Students must practice these AP Inter 2nd Year Accountancy Important Questions 2nd Lesson Depreciation to boost their exam preparation.
AP Inter 2nd Year Accountancy Important Questions 2nd Lesson Depreciation
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is depreciation?
Answer:
Depreciation is the permanent and gradual decrease in the value of a fixed asset every year.
(OR)
“Depreciation is the permanent and continuing diminution in the quality, quantity or the value of an Asset”. – Pickles
![]()
Question 2.
What are the causes of depreciation ? [May ’22; Mar. ’20,’19,’17 (AP)]
Answer:
The main causes of depreciation are
- Wear and Tear
- Physical Forces
- Obsolescence
- Depletion
- Passage of time (or) Expiration of Legal Rights
- Accidents
Question 3.
What is obsolescence ?
Answer:
Some assets become obsolescence or obsolete or out dated when new models enter into the market with latest technology. So old assets are replaced by new and modern assets with good facilities. Thus old assets losses its value, which is called deprecia¬tion due to obsolescence.
Question 4.
What is depletion?
Answer:
Some assets may be exhausted with the extraction of raw-materials out of ores. Hence they depreciate due to depletion. Ex: Mines, Quarries, Oil wells etc.
Question 5.
Write different methods of providing depreciation.
Answer:
There are several methods of providing depreciation. The following are the important methods of providing depreciation.
- Straight Line Method
- Reducing Balance Method
- Annuity Method
- Depreciation Fund Method
- Insurance Policy Method
- Revaluation Method
- Depletion Method
- Machine Hour Rate Method
Question 6.
What is Straight Line Method?
Answer:
Under this method, depreciation is calculated at a fixed percentage on original value of the asset in every year. Thus the amount of annual depreciation is uniform in every year. This method is also called as Fixed instalment method or Equal instalment method or Original cost method.
Question 7.
What is Reducing Balance Method? [May ’17 (AP)]
Answer:
Under this method depreciation is charged at a fixed percentage on the book value of the asset or value of asset at the beginning of that particular year. Value of asset is decreasing every year and depreciation calculated on reduced asset is decreasing. Hence it is known as “Reducing Balance Method” and also known as “Diminishing Balance Method” or “Written Down Value Method”.
![]()
Question 8.
What is the formulae for calculating Annual depreciation and Rate of depreciation? [Mar ’18 (AP)]
Answer:

∴ Note: Cost of the Asset includes, Purchase price + Carriage + Installation charges.
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define depreciation. What are the main causes of depreciation ? [Mar ’17 (AP)]
A. Definition:
Pickles, “Depreciation is the permanent and continuing diminution in the quality, quantity or the value of an asset”.
R.N. Carter, “Depreciation is the gradual and permanent decrease in the value of an asset from any cause”.
Causes of depreciation: The main causes of depreciation are
a) Wear and Tear: When the fixed assets are put to use in the business operations for earning revenue, the value of asset may be decreased. It is said to be due to Wear and Tear.
b) Physical Forces: When the assets are exposed to the forces of nature like weather, winds, rains etc., the value of such assets may decrease even if they are not in use,
c) Obsolescence: Some assets became obsolete or outdated when new models enter into the market. So it is replaced by new and modern facilities with latest technol¬ogy. Thus the old assets looses it value.
d) Depletion: Some assets may be exhausted with the extraction of raw-materials out of them. Ex: Mines, Quarries, Oil wells etc. Hence they depreciate due to depletion.
e) Passage of time or Expiration of Legal Rights: Some assets may have a fixed life period. After the expiry of its time bound the assets may become useless. Ex: Patents, copy rights, leases etc.
f) Accidents: The assets may reduce in value because of the accident. It is a permanent loss. Ex: Fire, Earth Quake, Floods etc.
Question 2. Define depreciation. Explain the need of providing depreciation.
Answer:
Definition:
Pickles, “Depreciation is the permanent and continuing diminution in the quality, quantity or the value of an asset”.
R.N. Carter, “Depreciation is the gradual and permanent decrease in the value of an asset from any cause”.
Need for depreciation: The need for providing depreciation arises due to –
a) To ascertain true profit or loss: The true profit or loss can be ascertained only when depreciation is debited to the profit and loss account along with other revenue expenses, which is incurred for the purpose of earning revenue.
b) To present true and fair financial position: Balance sheet shows the true financial position of the firm. As such to prepare Balance Sheet assets must be shown at their correct values by deducting value of depreciation.
c) To have funds for replacement of assets: A portion of profits is set aside in the form of depreciation every year. This accumulated amount will be available for replacement of the discarded asset.
d) To ascertain the true cost of production: Depreciation is charged to ascertain the true cost of production.
e) To fulfill the legal requirements: In case of joint stock companies it is compulsory to provide depreciation on fixed assets.
Question 3.
Explain the meaning, merits and demerits of Straight Line Method.
Answer:
Under this method depreciation is calculated at a fixed percentage on original value of the asset in every year. It is uniform in every year, this method is also known as “Fixed Instalment Method” or “Original Cost Method”.
Merits:
- It is very easy to understand.
- It is very simple to calculate depreciation.
- Assets can be depreciated to the scrap value or zero value.
- The method is suitable for estimated life period of assets.
- Depreciation is uniform throughout life.
Demerits:
- Depreciation will be remain same throughout the life of the asset. But in reality depreciation and repairs will be lesser in the earlier years and more in later years.
- It becomes difficult to ascertain depreciation for additions made.
- This method is not recognized by income-tax authorities.
- It is difficult to estimate the life of the asset accurately.
Question 4.
Explain the meaning, merits and demerits of Reducing Balance Method.
Answer:
Under this method depreciation is charged at a fixed percentage on the book value of the asset i.e., value of asset at the beginning in that year. Book value is reducing year by year by charging depreciation. This method is also known as “Diminishing Balance Method” or “Written Down Value Method”.
Merits:
- This method is logical i.e., Asset value decreases year by year and also depreciation goes on decreasing.
- Income Tax Act 1961 accept this method for tax purposes.
- This method is suitable for assets which have a longer life. .
- This method can be used where obsolescence rate is high.
Demerits:
- It is difficult to calculate the rate of depreciation.
- The book value of the asset does not become zero.
- It does not provide for the replacement of the asset on the expiry of its life.
![]()
Question 5.
What are the differences between Straight Line Method and Reducing Balance Method ?
Answer:
| Straight line method | Reducing Balance Method | |
| 1. Calculation | Depreciation is calculated on the original cost. | Depreciation is calculated on the value of asset in the year in which it is calculated. |
| 2. Amount of depreciation | The amount of depreciation is uniform throughout the life of the asset. | The amount depreciation is decreases year after year. |
| 3. Total charges against profit & loss a/c | Under this method depreciation plus repairs increases year after year. Because repairs increases. | Total depreciation and repairs expenses remain similar every year. |
| 4. Recognition by Income Tax Law | This method is not recognized by Income Tax. | This method is recognized by Income Tax Act. |
| 5. Suitability | This method is suitable for assets which have fixed life. | This method is suitable for assets which have no fixed life. |
Question 6.
What are the entries required for calculation of depreciation ?
Answer:
The following journal entries are required –
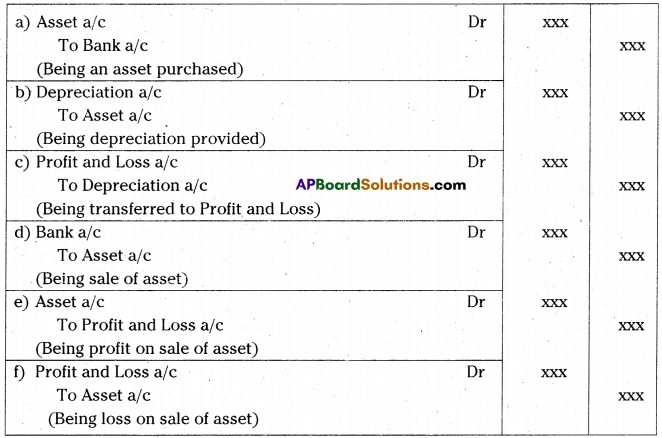
Exercise
Fixed Installment Method (or) Straight Line Method
Question 1.
Praveen traders purchased machine for Rs. 80,000. The life of the machine is estimated at 10 years and the residual value is Rs. 10,000. Calculate the annual amount of depreciation according to Straight Line Method. [Ans. Rs. 7,000]
Answer:
Original cost of the Machinery = Rs. 80,000
Estimated residual value = Rs. 10,000
Estimated useful life of the Machine = 10 years.

Amount of depreciation = Rs. 7000.
Question 2.
A machine is purchased for Rs. 40,000. It is estimated that the useful life of the machine is 9 years and residual value is Rs. 4,000. You are required to find out the annual amount of depreciation and the rate of depreciation under the Straight Line Method. [Ans. Rs. 4,000 and 10%]
Answer:
Original cost of the machine = Rs. 40,000
Estimated residual value = Rs. 4000
Estimated life of the machine = 9 years
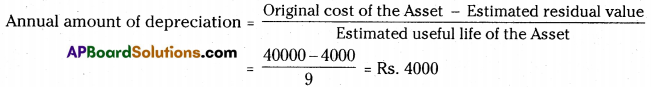
∴ Annual amount of depreciation = Rs. 4000.
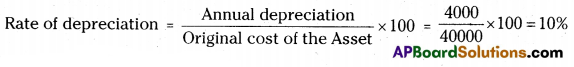
∴ Rate of depreciation = 10%
![]()
Question 3.
A truck is purchased for Rs. 50,000. It is estimated that the useful life of the truck is 10 years and residual value is Rs. 5,000. Calculate the annual amount of depreciation and the rate of depreciation under the Straight Line Method.[Ans. Rs. 4,500 and 9%]
Answer:
Original cost of the truck = Rs. 50,000
Estimated residual value = Rs. 5000
Estimated useful life period = 10 years
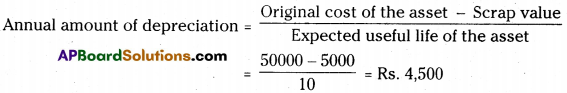
∴ Annual amount of depreciation = Rs. 4,500.

Rate of depreciation on truck = 9%
Question 4.
On 1st April 2010 Anand traders purchased a machine for Rs. 2,60,000 and spent Rs. 40,000 on its installation. It is estimated that working life is 10 years and after 10 years its scrap value will be Rs. 20,000. Books are closed on 31st March every year.
Write necessary journal entries and prepare machine account for the first three years in the books of Anand traders according to the Straight Line Method. [Ans. Balance Rs. 2,16,000]
Answer:
Original cost of the Machine = Rs. 2,60,000 + Rs. 40,000 = Rs. 3,00,000
Estimated scrap value of the machine = Rs. 20,000
Estimated useful life of the machine = 10 years
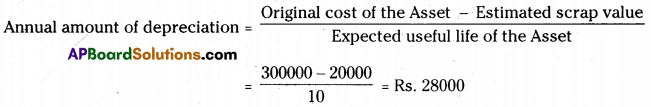
∴ Annual amount of depreciation = Rs. 28000.
Journal Entries in the books of Anand traders
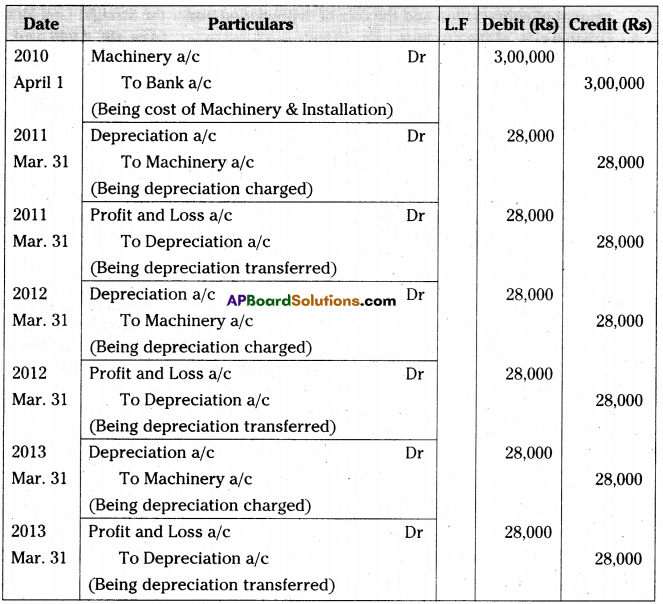
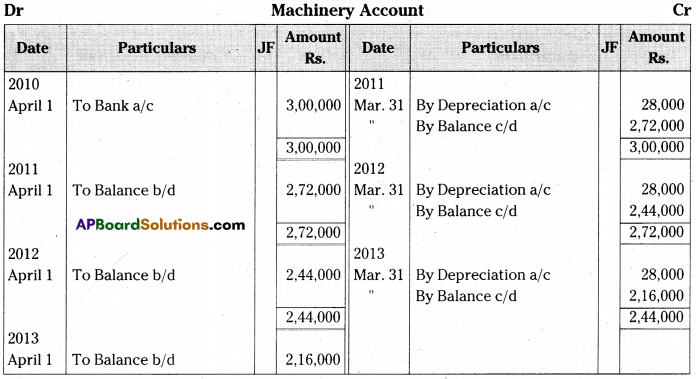
Question 5.
On 1st July 2011, Neeharika & Co purchased a printing machine for Rs. 2,16,000 and spent Rs. 24,000 on its installation. It was estimated that the effective useful life of the printing machine will be 12 years and its scrap value will be Rs. 24,000. The books are closed on 31st December every year.
Prepare printing machine account and depreciation account for first three years according to the Straight Line Method. [Ans. Balance Rs. 1,95,000]
Answer:
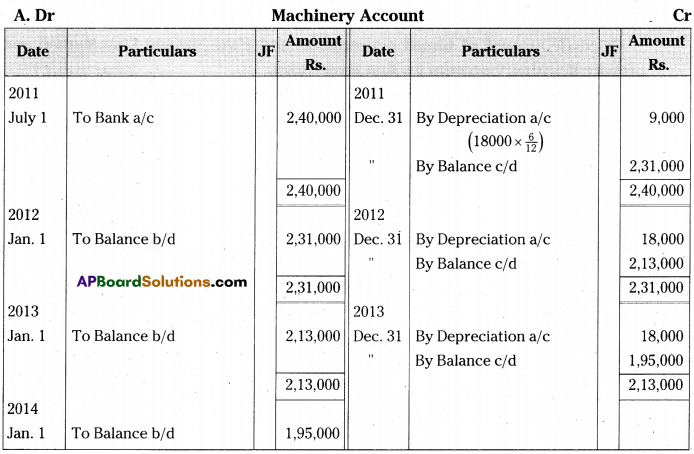
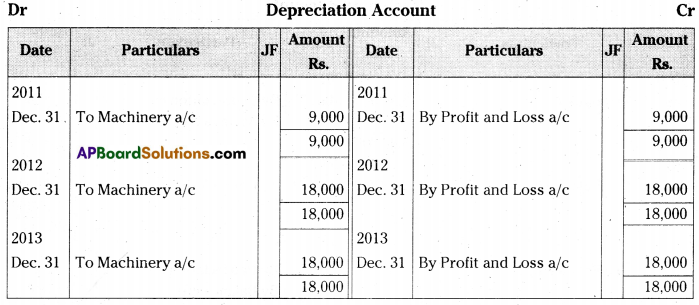
Note: Original value of Machinery = Rs. 2,16.000 + 24,000 = 2,40,000. Estimated residual value of Machinery = Rs. 2.40,000 Estimated useful life of the Machinery =12 years.
∴ Annual amount of depreciation =(2,40,000-24,000)/12
= Rs. 18,000.
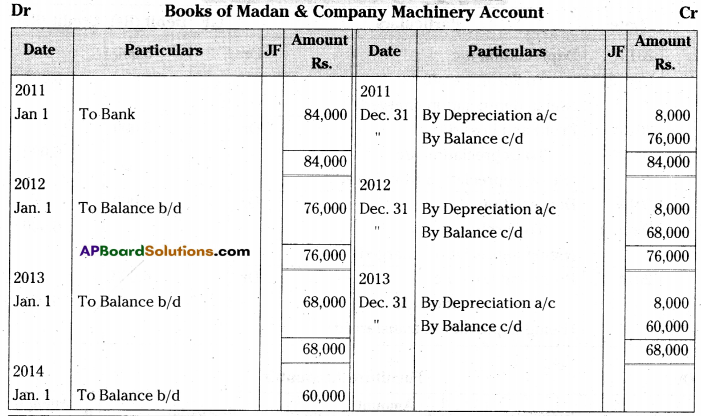
Question 6.
Madan & Company purchased machinery on 1st January 2011 for Rs. 80,000 and spent Rs. 4,000 for its installation. The estimated life of the machinery is 10 years with a scrap value of Rs. 4,000. Books are closed on 31st December every year.
Calculate amount of annual depreciation under the Straight Line Method and prepare machinery account for first three years.
[Ans. Annual Depreciation Rs. 8,000; Balance Rs. 60,000]
Answer:
Original cost of the Machinery = Rs. 80,000 + 4,000 = 84,000/-
Estimated scrap value of Machinery = Rs. 4,000
Estimated useful life of the Machinery =10 years.

∴ Annual amount of depreciation = Rs. 8,000.
Books of Madan & Company Machinery Account
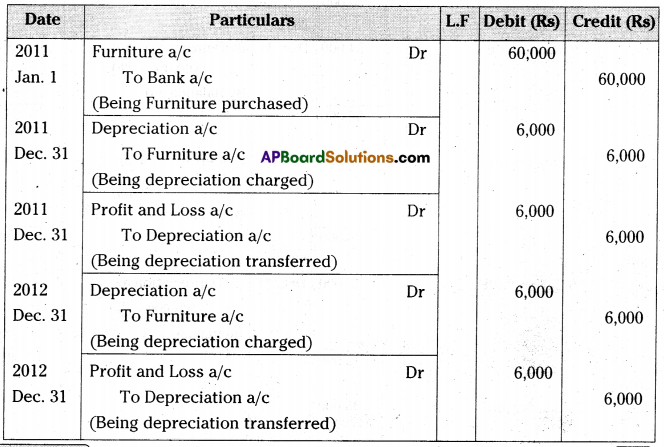
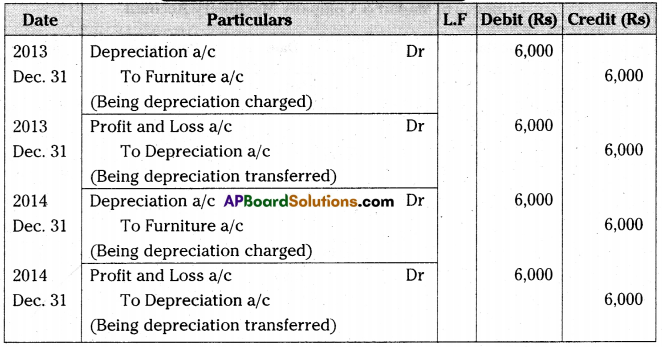
Question 7.
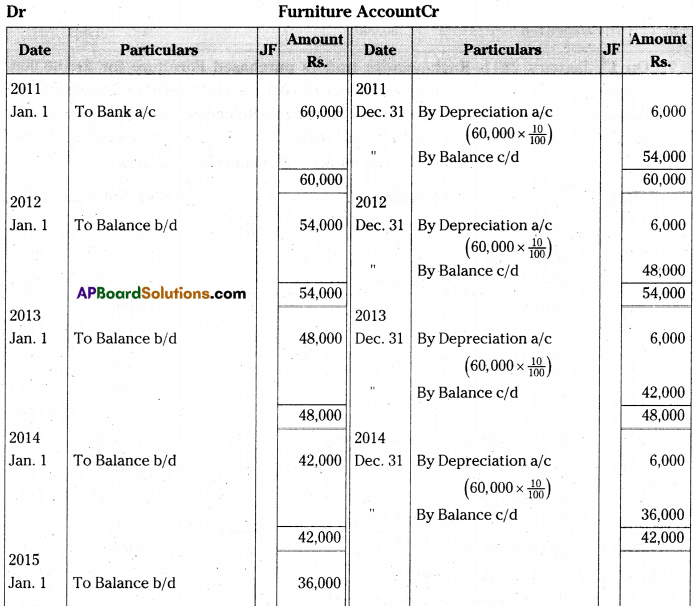
On 1st January 2011, Raghavendra traders purchased Furniture for Rs. 60,000. Depreciation is to be calculated at the rate of 10% p.a. on Straight Line Method. The books are closed on 31st December every year. Write necessary journal entries and prepare Furniture Account for first four years. [Ans. Balance Rs. 36,000]
Answer:
Journal Entries in the books of Raghavendra Traders
Question 8.
On 1st October 2011 Jagannadham & Sons purchased a machine for Rs. 90,000 and spent Rs. 10,000 for its installation. The books are closed on 31st March every year. The firm writes-off depreciation at the rate of 10% on original cost every year. Prepare Machine Account and Depreciation Account for first three years.
[Ans. Balance Rs. 75,000]
Answer:
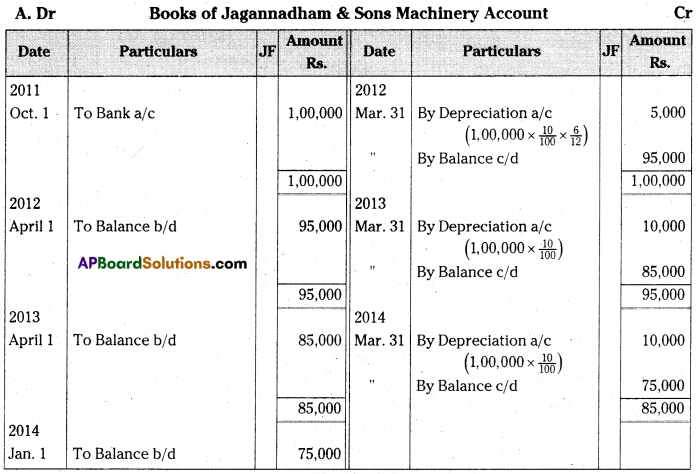
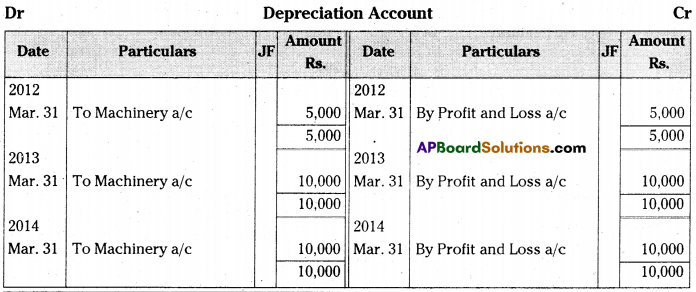
![]()
Question 9.
Venugopal traders limited purchased machinery on 1st July 2010 for Rs. 50,000 and spent Rs. 2,000 on its installation. Depreciation is to be provided @ 10% p.a. under Straight Line Method. Books of account are closed on 31st December every year.
Show the machinery account for the first three years. [Ans. Balance Rs. 39,000]
Answer:
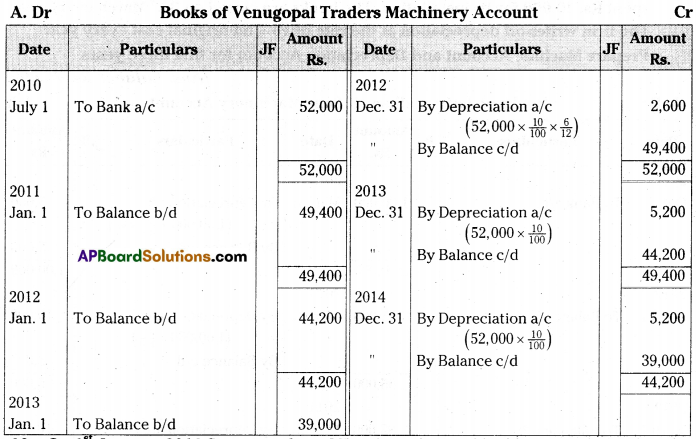
Question 10.
On 1st January 2011 Suma purchased Furniture for Rs. 80,000. Depreciation is to be provided annually at 10% under Straight Line Method. On 31st December 2013 furniture was sold for Rs. 40,000.
Show the Furniture Account assuming that the books are closed on 31st December every year. [Ans. Loss on sale of Furniture Rs. 16,000] [May 2022]
Answer:
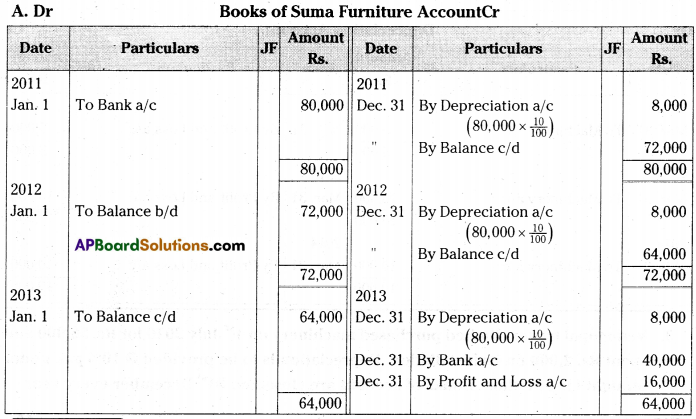
Question 11.
Suneetha traders purchased a second hand machine for Rs. 72,000 on 1st January 2011 and spent 8,000 on repairs and installed the same. Depreciation is written-off at 10% p.a. on the Straight Line Method. On 30th June 2013 the machine was sold for Rs. 50,000.Prepare machinery account assuming that the accounts are closed on 31st December every year. [Ans. Loss on sale of Machine Rs. 10,000] [Mar ’19, ’17 (AP)]
Answer:
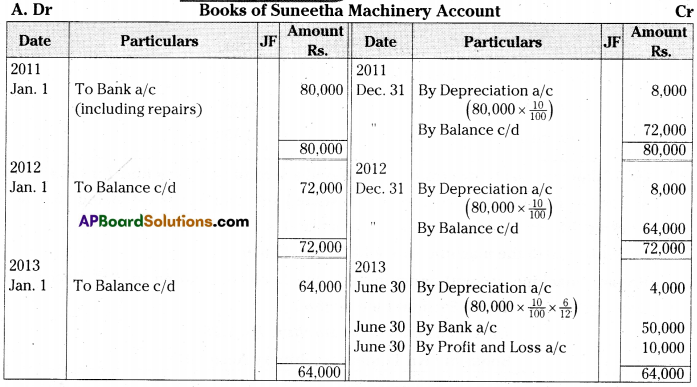
Question 12.
Ranadheer & Co purchased a machine for Rs. 60,000 on 1st January 2011. Deprecia¬tion is calculated @ 10% on Straight Line Method. On 1st April 2013 the company sold the machine for Rs. 36,000.
Prepare machine account assuming that the accounts are closed on 31st December every year. [Ans. Loss on sale of Machine Rs. 10,500] [Mar ’18 (AP)]
Answer:
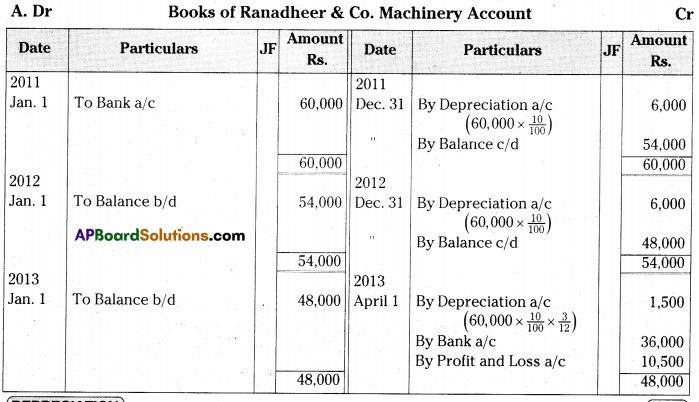
Notes: Calculation of profit or loss on the sale of machine.

Question 13.
On 1st January 2011, Siva traders purchased a second hand machine for Rs. 40,000 and spent Rs. 5,000 on repairs and installed the same. It is estimated that the working life of the machine is 10 years and scrap value is Rs. 2,500. On 31st December 2013 the machine was sold for Rs. 25,000.
Prepare machine account assuming that the books are closed on 31st December every year according to Straight Line Method.
[Ans. Loss on sale of Machine Rs. 7,250]
Answer:
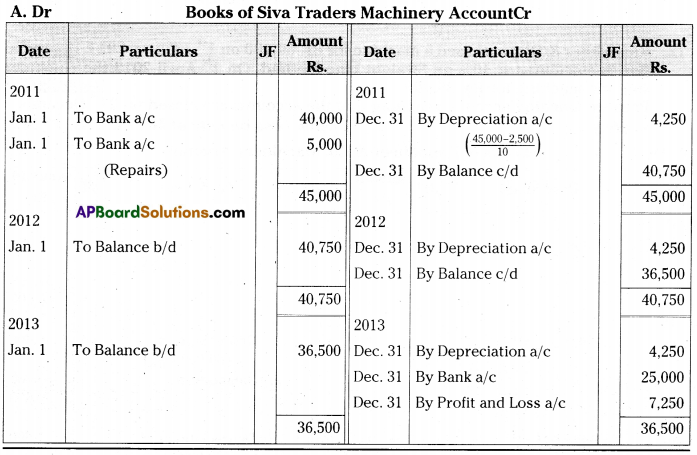
Question 14.
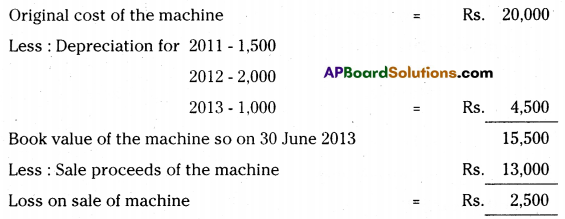
Manoj & Company purchased a second hand machine for Rs. 18,000 on 1st April 2011 and spent Rs. 2,000 on repairs and installed the same. Depreciation is written- off at 10% p.a. on Straight Line Method. On 30th June 2013 it was sold forRs. 13,000.
Prepare machine account assuming that the accounts are closed on 31st December every year. [Ans. Loss on sale of Machine Rs. 2,500]
Answer:
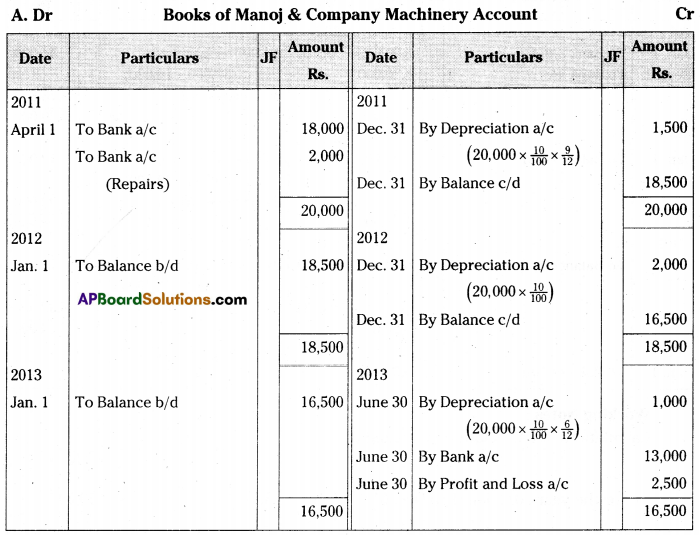
Notes: Calculation of profit or loss on the sale of machine.
Question 15.
Ramesh & Co purchased machinery on 1st January 2011 for Rs. 3,00,000. On 1st September 2011, another machine was purchased for Rs. 4,20,000. Depreciation is provided on machinery at 10% p.a. on Straight Line Method. Books are closed on 31st December every year. Prepare machinery account for three years. [Ans. Balance Rs. 5,32,000]
Answer:
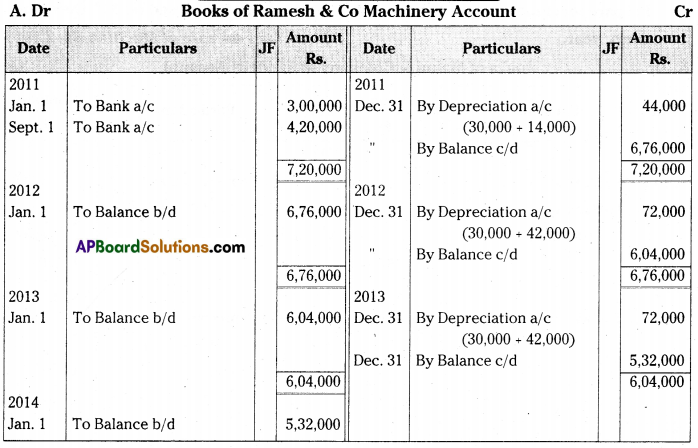
Working Notes:
Calculation of depreciation on Machines:
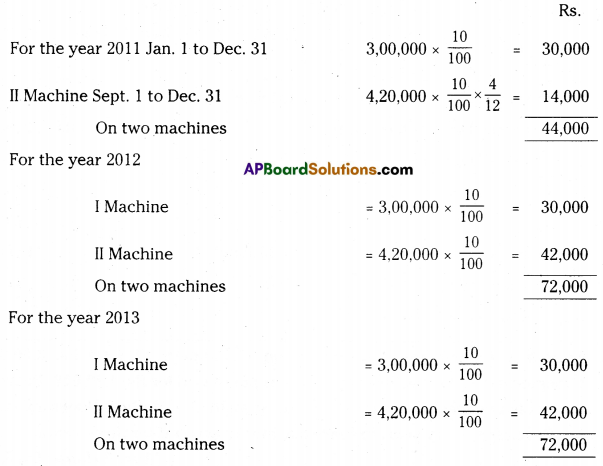
![]()
Question 16.
Andhra Sugars Ltd. purchased a plant for Rs. 1,00,000 on 1st January 2011. On 1st July in the same year additional plant was purchased for Rs. 50,000. On 1st October 2013 the plant purchased on 1st January 20 I 1 having become obsolete, was sold for Rs. 60,000. On the same date a fresh plant was purchased for Rs. 1,25,000. Depreciation is provided at 10% p.a. on Straight Line Method.
Prepare plant account for three years assuming that the accounts are closed on 31st December every year .[Ans. Loss on sale of plant Rs. 12,500; Balance Rs. 1,59,375]
Answer:
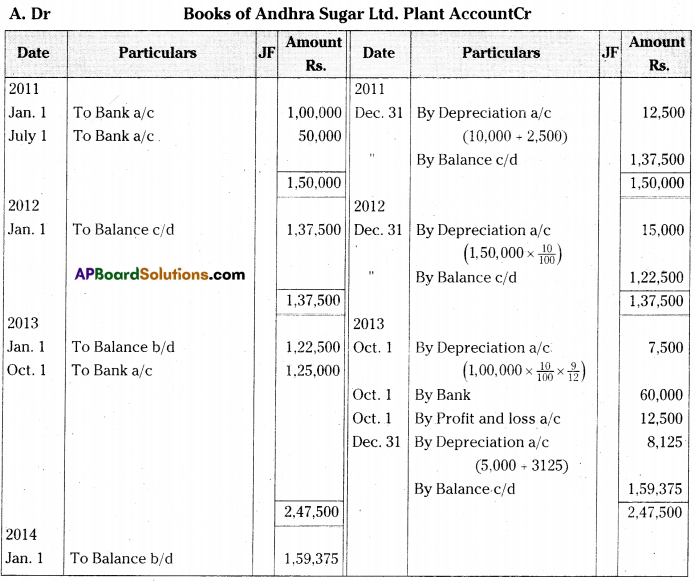
Working Notes:
Calculation of depreciation on Machines:

iii) CalcuIation profit and Loss on sale of I Machine:

Question 17.
On 1st July 2010 Ganga & Co purchased second hand machine for Rs. 40,000, and spent Rs. 6,000 on repairs. On 1st January 2011 a new machine was purchased for Rs. 24,000. On 30th June 2012 the machine purchased on 1st January 2011 was sold for Rs. 16,000 and another machine was installed at a cost of Rs. 30,000. The company writes-off depreciation @ 10% p.a. on original cost every year on 31st March.
Show the machinery account for three years.
[Ans. Loss on sale of machine Rs. 4,400; Balance Rs. 61,100]
Answer:
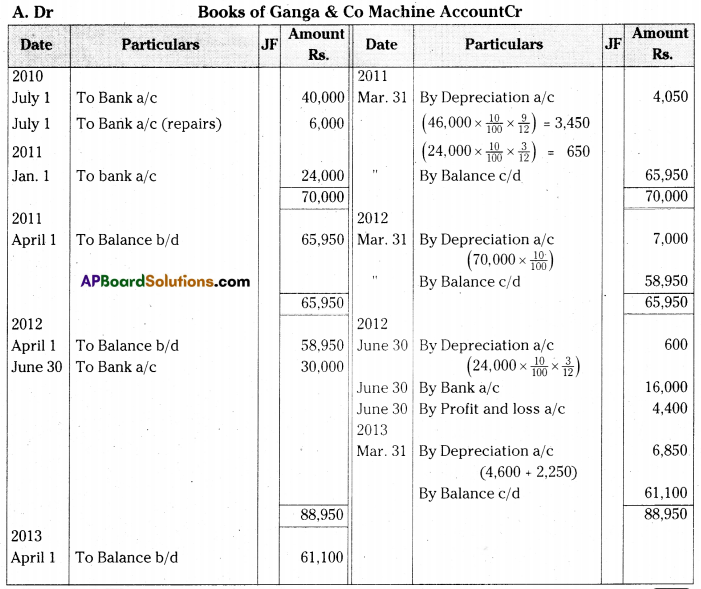
Working Notes:
Calculation of depreciation on Machines:
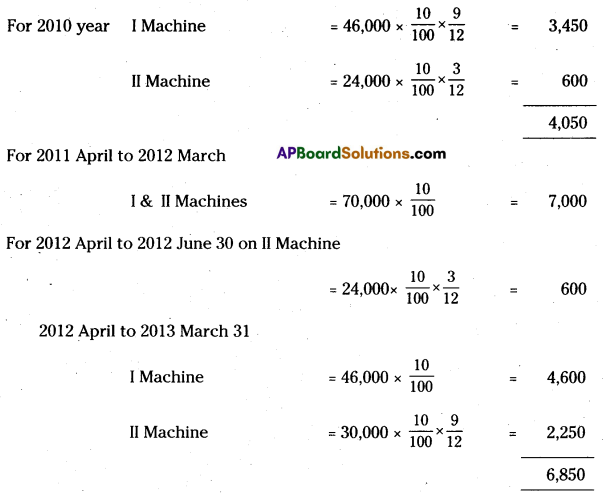

Question 18.
Rama transport company purchased 6 trucks at Rs. 5,00,000 each on 1st January 2011. The company writes-off depreciation @ 10% p.a. on original cost. The books of account are closed on 31st December every year. On 1st July 2013 on of the trucks is involved in an accident and completely destroyed. A sum of Rs. 2,50,000 is received from insurance company in full settlement. Prepare Trucks Account for first three years.
[Ans. Loss on truck destroyed Rs. 1,25,000; Balance Rs. 17,50,000]
Answer:
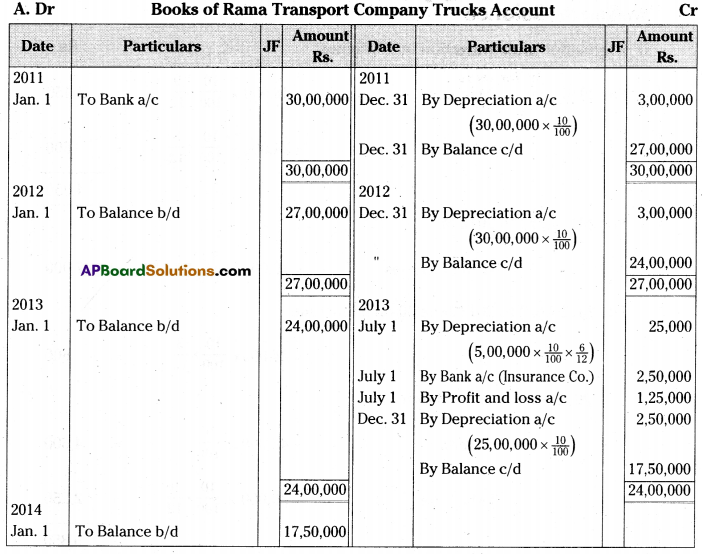
Working Notes:
Calculation of depreciation on Trucks:
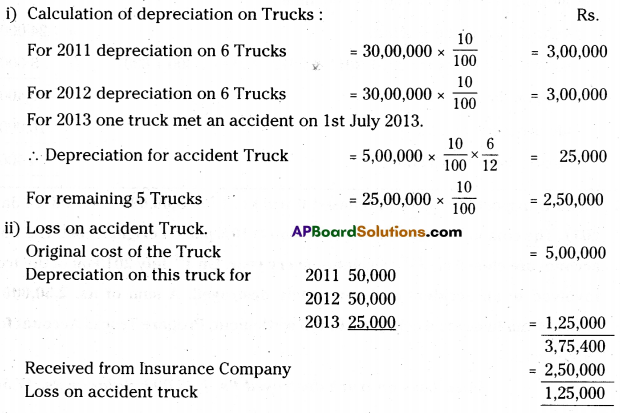
Reducing Balance Method
Question 19.
Kushal textile mills purchased machinery on 1st April 2011 for Rs. 4,00,000 and spent Rs. 20,000 for its installation. Depreciation is provided @10% p.a. on Reduc¬ing Balance Method Books are closed on 31st March every year.
Write necessary journal entries and prepare Machinery Account and Depreciation Account for first three years. [Ans. Balance Rs. 3,06,180]
Answer:
Journal Entries in the books of Kushal Textile Mills
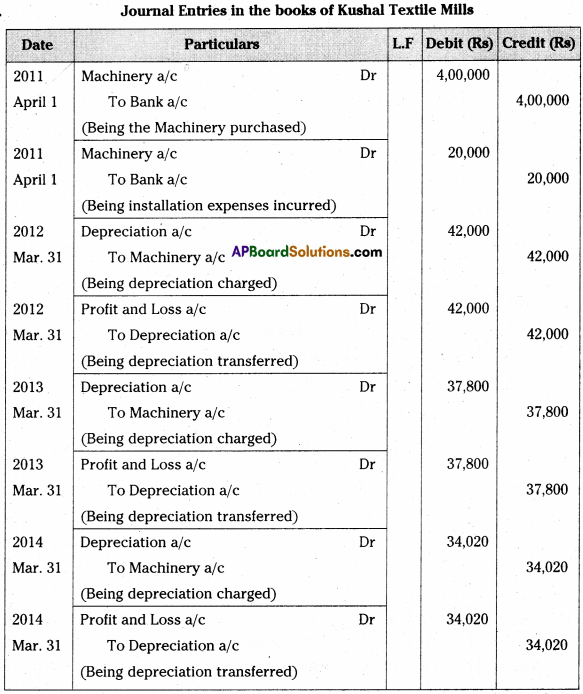
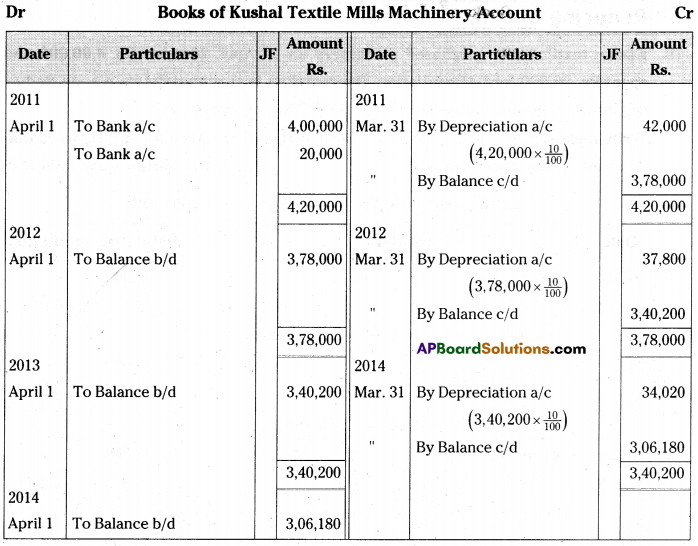
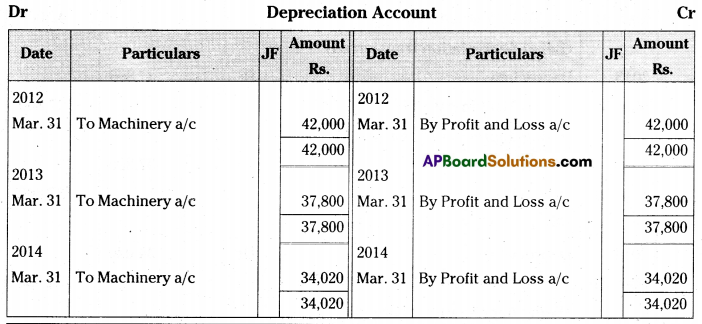
Question 20.
On 1st July 2010 Pradeep & Co purchased machinery for Rs. 50,000. Depreciation is written-off at the rate of 10% p.a. under Reducing Balance Method. Show the Machinery Account for 3 years assuming that the books are closed on 31st December every year. [Ans. Balance Rs. 38,475]
Answer:
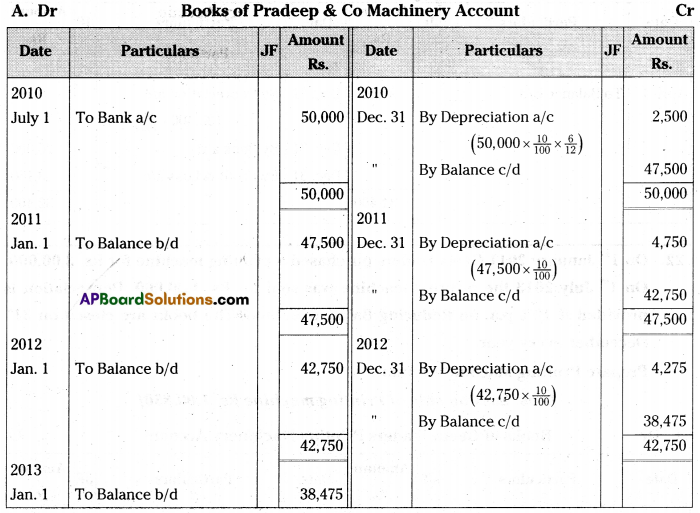
![]()
Question 21.
On 1st January 2012 Siva & Co purchased a second hand machinery for Rs. 34,000 and spent Rs. 6,000 on its repairs and installed the same. On 31st December 2014 the machinery was sold for Rs. 26,000. The books are closed on 31st December every year. Depreciation is provided @ 10% p.a. on Reducing Balance Method. Show the Machinery Account./Aris. Loss on sale of machinery Rs. 3,160]
Answer:
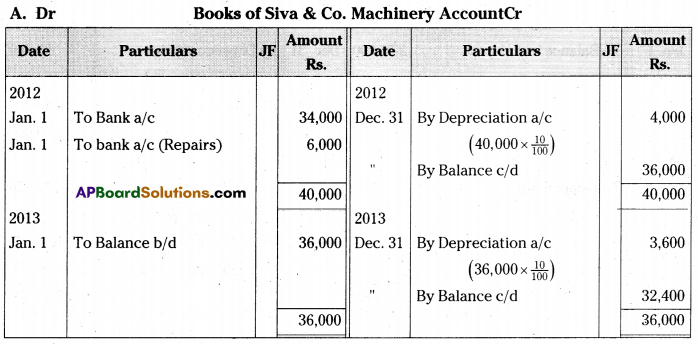
Question 22.
On 1st January 2011 Geeta traders purchased a printing machine for Rs. 3,00,000. On 1st July 2013 the printing machine was sold for Rs. 1,30,000. Depreciation is provided @10% p.a. on Reducing Balance Method. The books are closed on 31st December every year. –
Prepare Printing Machine Account.
[Ans. Loss on sale of Printing machine Rs. 1,00,850]
Answer:
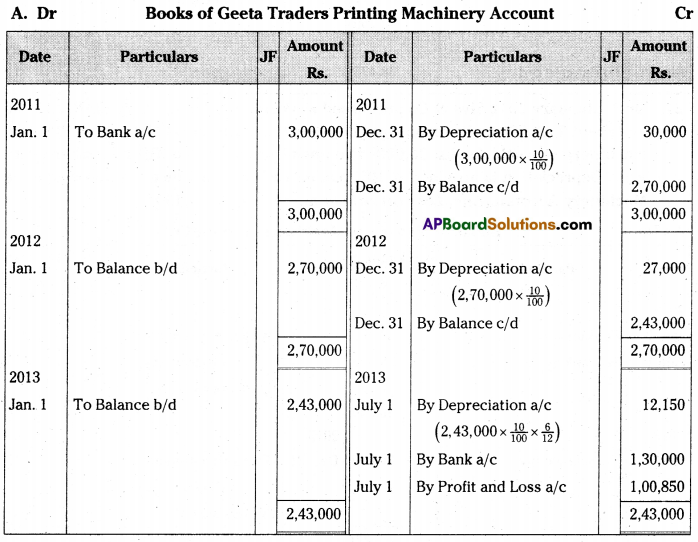
Question 23.
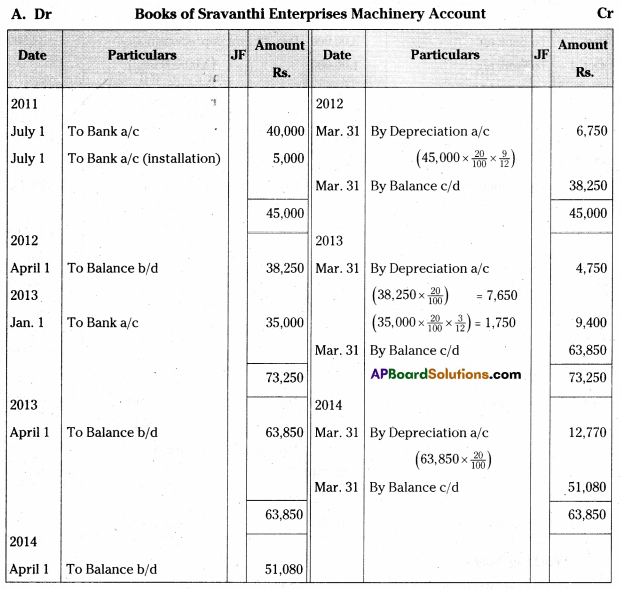
Sravanthi enterprises purchased a machine for Rs. 40,000 on 1st July 2011 and spent Rs. 5,000 on its installation. Another Machine for Rs. 35,000 was purchased on 1st January 2013. Depreciation is charged @ 20% p.a. on Reducing Balance Method. Books are closed on 31st March every year.
Prepare Machinery Account for three years. [Ans. Balance Rs. 51,080]
Answer:
Question 24.
On 1st January 2012 Swathi & Co purchased plants for Rs. 3,00,000. On 1st October 2012 another plant was purchased for Rs. 1,00,000. Depreciation is charged @10% p.a. on Reducing Balance Method. On 1st October 2013, the first plant was sold for Rs. 2,20,000.
Prepare plant account for three years assuming that the accounts are closed on 31st December every year.
[Ans. Loss on sale of plant Rs. 29,750; Balance Rs. 78,975]
Answer:
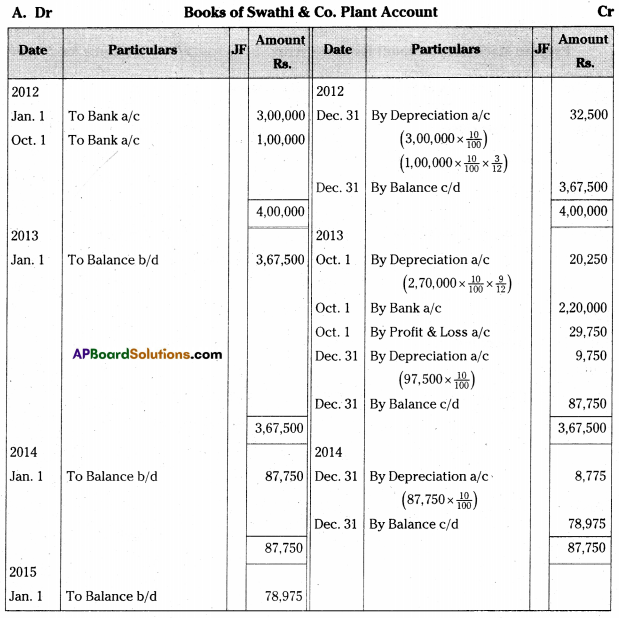
Working Notes:
i) Depreciation on plant from 1-1-2012 to 31-12-2012.

ii) Depreciation on 1st plant for 9 months.
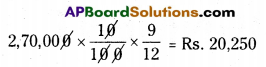
![]()
iii) Profit or loss on sale of 1st plant.

iv) Depreciation on 2nd plant from 1-1-13 to 31-12-13.
97,500 x 10/100 = 9,750/-
v) Depreciation on 2nd plant from 1-1-14 to 31-12-14.
87,750 x 10/100 = 8,775/-