Andhra Pradesh BIEAP AP Inter 2nd Year Botany Study Material 6th Lesson Plant Growth and Development Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP Inter 2nd Year Botany Study Material 6th Lesson Plant Growth and Development
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define plasticity. Give an example.
Answer:
Ability of plants to follow different pathways in response to the environment or phases of life to form different kinds of structures in called plasticity.
Ex : Heterophily.
Question 2.
What is the disease that formed the basis for the identification of gibberellins in plants? Name the causative fungus of the disease.
Answer:
Bakane (foolish seedling) disease in rice seedlings. It is caused by a fungal pathogen Gibberella fujikuroi.
Question 3.
What is apical dominance? Name the growth hormone that causes it.
Answer:
Growing Apical bud inhibits, the growth of Axillary buds is called Apical dominance. It is caused by Auxins.
Question 4.
What is meant by bolting ? Which hormone causes bolting?
Answer:
Sudden elongation of internodes prior to flowering is called bolting. It is caused by Gibberellins.
Question 5.
Define respiratory climactic. Name the PGR associated with it.
Answer:
The rise in the rate of respiration during the ripening of fruits is known as respiratory climatic. It is associated by ethylene.
![]()
Question 6.
What is Ethephon? Write its role in agricultural practices.
Answer:
It is an Ethylene releasing chemical formulation. It hastens fruit ripening in tomatoes and apples and accelerates abscission in flowers and fruits. It promotes female flowers in cucumbers, there by increasing the yield.
Question 7.
Which of the PGRs is called stress hormone and why?
Answer:
ABC [Abscisic acid] is called stress hormone. ABA stimulates the closure of stomata in the epidermis and increases the tolerance of plants to various kinds of stresses.
Question 8.
What do you understand by vernalisation?
Answer:
The method of inducing flowering quantitatively or qualitatively on exposure to low temperature is called vernalisation. It prevents precocious reproductive development late in the growing season, and enables the plant to have sufficient time to reach maturity. It specially refers to the promotion of flowering. It also stimulates a subsequent photoperiodic flowering response in biennials, [cabbage, carrot]
![]()
Question 9.
Define the terms quiescence and dormancy.
Answer:
The condition of a seed when it is unable to germinate only because favourable external condition normally required for growth are not present is called quiescence.
The condition of a seed when it fails to germinate because of internal conditions even though external conditions are suitable is called dormancy.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write a note on agricultural / horticultural applications of auxins.
Answer:
- IBA, NAA and IAA help to initiate rooting in stem cuttings, widely used for plant propagation in horticulture.
- Auxins like 2,4-D, 2,4,§-T acts as herbicides and kills broad leaved dicot weeds to prepare weed – free lawns.
- Auxins stimulates fruit growth. Ex : Tomatoes.
- Auxins induces flowering in pineapple.
- Prevents pre harvest fruit drop.
Question 2.
Write the physiological responses of Gibberellins in plants.
Answer:
- Gibberellins delay senescence. Thus fruits can be left on the tree longer so as to extend the market period. .
- Spraying of Gibberellins on sugarcane crop, increases the length of the stem, thus increasing the yield as much as 20 tonns per acre.
- GA hastens the maturity period of conifers thus leading to early seed production.
- GA also promotes bolting in cabbages, beet etc.,
- They also produce parthenocarpic fruits in grapes and tomato.
- Gibberellins favour the formation of male flowers in cucurbita.
Question 3.
Write any four physiological effects of cytokinins in plants.
Answer:
- Cytokinins induces cell division.
- They help to produce new leaves, chloroplasts in leaves, lateral shoot growth and adventitious shoot formation.
- Cytokinins help to overcome apical dominance.
- They promote nutrient mobilisation which helps in the delay of senescence.
- Cytokinins help in the opening of stomata by increasing the concentration of k+ ions in guard cells.
Question 4.
What are the physiological prodesses that are regulated by ethylene in plants?
Answer:
- Ethylene promotes the ripening of fruits.
- Ethylene promotes the senescence and abscission of leaves and flowers.
- Ethylene breaks seed and bud dormancy, initiates germination in peanut seeds and sprouting of potato tubers.
- Ethylene promotes rapid intemode/petiole elongation in deep water rice plants.
- It also promotes root growth and root hair formation, thus helping plants to increase their absorption surface.
- Ethylene is used to initiate flowering (mango) and for synchronising fruit set in pineapples.
- It promotes female flowers in cucumbers, thereby increasing the yield.
![]()
Question 5.
Write short notes on seed dormancy.
Answer:
The inability of seed to germinate or grow is called dormancy. It may be due to either external factors or internal factors.
Internal factors:
1) Immature embryo :
The embryo has not reached morphological maturity to germinate.
Ex : Ranunculus.
2) Hard seed coat:
In fabacea members, seeds have hard seed coats which prevent uptake of oxygen or water. It can be broken by scarification in which the hard seed coat is ruptured or weakened.
3) Chemicals :
Seeds of some plants (tomato) contain chemical compounds which inhibit their germination.
External factors:
1) Low temperature treatment :
Many seeds (polygonum) with not germinate until they have been exposed to low temperatures in moist conditions in the presence of oxygen for weeks to months. The practice of layering the seeds during winter in moist sand and peat is called stratification or prechilling.
2) Seeds of many domestic plants may be limited only by lack of moisture or warm temperature.
Question 6.
Which one of the plant growth regulators would you use if you are asked to.
a) Induce rooting in a twig
Answer:
Auxins
b) Quickly ripen a fruit
Answer:
Ethylene
c) Delay leaf senescence
Answer:
Cytokinins
d) Induce growth in axillary buds
Answer:
Cytokinins
e) ‘Bolt’ a rosette plant
Answer:
Gibberellins
f) Induce immediate stomatal closure in leaves
Answer:
Abscisic acid
g) Overcome apical dominance
Answer:
Cytokinins
h) Kill dicotyledonous weeds
Answer:
Auxins – 2, 4 – D
Question 7.
Describe briefly, a) Sigmoid growth curve, b) Absolute and relative growth rates.
Answer:
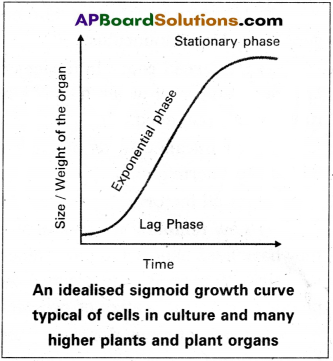
a) Sigmoid Growth Curve : It consists of 3 phases namely
1) lag phase
2) log pase
3) stationary phase.
1) Lag phase :
Growth is slow
2) Log phase :
Growth increases rapidly at an exponential rate
3) Stationary phase :
Limited nutrient supply, slows down the growth leading to a stationary phase. If we plot the parameter of growth against time, we get a typical sigmoid or S-curve.
b) Absolute and relative growth rates :
Measurement and comparision of the total growth per unit time is called absolute growth rate. The growth of the given system per unit time expressed on a common basis, e.g., per unit initial parameter is called relative growth rate.
Long Answer Question
Question 1.
List five natural plant growth regulators. Write a note on discovery, physiological functions and agricultural / horticultural applications of any one of them.
Answer:
Auxins, Gibberellins, Cytokinins, Abscisic acid, Ethylene
Auxins:
Discovery :
Observation of Charles Darwin and his son Francis Darwin, that the coleoptiles of canary grass responded to unilateral illumination by growing towards the light. It was concluded that the tip of the coleoptile was the site of transmittable influence that caused the bending of the entire coleoptile. Auxin was isolated by F.W. Went from the tips of coleoptiles of oat seedlings.
Physiological functions :
- Auxins help of initiate rooting in stem cuttings.
- Auxins promote flowering in pineapples.
- They help to prevent fruit and leaf drop at early stages but promote the abscission of older mature leaves and fruits.
- Auxins promote apical dominance.
- Auxins also induce parthenocarpy in tomatoes.
- They are widely used as herbicides 2,4-D widely used to kill dicotyledonous weeds.
- Auxins also controls zylem differentiation and help in cell division.
Agricultural / Horticultural applications ;
- Auxins help to initiate rooting in stem cuttings, widely used for plant propagation in Horticulture.
- Auxins, 2, 4-D widely used as herbicide ie, kills dicotyledonous weeds to prepare a weed free-lawns.
Intext Questions
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks with appropriate word/words.
a) The phase in which growth is most rapid is ………… .
b) Apical dominance as expressed in dicotyledonous plants is due to the presence of more ………… in the apical bud than in the lateral ones.
c) In addition to ouxin, a …………. must be supplied to the culture medium to obtain a good callus in plant tissue culture.
d) ………….. of vegetative plants are the sites of photoperiodic perception.
Answer:
a) LOg phase or exponential phase
b) Auxins
c) Cytokinin
d)Shootapices of plants
![]()
Question 2.
Gibberellins promote the formation of Male flowers on genetically Modified (dwarf) plants in cannabis whereas Ethylene promotes formation of Female flowers on genetically Modified (dwarf) plants.
Question 3.
Classify the following plants into long day plants(LDP), short day plants(SDP) and Day Neutral plants(DNP). Xanthium, Spinach, Henbane (Hyoscyamus), Rice, Strawberry, Bryophyllum, niger, Sunflower, Tomato, Maize.
Answer:
Long day plants – Henbane, Spinach,
Short day plants – Xanthium, Sunflower, Rice, Tomato
Day nutral plants : Maize, Bryophyllum
Question 4.
A farmer grows cucumber plants in his field. He wants to increase the number of female flowers. Which plant growth regulator can be applied to achieve this?
Answer:
Ethyline.
Question 5.
Where are the following hormones synthesized in plants?
a) IAA b) Gibberellins c) Cytokinins.
Answer:
a) IAA – growing apices of the stems and roots.
b) Gibberellins : Fungal pathogen, Gibberella fujikuroi.
c) Cytokinins – roots apices, shoot…, young fruits.
Question 6.
Light plays an important role in the life of all organisms. Name any three physiological processes in plants which are influenced by light.
Answer:
Growth, differentiation and development.
Question 7.
Growth is one of the characteristics of all living organisms. Do unicellular organisms also grow? If so, what all the parameters?
Answer:
Yes, unicellar organisms also grow, some parameters are increase in fresh weight, length, area, volume and cell number.
Question 8.
Rice seedlings infected with fungus Gibberella fujikuroi are called Foolish seedlings. What is the reason?
Answer:
The fungus cause foolish seeding disease in rice which show, plant grow. Very tall, become pale, produce less tillers and less yield.
Question 9.
Why isn’t any one parameter good enough to demonstrate growth throughout the life of a flowing plant?
Answer:
One parameter is not good enough to demonstrate growth because various parts show growth… is estimated in different parameters Eg: Growth of the pollentube is measured interms of the length, increase in surface are dexoles growth in a dorsiventral leaf.
Question 10.
‘Both growth and differentiation in higher plants are open’ Comment.
Answer:
Both growth and diffentitation in higher plants are open because, cells/tissues arising out of the same meristem have different structures of maturity and their location. Eg. : Cells away from root apical meristem differentiate as root cap cells, while those pushed to the periphery nature as epidermis.
Question 11.
Both a short day plant and a long day plant can produce flowers simutaeneously in a given place’. Explain.
Answer:
5 me plants require the exposure to light for a period exceeding critical duration and some require a light for a period less than critical duration for flowing.
Question 12.
Would a defoliated plant respond to photoperiodic cycle? Why?
Answer:
No, because some hormonal substance migraterwom leaver to shoot apices for induce flowing.
![]()
Question 13.
What would be expected to happen if
a) GAj is applied to rice seedlings.
b) Dividing cells stop differentiating.
c) A rotten fruit gets mixed with unripe fruits.
d) You forget to add cytokinnin to culture medium.
Answer:
a) Appearance of disease symptoms (Bakane disease) in uninfected rice seedings.
b) Growth of the plant body in stopped.
c) Unripe fruits became ripened due to ethylene.
d) Initiation of heafy shoots is inhibited.