: The action potential reaches AVN. It is a relay centre. The electrical impulses pass through a bundle of His and Purkinje fibres. This causes ventricular systole.
- It lasts for about 0.3 sec.
- The atria undergo relaxation coinciding with the ventricular systole.
- It increases the pressure causing the closure of the AV valves.
- It results in the production of the first heart sound known as ‘Lub’.
- This prevents the ‘backflow’ of blood.
- As the ventricular pressure increases further, the semilunar valves are open. This allows the blood to flow into the aortic arches.
(c) Cardiac diastole: The ventricles now relax and the ventricular pressure falls.
This causes the closure of the semilunar valves which prevents the back flow of blood.
- It lasts for about 0.4 sec.
- This results in the production of the second heart sound known as ‘Dup’.
- All the heart chambers are now again in a relaxed state (joint diastolic phase). Soon another cardiac cycle begins.
3) Cardiac Output: The volume of blood pumped out by each ventricle for each heart beat is
known as stroke volume. The volume of blood pumped out by the heart from each ventricle per minute is termed as cardiac output. .
Cardiac output = stroke volume(70ml) x No.of beats per minute(72 beats)= 5040 ml/min or approximately 5 liters.
4) Double Circulation: There are two independent circulations.
(i) Pulmonary circulation: Blood from the right ventricle flows through pulmonary arteries to lungs. The blood is aerated and goes back to left atrium through pulmonary veins.
(ii) Systemic Circulation: The left ventricle pumps the blood through systemic arch to various parts of the body through arteries. Blood collected from various parts of the body by veins and brought back to the right atrium through venaecavae.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The volume of blood pumped out by each Ventricle in each heart beat is called
1. Cardiac output
2. Heart rate
3. Vital capacity
4. Stroke volume
Answer:
4. Stroke volume
Question 2.
Christmas factor is also known as
1. Antihaemophilic factor A
2. Plasma thromboplastin antecedent
3. Antihaemophilic factor C
4. Plasma thromboplastin component
Answer:
4. Plasma thromboplastin component
Question 3.
Which of the following is antagonistic to vitamin K?
1. Coumarin
2. Warfarin
3. Heparin
4. EDTA
Answer:
2. Warfarin
Question 4.
Sinoatrial node (SAN) is present in the right upper corner of the
1. Right atrium
2. Right ventricle
3. Left atrium
4. Left ventricle
Answer:
1. Right atrium
![]()
Question 5.
AV bundle arises from
1. Atrioventricular valves
2. Atrioventricular node
3. Fossa ovalis
4. Sinoatrial node
Answer:
2. Atrioventricular node
Question 6.
In the cardiac cycle, the duration of atrial systole is
1. 0.8 sec.
2. 0.1 sec.
3. 0.3 sec.
4. 0.4 sec.
Answer:
2. 0.1 sec.
Question 7.
‘Lub’ sound in the beat is due to the closure of
1. Semilunar valve during ventricular systole
2. AV valves during ventricular diastole
3. Semilunar valves during ventricular diastole
4. AV valves during ventricular systole
Answer:
Question 8.
‘Dup’ sound in the beat is due to the closure of
1. Semilunar valves during ventricular systole
2. AV valves during ventricular diastole
3. Semilunar valves during ventricular diastole
4. AV valves during ventricular systole
Answer:
4. AV valves during ventricular systole
Question 9.
Heart wall is made of
1. Myocardium
2. Epicardium
3. Endocardium
4. All the above
Answer:
3. Endocardium
Question 10.
The layer which is responsible for the difference in thickness of chambers of heart is
1. Epicardium
2. Endocardium
3. Myocardium
4. Pericardium
Answer:
4. Pericardium
Question 11.
Pulmonary valve prevents the backward flow of
1. Oxygenated blood into the right ventricle
2. Deoxygenated blood into the left ventricle
3. Deoxygenated blood into the right atrium
4. Deoxygenated blood into the right ventricle
Answer:
3. Deoxygenated blood into the right atrium
Question 12.
Thrombin converts
1. Insoluble fibrinogen to insoluble fibrin
2. Soluble fibrinogen to insoluble fibrin
3. Soluble fibrinogen to soluble fibrin
4. Insoluble fibrinogen to soluble fibrin
Answer:
4. Insoluble fibrinogen to soluble fibrin
Question 13.
The human heant is
1. Endodermal
2. Mesodermal
3. Ectodermal
4. Ecto-endodermal
Answer:
2. Mesodermal
Question 14.
Lymph vessels are
1. Thick-walled and valvular
2. Thick-walled and nonvalvular
3. Thin-walled and valvular
4. Thin-walled and nonvalvular
Answer:
3. Thin-walled and valvular
Question 15.
In human heart, the left atrium receives blood from
1. Three caval veins
2. Four pulmonary veins
3. Three pulmonary veins
4. Caval veins and coronary sinus
Answer:
2. Four pulmonary veins
![]()
Question 16.
Lymph lacks
1. Erythrocytes
2. Plasma proteins
3. Leucocytes
4. Immunoglobulins
Answer:
1. Erythrocytes
Question 17.
AH the arteries
1. carry oxygenated blood
2. carry blood away from the heart
3. carry deoxygenated blood
4. carry blood towards the heart
Answer:
2. carry blood away from the heart
Question 18.
Only deoxygenated blood passes through
1. Left side of the heart
2. Systemic circulation
3. Right side of the heart
4. Pulmonary circulation
Answer:
3. Right side of the heart
Question 19.
Normal blood pressure is
1. 140/90 mm Hg
2. 120/80 mm Hg
3.110/70 mm Hg
4. 100/50 mm Hg
Answer:
2. 120/80 mm Hg
Question 20.
Cardiac output=
1. Stroke volume + No. of beats per minute
2. Stroke volume X No. of beats per minute
3. Stroke volume / No. of beats per minute
4. No. of beats per minute / stroke volume
Answer:
2. Stroke volume X No. of beats per minute
Question 21.
Blood pressure is measured using
1. Sphygmomanometer
2. Calorimeter
3. Spirometer
4. Haemocytometer
Answer:
1. Sphygmomanometer
Question 22.
Normal systolic blood pressure at rest is
1. 120mmHg
2. 140mmHg
3. 80 mm Hg
4. 90 mm Hg
Answer:
1. 120mmHg
Question 23.
Bean-shaped nucleus is found in
1. Lymphocytes
2. Eosinophils
3. Basophils
4. Monocytes
Answer:
4. Monocytes
Question 24.
In the animal body, blood bank is
1. Heart
2. Spleen
3. Lungs
4. Liver
Answer:
2. Spleen
![]()
Question 25.
Platelets are formed from
1. Leucocytes
2. Lymphocytes
3. Megakaryocytes
4. Myocytes
Answer:
3. Megakaryocytes
Question 26.
Erythroblastosis foctalis results when the blood group of father and mother are respeetively
1. Rh+ and Rh+
2. Rh+ and Rh-
3. Rh- and Rh+
4. Rh- and Rh-
Answer:
2. Rh+ and Rh-
Question 27.
Which of the following is/are referred to as positive waves in ECCJ?
(i) P
(ii) R
(iii) T
(iv) Q
(V) S
1. only(i)
2. only(ii)
3.(ii)and(v)
4. (iii), (iv) and(v)
Answer:
2. only(ii)
Question 28.
The hormone erythropoietin is produced by
1. Liver
2. Spleen
3. Kidney
4. Bone marrow
Answer:
3. Kidney
Question 29.
The WBC count which is raised in people with allergic condition such as asthma or hay fever
1. Neutrophils
2. Basophils
3. Acidophils
4. Lymphocytes
Answer:
3. Acidophils
Question 30.
Closed circulatory system is found in
1. Arthropods and Annelids
2. Annelids and Molluscs
3. Annelids and Vertebrates
4. Arthropods and Vertebrates
Answer:
3. Annelids and Vertebrates
Question 31.
Hypophyseal portal system is not related with
1. hypothalamus
2. Anterior Pituitary
3. Posterior Pituitary
4. Hypophyseal Vein
Answer:
3. Posterior Pituitary
![]()
Question 32.
Arteries and veins can be differentiated structurally from each other on the basis of thickness of wall which is mainly due to difference in
1. Tunica adventitia
2. Tunica media
3. Tunica intima
4. Endothelium only
Answer:
2. Tunica media
Question 33.
According to Starling’s law of heart, cardiac output is directly related to
1. Size of auricles
2. Heart rate
3. End systolic volume
4. Amount of blood returning to heart
Answer:
4. Amount of blood returning to heart
Question 34.
Strangled chest the common term for
1. Heartburn
2. Angina
3. Stenosis
4. Rheumatic heart
Answer:
2. Angina
Question 35.
Platelet derived growth factor (PI)CF) plays an essential role in causing a heart disease called
1. Atherosclerosis
2. Fibrillation
3. Rheumatic heart disease
4. Arrhythmia
Answer:
1. Atherosclerosis
Question 36.
Cardia output is blood
1. Received by heart per minute
2. Pumped by ventricles per sec
3. Pumped by left ventricle per minute
4. Pumped by left ventricle per hour
Answer:
3. Pumped by left ventricle per minute
Question 37.
If the number of beats per minute are 75 and stroke volume is 78 ml, then the cardiac output would be
1. 5250 mL
2.7000mL
3. 5850 mL
4. 6580mL
Answer:
3. 5850 mL
Question 38.
A doctor said that the patient is in nodal rhythm, then he meant that
1. SA node restarts functioning
2. SA node fails and AV node generates impulse
3. SA node gets inflamed
4. Cardiac failure
Answer:
2. SA node fails and AV node generates impulse
Question 39.
The papillary muscles are helpful in
1. Movement of eye balls
2. Movement of eye lid
3. Closing & opening the valves of heart
4. Movement of pinnae
Answer:
3. Closing & opening the valves of heart
Question 40.
The enzyme which helps in coagulation of blood in sanguivores is
1. Rennin
2. Chymotrypsin
3. Trypsin
4. Pepsin
Answer:
3. Trypsin
![]()
Question 41.
Post caval opening in right auricle is guarded by
1. Arterio-ventricular valve
2. Tricuspid valve
3. Bicuspid valve
4. Eustachain valve
Answer:
4. Eustachain valve
Question 42.
Fossa ovalis in the heart is located in
1. Right atrium
2. Left atrium
3. Interventricular septum
4. Interatrial septum
Answer:
4. Interatrial septum
Question 43.
The relationship that reveals heart rate is inversely proportional to blood pressure is
1. Henry law
2. Marey’s law
3. Dalton law
4. Starling law
Answer:
2. Marey’s law
Question 44.
Chordae tendineae is
1. Cardiac muscle
2. Smooth muscle
3. Skeletal muscle
4. Fibrous connective tissue
Answer:
4. Fibrous connective tissue
Question 45.
In hypertension, increase in blood pressure is beyond systolic
1. 90mmHg
2. 220mmHg
3. 160mmHg
4. 140mmHg
Answer:
4. 140mmHg
Question 46.
The human heart is not related to
1. Chordae tendineae
2. Pacemaker
3. Neurogenic
4. Mitral valve
Answer:
3. Neurogenic
Question 47.
A patch of nodal tissue responsible for initiating the rhythmic contractile activity of heart is present in
1. Lower left comer of the left ventricle
2. Upper right comer of the right atrium
3. Lower left comer of the right ventricle
4. Upper left comer of the left atrium
Answer:
2. Upper right comer of the right atrium
Question 48.
Identify the correct statement
1. Blood – Plasma + RBC + WBC + Platelets
2. Plasma = Blood – lymphocytes
3. Serum = Blood + Fibrinogen
4. Lymph = Plasma + Blood + WBC
Answer:
1. Blood – Plasma + RBC + WBC + Platelets
Question 49.
Parasympathetic neural signals affect the working of the heart by
1. Reducing both heart rate and cardiac output
2. Increasing heart rate without affecting the cardiac output
3. Increasing both heart rate and cardiac output
4. Decreasing heart rate but increasing cardiac output
Answer:
1. Reducing both heart rate and cardiac output
![]()
Question 50.
………… is known as lesser circulation
1. Coronary circulation
2. Pulmonary circulation
3. Portal circulation
4. Systemic circulation
Answer:
2. Pulmonary circulation