Students can go through AP Inter 2nd Year Civics Notes 9th Lesson Union-State Relations will help students in revising the entire concepts quickly.
AP Inter 2nd Year Civics Notes 9th Lesson Union-State Relations
→ The centre – state relations is the most important aspect of a federal system.
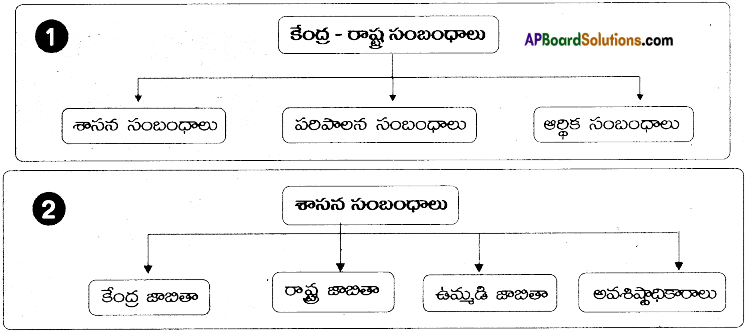
→ The, union and state relations are divided into three heads. They are
- Legislative
- Administrative and
- Financial relations.
→ The central Government has more powers than the states in legislative, administrative and financial matters.
→ Our constitution divides the powers into three lists viz., the union list, the state list and the concurrent list.
→ Union list at present comprises Hundred subjects.
→ State list at present comprises sixty two subjects.
→ All present there are 52 subjects in the concurrent list.
![]()
→ The residuary powers are given to the union government.
→ The governor plays key role in the union – state relations.
→ Finance commission is appointed by the president for every 5 years.
→ The purpose of the finance commission is to recommend the distribution of taxes and grants between states.
→ The states have to depend on the centre for financial aid in many respects.
→ When a constitutional emergency is declared in the state, Parliament is empowered to make laws for the state.
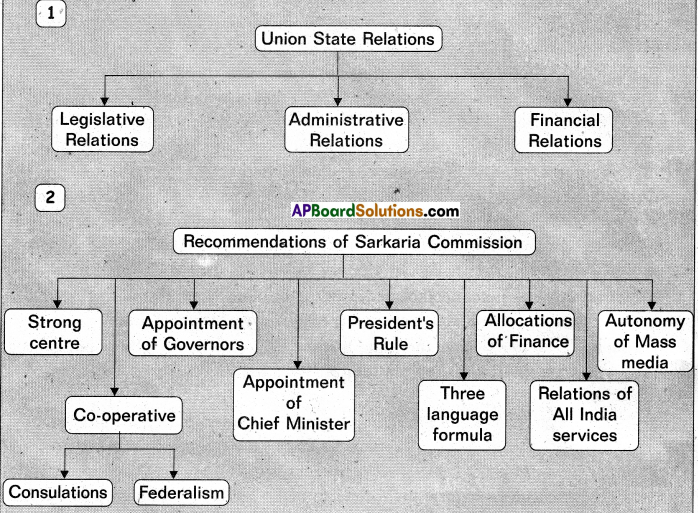
→ Sarkaria commission was appointed in March, 1983 to review centre – state relations.
→ A permanent Inter State council called the Inter Government council should be set¬up under Article 263.
→ The Inter State Council settles the disputes which arise between states.
→ NITI Ayog, National Development.Council, National Integration Council and Inter State Council are extra constitutional devices of union government.
Synopsis
- The Constitution of India ¡s federal in form but is unitary in character.
- The Constitution of India, divided all the powers – Legislative, executive and financial between the Union and States.
- The Union-State relations in India can be discussed under three heads. They are 1) Legislative relations, 2) Administrative relations and 3) Financial relations.
- The Constitution of India makes three fold distributions of Legislative powers between the Union and States. They are 1) the Union List 2) the State List and 3) the Concurrent list.
- The Union Parliament has exclusive powers to make saws on the issues of Union list.
- At present, Union list consists to 100 subjects, State list contains 62 subjects and Concurrent list contains 52.
- The powers which are not included in any three lists are called ‘Residuary powers’.
- The President of India Constitutes a Finance Commission with Chairman and four members.
- The Planning Commission was replaced by ‘NITI Aayog’ (National Institute for Transforming India) on 1st January 2015.
- National Development Council was set up In 1952.
→ భారత సమాఖ్యలో కేంద్ర, రాష్ట్ర సంబంధాలు ముఖ్యమైనవి.
→ రాజ్యాంగ నిర్మాతలు బలమైన కేంద్రం గల సమాఖ్య విధానాన్ని రూపొందించారు.
→ ప్రస్తుత కేంద్ర, రాష్ట్ర సంబంధాలు 1935 భారత ప్రభుత్వ చట్టంపై ఆధారపడి రూపొందింపబడ్డాయి.
→ కేంద్రంలోను, రాష్ట్రంలోను వేరువేరు రాజకీయ పార్టీలు అధికారంలో ఉన్నప్పుడు కేంద్ర, రాష్ట్రాల మధ్య వివాదాలేర్పడతాయి.
→ కేంద్ర, రాష్ట్రాల మధ్య సంబంధాలు
- శాసన
- పరిపాలన
- ఆర్థిక సంబంధాలుగా విభజింపబడ్డాయి.
→ కేంద్ర ప్రభుత్వానికి శాసన, పరిపాలన, ఆర్థిక విషయాలలో రాష్ట్ర ప్రభుత్వాని కంటే ఎక్కువ అధికారాలున్నాయి.
→ పరిపాలనాంశాలు మూడు జాబితాలుగా విభజింపబడ్డాయి.
![]()
→ ఆ మూడు జాబితాలను
- కేంద్ర జాబితా,
- రాష్ట్ర జాబితా,
- ఉమ్మడి జాబితా అంటారు.
→ ప్రస్తుతం కేంద్ర జాబితాలోని అంశాలు 99.
→ ప్రస్తుతం రాష్ట్ర జాబితాలోని అంశాలు 61.
→ ప్రస్తుతం ఉమ్మడి జాబితాలోని అంశాలు 52
→ అవశిష్టాధికారాలు కేంద్ర ప్రభుత్వానికి ఇవ్వబడ్డాయి.
→ కేంద్ర, రాష్ట్ర సంబంధాల నిర్వహణలో గవర్నర్ల పాత్ర ఎంతో కీలకమైంది.
→ ఇటీవల కాలంలో గవర్నర్ల పాత్ర వివాదాస్పదంగా మారింది.
→ రాష్ట్రాలకు ఆర్థిక వనరుల పంపిణీ సిఫారసుకై ఆర్థిక సంఘాన్ని కేంద్ర ప్రభుత్వం నియమిస్తుంది.
→ రాష్ట్రపతి ఆర్థిక సంఘాన్ని 5 సంవత్సరాల కాలానికి నియమిస్తాడు.
→ రాష్ట్రాలు ఆర్థిక వనరులకు కేంద్రంపై ఆధారపడి ఉన్నాయి.
→ ఏదైనా రాష్ట్రంలో రాష్ట్రపతి పాలన విధిస్తే ఆ రాష్ట్రమునకు కావలసిన చట్టాలను పార్లమెంటు చేస్తుంది.
→ 1983లో కేంద్ర, రాష్ట్ర సంబంధాలపై సలహాలిచ్చేందుకు సర్కారియా కమీషన్ను ఏర్పాటు చేశారు.
→ రాజ్యాంగంలోని 263వ అధికరణ క్రింద అంతర్ రాష్ట్ర మండలిని ఏర్పాటు చేయాలి.
→ అంతర్ రాష్ట్ర మండలి రాష్ట్రాల మధ్య ఏర్పడే తగాదాలను పరిష్కరిస్తుంది.