Students can go through AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Notes 12th Lesson Organic Compounds Containing C, H and O will help students in revising the entire concepts quickly.
AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Notes 12th Lesson Organic Compounds Containing C, H and O
→ Alcohols and Phenols are formed when a hydrogen atom in a hydrocarbon is replaced by – OH group.
→ The substitution of a hydrogen atom in a hydrocarbon by an alkoxy (or) aryloxy group results in the formation of ethers.
→ On the basis of no.of -OH groups present in alcohols and phenols they are classified into monohydric, dihydric (or) poly hydric compounds.
→ Compounds containing CSp3 : -OH bond are 1°, 2° and 3° – alcohols, allylic, benzylic alcohols.
→ Compounds containing CSp2 -OH bond are vinylic alcohol.
![]()
→ On the basis of attached alkyl group Ethers are classified into symmetrical and unsymmetrical Ethers.
→ Alcohols are prepared by the acid catalysed hydration, hydroboration, oxidation, reduction of carbonyl compounds, from Grignard reagents etc.
→ Phenols are prepared from halo arenes, Diazonium salts, Cumene etc.
→ Alcohols and Phenols are having high boiling points when compared to the hydrocarbons, ethers, haloalkanes and haloarenes of comparable molecular masses.
→ Phenols are more acidic than alcohols due to the resonance stabilisation of phenoxide ion.
→ Kolbe’s reaction: Phenol reacts with sodium hydroxide and followed by the reaction of Co2 in presence of H+ to form salicylicacid.
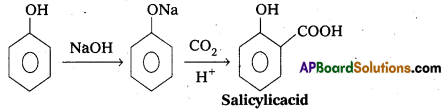
→ Reimer-Tiemann reaction: Phenol reacts with chloroform in presence of base to form salicylaldehyde.
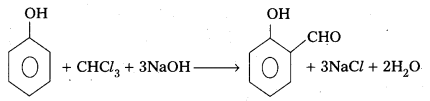
→ Ethers are prepared by the dehydration of alcohols, Williamson’s synthesis.
→ Williamson’s synthesis : When alkyl halide reacts with sodium alkoxide to form Ether.
R – X + R’ – ONa → R – O – R’ + NaX