Students can go through AP Inter 2nd Year Physics Notes 12th Lesson Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter will help students in revising the entire concepts quickly.
AP Inter 2nd Year Physics Notes 12th Lesson Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
→ Cathode rays consists of electrons. These are negatively charged particles.
→ Electron was discovered by J.J. Thomson.
→ Specific charge : The ratio of charge to the mass of particles is called specific charge. Specific charge = e/m. Units in S.I. system coulomb/kg.
→ Electron volt: The K.E. acquired by an electron when accelerated through a p.d. of 1 volt.
1 eV = 1.6 × 10-19 J.
→ Force on electron due to electric field F = Ee.
→ Force on electron moving perpendicular to magnetic field F = BeV
![]()
→ Millikan determined the charge of electron accurate.
→ Charge of electron e = 1.6 × 10-19 C and mass of electron m = 9.1 × 10-31 kg.
→ The principle behind Millikan experiment is study of the motion of charged oil drops under free fall due to gravity and in an uniform electric field.
→ The emission of electron from a metal surface when illuminated by light or any other radiation of suitable wavelength is called photoelectric emission or effect.
→ The electrons emitted here are called photoelectrons.
→ The metals’which emit electrons are called photometals. Ex: Lithium, Sodium, Potassium.
→ Stopping potential: If V is the stopping potential of electron, the energy of the electron is eV
→ Stopping potential is independent of intensity of incident radiation.
→ The quantum of energy is given by E = hv = \(\frac{\mathrm{hc}}{\lambda}\)
→ Einstein equation of photoelectric effect hv = \(\frac{1}{2}\) mυ2 + Φ0.
→ Photocells are based on application of photoelectric effect.
→ Photomultiplier is a device which amplifies very weak light signals.
→ When fast moving electrons are suddenly stopped by metals x-rays are produced in addition to large amount of heat.
![]()
→ The minimum energy required by an electron to escape from the metal surface is called work function (Φ0).
→ The work function of platinum is the highest (Φ0 = 5.65 eV). While it is the lowest (Φ0 = 2.14 eV) for caesium (cs).
→ When light of suitable frequency illuminates a metal surface, electrons are emitted from the metal surface. These photo (light) generated electrons are called photoelectrons. This process is called photoelectric emission.
→ The minimum cut off frequency below which no photoelectric emission is possible, called threshold frequency (V0).
→ Hisenberg’s uncertainty principle : “It is not possible to measure both the position and momentum of an electron at the same time exactly”. i.e. ∆x ∆p = h.
Formulae
→ Stopping potential and max K.E are related as ev0 = \(\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{~m} v_{\max }^2\) or v0 ∝ \(\mathrm{m} v_{\max }^2\)
→ Energy, E = hv = \(\frac{\mathrm{hc}}{\lambda}\)
→ Momentum, P = \(\frac{\mathrm{hv}}{\mathrm{c}}=\frac{\mathrm{h}}{\lambda}\)
→ Einsteins photoelectric equation
hv = hv0 + \(\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{~m} v_{\max }^2\); \(\frac{\mathrm{hc}}{\lambda}\) = w + \(\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{~m} v_{\max }^2\)
![]()
→ Wavelength λ = \(\frac{\mathrm{h}}{\mathrm{mv}}\)
→ Mass in motion,
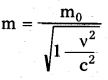
→ λ = \(\frac{12.27}{\sqrt{\mathrm{V}}}\) nm
→ λ = \(\frac{\mathrm{h}}{\mathrm{p}}=\frac{\mathrm{h}}{\mathrm{mv}}=\frac{\mathrm{h}}{\sqrt{2 \mathrm{mE}}}=\frac{\mathrm{h}}{\sqrt{2 \mathrm{mev}}}\)