Students can go through AP Inter 2nd Year Economics Notes 3rd Lesson National Income will help students in revising the entire concepts quickly.
AP Inter 2nd Year Economics Notes 3rd Lesson National Income
→ Several estimates National Income were prepared Dadabhai Nouroji (1868), William Digby (1899), Find lay ShiraH (1971, 1922 and 1931), Shah and Kham batta (1921) Dr. V.K.R.V. Rao (1925-29) and (1931-32) and R.C. Desai (1931-40).
→ C.S.O. is estimating National income adopting product method in primary sectors and secondary sectors, income method in tertiary sector and expenditure method in construction.
→ The growth or percapita income at constant prices is an indicator or the change in the standard or living people.
→ Sectoral contribution to national income – contribution of the primary sector – contribution of secondary sector – contribution of tertiary sector.
→ Two basic causes of income inequalities – The existing system based on the institution or private property – The law of inheritance.
![]()
→ Types of employment – structural unemployment
- Disguished unemployment – Seasonal unemployment
- Cyclical unemployment – Technological unemployment
→ Uniform Recall Period (URP) – The consumption expenditure for all items except 5 non-food commodities w,ere collected for 3 days URP to estimate the poverty in the country.
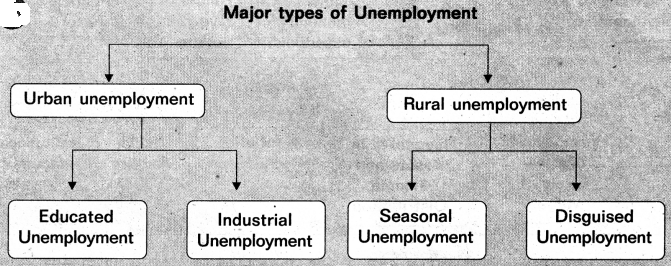
→ Unemployment indicates a situation where the total number of job vacancies is much less than total number of job seekers in the country. Rural unemployment or two types (i) Seasonal unemployment, disguised unemployment. Urban employment is or two types :
- Industrial unemployment
- Education unemployment.
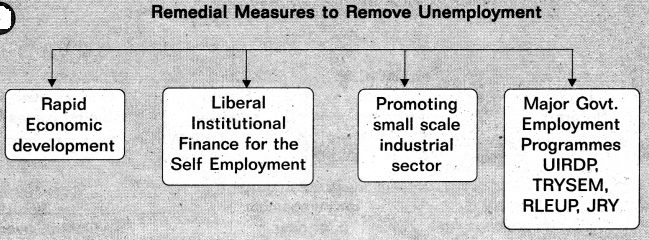
→ Rural works programme, small farmers development agency, Agro service centres. Dry land agricultural development, Area development schemes and programmes like food for work IRDP, TRYSEM, PMRY, Jawahar Rozgar Yojana etc, are the measures taken by governments to reduce unemployment problem.
→ Poverty is a situation where a part of the society is unable to satisfy the basic minimum necessities such as food, shelter and clothing.
→ Poverty line refers to the cut off level of annual income of the household that is needed for human substances.
→ High growth rate of population unemployment under exploitation or natural resources low level of capital and technology. Social and political factors are some of the causes for poverty.
→ The credit facilities provided by the banks and co-operative credit societies at low interest rates to poor people are called micro-credits.
→ Self Help Group (SHG) is an instrument for delivery of Micro-credit to the poor people. The main aims of these SHG are social welfare, mutual aid, economic uplif iment assistance to fellow members etc.
![]()
→ Absolute poverty: A person whose income or consumption expenditure is so mearge that he lies below the subsistance level they can called absolute poverty.
→ TRYSEM : This was initiated in 1979 with the objective of tackling unemployment problem among the rural youth. It aimed at training about 2 lakh rural youth every year to enable to become self employed. The TRYSEM was merged into Swarnajayanthi Gram Swarozgar Yojana in April 1999.
→ Disguised unemployment: A person whose marginal productivity is zero or when more people are engaged in a job than actually required.
![]()
→ Micro Finance : The provision of thrift, credit and other financial services and products of very small quantity to the poor in rural, semi-urban and urban areas for enabling them to raise their incomes and improving living standards.
→ Percapita income : It is estimated dividing National income by population of the country as per the formula given below.
Percapita income = \(\frac{\text { National income }}{\text { Population }}\)
→ The net money value of all final goods and Services produced in a country, usually, during a period of one year, valued at current market prices, without duplication is known as “National Income”.
→ The trends in the changes in National Income of India indicate that some real development has taken place only during post-reforms period i.e., after 1991.
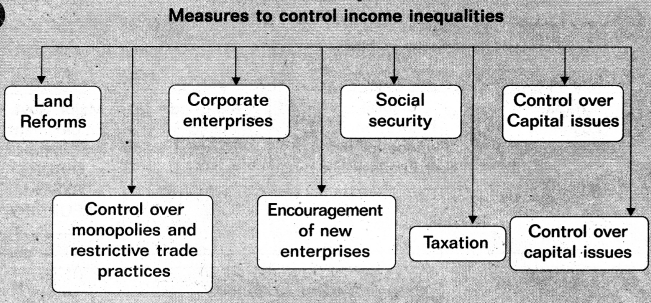
→ Some of the important causes of Income inequalities In India are — Inequality in land ownership excessive concentration of assets In private corporate sector, Inequality in professional training, Inflation and uncontrolled rise in the general price level, Inequality in the availability of credit facilities, Urban biased private investment, etc.
→ Some of measures to control income inequalities are — Effective Implementation of land reforms, Control over monopolies and restrictive trade practices, Encouraging co-operative enterprises, Encouraging new enterprises providing better social security, Implementation of progressive taxation, Proper control over capital issues, etc.
→ The various types of unemployment are — Seasonal unemployment, Disguised unemployment, Cyclical unemployment, Structural unemployment, Under employment, Frictional unemployment, etc.
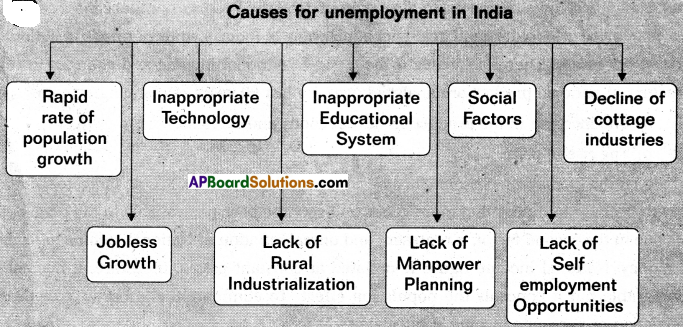
→ Some of the important causes of unemployment in India are — Rapid growth of population, jobless growth, inappropriate technology, lack of rural Industrialisation, defective/inappropriate educational system, lack of proper manpower planning, various social factors, decline of cottage industries, lack of self-employment opportunities, etc.
→ Some of the important measures that may reduce unemployment are — Accelerating economic development in the country, Providing liberal institutional finance to self-employed encouraging small scale industrial sector, Implementing various government sponsored employment generation programmes. etc.
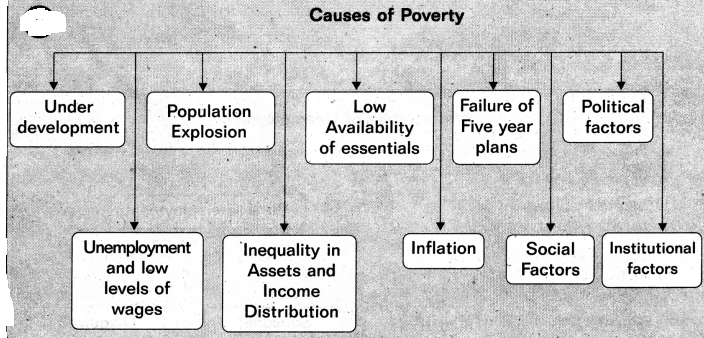
→ Some of the important causes of poverty in India are — Under development of the Indian Economy, Large Scale Unemployment coupled with low wages, population explosion, Inequality ¡n income and asset distribution, Low availability of essential goods, Inflation, failures of five year plans, political factors, institutional factors and social backwardness, etc.
→ Some of the important remedial measures that can reduce poverty in India are — Adoption of pro – poor strategy, Encouraging the growth rate in agricultural sector. Increasing productivity and job quality in unorganised sector. Improving the share of wages in GDP, Empowerment of poor through education and skill development, Empowerment of poor through better health and housing facilities, etc.
→ The different poverty concepts are — Absolute poverty, Relative poverty, Poverty line, Urban poverty, Rural poverty, poverty ratio, poverty gap, etc.
→ The term Micro finance refers to the provision of financial services and meeting the small size of credit and financial needs of Urban and rural poor with the intention of improving their Quality of life and living standards.
→ మానవజాతి ఆర్థికసంక్షేమాన్ని కొలిచే ముఖ్య సాధనము జాతీయాదాయము.
→ ఒక సంవత్సర కాలంలో ఒక దేశంలో ఉత్పత్తిచేసిన అంతిమ వస్తుసేవల విలువల ద్రవ్యరూపమే జాతీయాదాయము.
→ భారత ప్రభుత్వం పి.సి. మహలనోబిస్, ఆచార్య డి.ఆర్. గార్గిల్, ఆచార్య వి.కె.ఆర్.వి.రావులతో కలసి ఆగష్టు 4, 1949 సం॥లో జాతీయాదాయ కమిటీని నియమించింది.
→ కేంద్ర గణాంకసంస్థ (C3O) జాతీయాదాయ అంచనాలను వర్తమానధరలలో మరియు స్థిర ధరలలో మదింపు చేస్తున్నది.
→ 2004-05 ధరల ప్రకారము 2013-14 సం॥ములో నికర జాతీయోత్పత్తి రూ.49,20,180 కోట్లుగాను, తలసరి జాతీయోత్పత్తి రూ. 74,380 గాను ఉంది.
→ 2013-14 (P.E.) సం॥లో స్థూల దేశీయోత్పత్తిలో వ్యవసాయము దాని అనుబంధ రంగాల వాటా 13.9 శాతముగాను, పారిశ్రామికరంగం వాటా 26.2 శాతంగాను, సేవలరంగం వాటా 59.9 శాతంగాను ఉంది.
→ 1990వ దశకం ప్రారంభంలో భారత ప్రభుత్వం నూతన ఆర్థిక విధానాన్ని ప్రకటించింది. 25 సం॥ముల సంస్కరణ కాలం గతించినా పేదరికము, అవస్థాపనా సౌకర్యాల కొరత, ఆర్థిక అసమానతలు మొదలగు సమస్యలు కొనసాగుతున్నాయి.
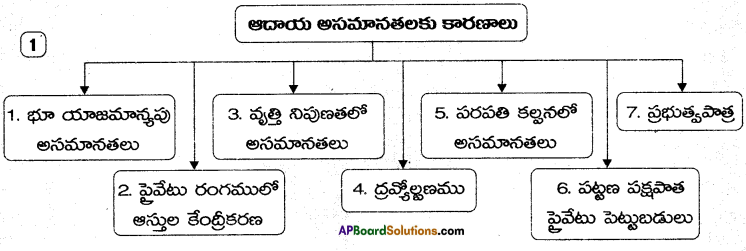
→ ఆదాయ అసమానతలకు భూ యాజమాన్యంలో అసమానత, ప్రయివేట్ కార్పోరేటు రంగంలో ఆస్తుల కేంద్రీకరణ, వృత్తి నైపుణ్యాలలో అసమానత, ద్రవ్యోల్బణము, నగరాలవైపు పెట్టుబడి, పరపతి సౌకర్యాలలో అసమానత. ప్రభుత్వపాత్ర. అసమంజసమైన పన్నుల విధానము మొదలైనవి కారణాలుగా చెప్పవచ్చును.
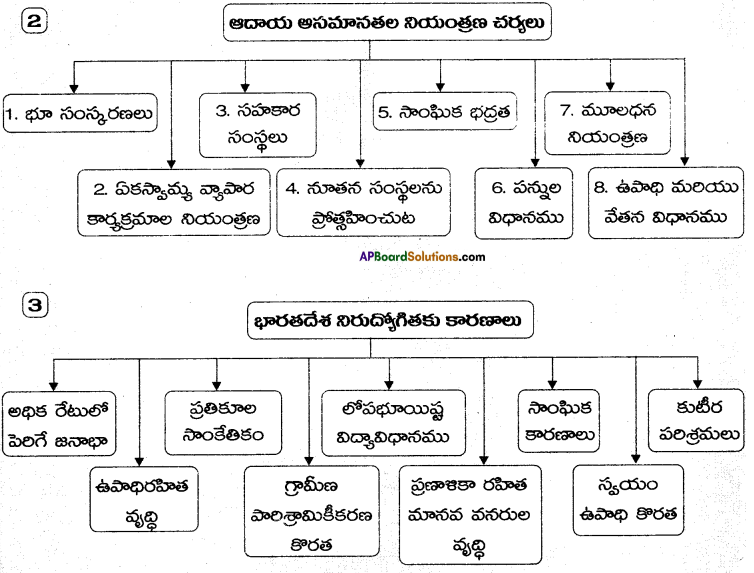
→ ఆదాయ అసమానతల నియంత్రణ చర్యలు : భూ సంస్కరణలు, ఏకస్వామ్య వ్యాపార కార్యకలాపాల నియంత్రణ, సహకార సంస్థలు, నూతన సంస్థలను ప్రోత్సహించుట, సాంఘిక భద్రత, పన్నుల విధానము, ఉపాధి మరియు వేతన విధానము, చిన్నతరహా పరిశ్రమలను ప్రోత్సహించటము.
→ ఆచార్య పిగూ ప్రకారం “వ్యక్తి పనిచేయాలనే కోరిక ఉన్నప్పటికి పని కల్పించకపోవడాన్ని నిరుద్యోగితగా” పేర్కొనెను.
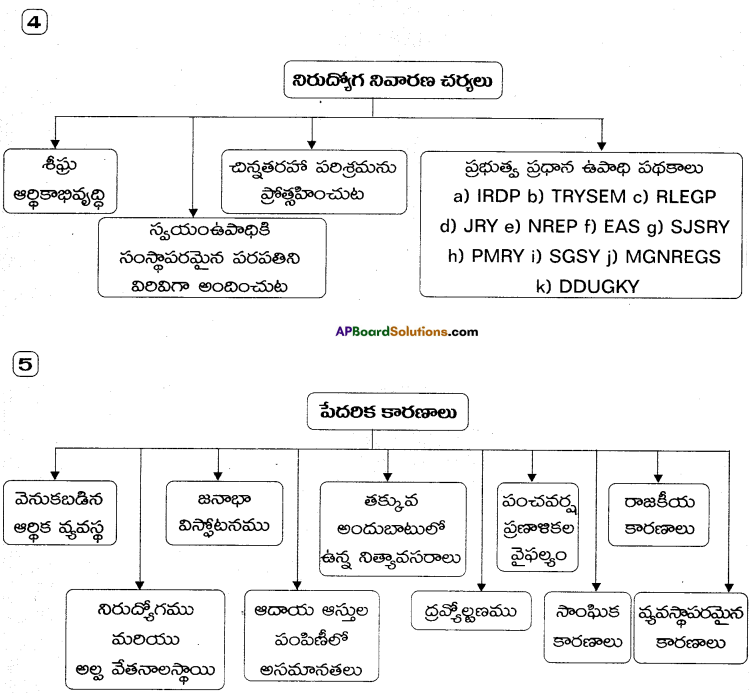
→ నిరుద్యోగితకు కారణాలు: జనాభా వృద్ధిరేటు అధికంగా ఉండటము, ఉపాధి రహిత వృద్ధి, ప్రతికూల సాంకేతికం, గ్రామీణ పరిశ్రమలు విస్తరించకపోవటం, లోపభూయిష్టమైన విద్యా విధానము, మానవ వనరుల వృద్ధిలో లోపము, సాంఘిక కారణాలు, స్వయం ఉపాధిపై మక్కువ లేకపోవటం, కుటీర పరిశ్రమలు క్షీణించుట.
![]()
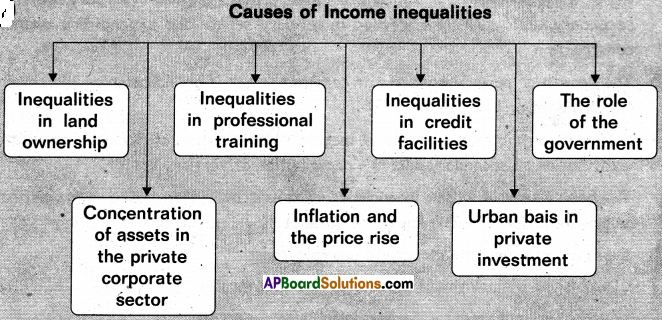
→ నిరుద్యోగిత నివారణ చర్యలు : వేగవంతమైన ఆర్థికాభివృద్ధి, స్వయం ఉపాధికి విరివిగా ఋణాలిచ్చుట, చిన్నతరహా పరిశ్రమలను ప్రోత్సహించుట. ప్రభుత్వం నిరుద్యోగితను తొలగించే దృఢ సంకల్పంతో అనేక ఉద్యోగితా పథకాలను అమలుచేయుట.
→ పేదరికము ఒక సాంఘిక ఆర్థిక సమస్య.
→ సాధారణ జీవన విధానానికి కూడా నోచుకోకుండా కనీస జీవనవిధానాన్ని కొనసాగించే వారందరిని పేదవారుగా పేర్కొనవచ్చును.
→ పేదరిక కారణాలు : వెనుకబడిన ఆర్థికవ్యవస్థ, నిరుద్యోగము మరియు అల్పవేతనాల స్థాయి, జనాభా విస్ఫోటనము. ఆదాయ, ఆస్తుల పంపిణీలో అసమానతలు, తక్కువ అందుబాటులో ఉన్న నిత్యావసరాలు. ద్రవ్యోల్బణము, పంచవర్ష ప్రణాళికల వైఫల్యం, సాంఘిక కారణాలు, రాజకీయ కారణాలు, వ్యవస్థాపరమైన
→ పేదరిక నిర్మూలన చర్యలు : సరళీకరణ: దేశీయ ఉత్పత్తి వృద్ధి కంటే పేదవారి వృద్ధ వ్యూహమును ఎంపిక చేసుకొనుట; వ్యవసాయ వృద్ధిరేటును పెంపొందించుట; అసంఘటిత రంగాలలో వృత్తినైపుణ్యాన్ని, ఉత్పాదకతను పెంచుట, విద్య, నైపుణ్యాలలో పేదవారిని శక్తివంతులను చేయుట; మంచి ఆరోగ్యవసతుల ద్వారా పేదవారిని శక్తివంతులను చేయుట; పేదవారికి గృహవసతి కల్పించుట, ఐ టి రంగాన్ని విస్తృతపరచి, నైపుణ్యాల ద్వారా పేదలను శక్తివంతులను చేయుట. జాతీయ ఉపాధి గ్రామీణ పథకము.
→ సూక్ష్మవిత్తము సహాయముతో పేదరికాన్ని నిర్మూలించుట.
→ ఒక దేశంలో ఒక సంవత్సర కాలంలో ఉత్పత్తి అయ్యే అంతిమ వస్తు సేవల నికర విలువను జాతీయాదాయం అంటారు.
→ జాతీయోత్పత్తిలోని అంశాలు, ఆర్థిక వ్యవస్థ నిర్మాణాన్ని తెలియజేస్తుంది.
→ మనదేశంలో ఆదాయ – సంపద పంపిణీలో అసమానతలు చోటుచేసుకున్నాయి. భారతదేశంలో నగరాల్లోని ఆదాయ అసమానతలు గ్రామాలలోని అసమానతల కంటే అధికంగా ఉన్నాయి.
→ ఆదాయ అసమానతలకు కారణాలు – భూ యాజమాన్యపు అసమానతలు, వృత్తి నిపుణతలో అసమానతలు, ప్రభుత్వ పాత్ర, ద్రవ్యోల్బణము, ప్రైవేటు రంగంలో ఆస్తుల కేంద్రీకరణ.
→ ఆదాయ అసమానతల నియంత్రణ చర్యలు – భూ సంస్కరణలు, సహకార సంస్థలు, సాంఘిక భద్రత, మూలధన నియంత్రణ, నూతన సంస్థలను ప్రోత్సహించుట, పన్నుల విధానం మొదలగునవి.
→ ఒక వ్యక్తి ప్రస్తుతం అమలులో ఉన్న వేతనానికి అసక్తి, శక్తి ఉన్నప్పుటికీ ఉద్యోగం లభించని స్థితిని నిరుద్యోగం అంటారు.
→ నిరుద్యోగితకు కారణాలు- ఉపాధి రహితవృద్ధి, శ్రామికశక్తి పెరుగుదల, ప్రతికూల సాంకేతికం, ప్రతికూల విద్యావిధానం, సరళీకరణ విధానం.
→ నిరుద్యోగితకు నివారణ చర్యలు – వృద్ధి రేటును వేగత్వరం చేయుట, ఉద్యోగ అవకాశాల కల్పన, ప్రభుత్వ పథకాలు మొదలగునవి.
→ కనీస అవసరాలు కూడా తీరని స్థితిని పేదరికం అంటారు.
→ పేదరికానికి కారణాలు : ఆర్థిక శక్తి కేంద్రీకరణ, సహజ వనరుల అల్ప వినియోగం, జనాభా ఒత్తిడి, నిరుద్యోగిత, తక్కువ విద్య, ద్రవ్యోల్బణం మొదలగునవి.
→ పేదరికం నిర్మూలన చర్యలు : ఆదాయ వనరుల అభివృద్ధి పథకాలు, ప్రత్యేక ప్రాంతాల అభివృద్ధి పథకం, వ్యవసాయాభివృద్ధి పెంచుట, ఉపాధి కల్పించుట, సూక్ష్మవిత్తము.