Students can go through AP Inter 2nd Year Civics Notes 2nd Lesson Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State Policy will help students in revising the entire concepts quickly.
AP Inter 2nd Year Civics Notes 2nd Lesson Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State Policy
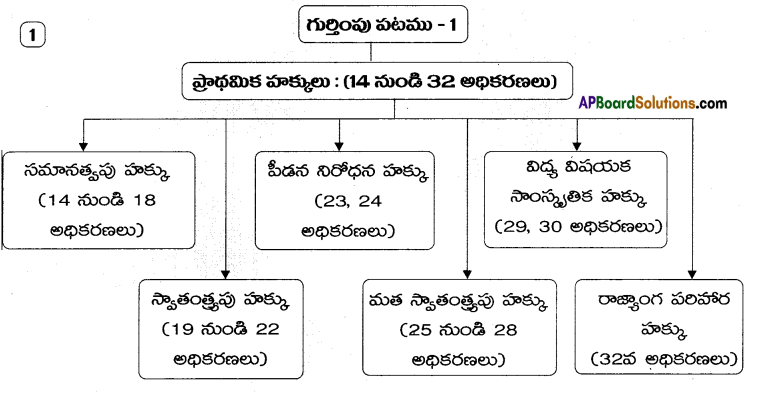
→ Fundamental rights are enriched in part-III of the constitution covering articles from 12 to 35.
→ In 1978, the 44th constitutional amendment deleted the right to property from the list of fundamental rights.
→ Right to constitutional remedies is the very soul and heart of the constitution.
→ Through 42nd constitutional amendment Act. 10 Fundamental duties were in corporated in part – IV of the constitution.
Article 19 provides now to Indian citizens six kinds of freedoms.
![]()
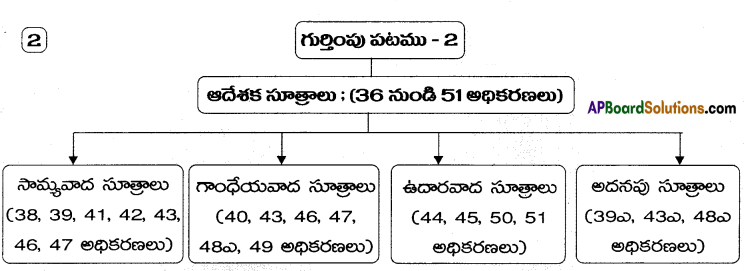
→ The directive principles of state policy are included in part – IV of the constitution covering articles from 36 to 51.
→ The directive principles are classified into three categories i.e. Socialist, Gandhian and Liberal principles.
→ The 42nd amendment gave precedence to directive principles than to the fundamental rights.
→ Directive principles are considered as New Year greeting by Sri Naseeruddin.
Fundamental Rights
- Right to Equality.
- Right to Freedom.
- Right against exploitation.
- Right to religious freedom.
- Right to Education and culture.
- Right to constitutional remedies.
Fundamental Duties
- To Respect constitutions, National Flag and National Anthem.
- To cherish the nobel ideals of freedom struggle.
- Defend the country and render national service when called upon to do so.
- Upholding and protecting sovereignty, unity and integrity.
- Protecting Natural Environment and Animal life.
- Protecting public property.
- To value and preserve the rich heritage and composite culture.
- To develop scientific temper, humanism.
- Strive towards excellence in all spheres of individual and collective activities.
- To provide educational opportunities by a parent or a guardian to the below age limit of six to fourteen years.
- To provide educational opportunities by the parent or guardian to his child or ward between the age of six and fourteen years.
![]()
Directive Principles
- Encouraging cottage industries.
- Introducing compulsory education.
- Improving standard of living.
- Improving Social, Economical and Political Conditions of weaker sections etc.
Synopsis
- Fundamental Rights are incorporated in Part – III from Articles 12 to 35 of the Indian Constitution.
- Fundamental Rights are an important feature of the Indian Constitution.
- Fundamental Rights are not absolute. State may impose some restrictions on the Fundamental Rights of the Citizens during – the emergency.
- Fundamental Rights are comprehensive, integrative and detailed in nature.
- Fundamental Rights are protected by the judicial Organisations in the country.
- The Constitution of India guarantees six Fundamental Rights to the citizens of the Nation.
- Directive Principles of State Policy are enumerated in Part IV from Articles 36 to 51 of the Indian Constitution.
- Directive Principles are fundamental in the governance of the country.
- Directive Principles are positive in nature as they extend the jurisdiction of the governments at various levels in India.
- Directive Principles are of three types. They are i) Socialist principles, ii) Liberal-intellectual principles and iii) Gandhian principles.
→ ప్రాథమిక హక్కులు ప్రజాస్వామ్యాన్ని అర్థవంతంచేస్తాయి.
→ ప్రాథమిక హక్కులను రాజ్యాంగంలోని 3వ భాగంలో 12వ అధికరణం నుండి 35వ అధికరణం వరకు ప్రస్తావించారు.
→ రాజ్యాంగం రూపొందించినప్పుడు 7 ప్రాథమిక హక్కులుండేది. ఇప్పుడు 6 ప్రాథమిక హక్కులు మాత్రమే కలవు.
→ 44వ రాజ్యాంగ సవరణ ద్వారా ఆస్తి హక్కును ప్రాథమిక హక్కుల జాబితా నుండి తొలగించి చట్టబద్ధమైన హక్కులుగా రూపొందించారు. 300 (ఎ) అధికరణం ఆస్తి హక్కుకు సంబంధించినది.
→ ప్రాథమిక హక్కులలోని రాజ్యాంగ పరిహార హక్కు అత్యంత విలువైనది. ఈ హక్కు ద్వారా పౌరులు తమ హక్కులకు భంగం వాటిల్లితే న్యాయస్థానాల ద్వారా రక్షణ పొందవచ్చు ఉన్నత న్యాయస్థానాలు రిట్లను జారీచేసి పౌరుల హక్కులను కాపాడతాయి.
→ 42వ రాజ్యాంగ సవరణ ద్వారా రాజ్యాంగానికి 10 ప్రాథమిక విధులు చేర్చబడ్డాయి.
→ ప్రాథమిక విధులను స్వరణ్ సింగ్ అధ్యక్షతన ఏర్పడిన ఒక సంఘం సూచించింది.
→ ప్రాథమిక విధులను న్యాయస్థానాల ద్వారా అమలు చేయడానికి వీలులేదు.
→ 19వ అధికరణం ప్రకారం పౌరులకు ఆరు రకాల స్వాతంత్ర్యాలు ఉంటాయి.
![]()
→ డాక్టర్ అంబేద్కర్ రాజ్యాంగ పరిహార హక్కును “ప్రాథమిక హక్కులకు ఆత్మవంటి” దని వర్ణించాడు.
→ భారత రాజ్యాంగం 42వ భాగంలో ఆదేశిక సూత్రాలను పేర్కొనడం జరిగింది.
→ భారతదేశాన్ని ఒక సంక్షేమ రాజ్యంగాను, వర్గరహిత రాజ్యంగాను ఏర్పరచడమే ఈ నియమాల లక్ష్యం.
→ ఆదేశక సూత్రాలు రాజ్యకలాపాల పరిధిని విస్తృతం చేశాయి.
→ ఈ సూత్రాలు శాసనపరమైనవి కావు. వీటిని అమలు జరపడంలో ఆయా ప్రభుత్వాలకు విచక్షణాధికారాలు ఉన్నాయి.
→ వీటిని సామ్యవాద సూత్రాలు, గాంధేయవాద సూత్రాలు, ఉదారవాద సూత్రలుగా వర్గీకరించడం జరిగింది.
→ 42, 44వ రాజ్యాంగ సవరణ చట్టాల ద్వారా ఆదేశక సూత్రాలకు ప్రాథమిక హక్కుల కంటే ఎక్కువ ప్రాధాన్యము ఉందని తెలిసింది.