Students get through AP Inter 1st Year Physics Important Questions 10th Lesson Mechanical Properties of Solids which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 1st Year Physics Important Questions 10th Lesson Mechanical Properties of Solids
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
State Hooke’s law of elasticity. [Imp.Q]
Answer:
Hooke’s Law Within the elastic limit, the stress is directly proportional to strain.
stress ∝ strain ⇒ stress = E (strain). Here E is called as modulus of elasticity.
Question 2.
State the units and dimensions of stress. [Imp.Q]
Answer:
Stress:
C.GS Unit : dyne cm-2
S.I Unit : N m-2 (or) pascal
Dimensional Formula : [ML-1T-2]
Question 3.
State the units and dimensions of modulus of elasticity. [Imp.Q]
Answer:
Modulus of elasticity :
C.GS Unit : dyne cm-2
S.I Unit : N m-2 (or) pascal
Dimensional formula: [ML-1T-2]
Question 4.
State the units and dimensions of Young’s modulus. [Imp.Q]
Answer:
Young’s modulus :
C.GS Unit : dyne cm-2
S.I Unit : N m-2 (or) pascal
Dimensional formula : [ML-1T-2]
Question 5.
State the units and dimensions of modulus of rigidity. [Imp.Q]
Answer:
Rigidity modulus :
C.GS Unit : dyne cm-2
S.I Unit : N m-2 (or) pascal
Dimensional formula : [ML-1T-2]
![]()
Question 6.
State the untis and dimensions of Bulk modulus. [Imp.Q]
Answer:
Bulk modulus :
C.GS Unit : dyne cm-2
S.I Unit : N m-2 (or) pascal
Dimensional formula : [ML-1T-2]
Question 7.
State the examples of nearly perfect elastic and plastic bodies. [Imp.Q]
Answer:
The nearest approach to a perfectly elastic body is a “quartz fiber”.
Examples of nearly perfect plastic bodies are clay and Dough.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define Hooke’s Law of elasticity, proportionality limit, permanent set and Breaking stress. [Imp.Q]
Answer:
Hooke’s Law :
Within the elastic limit, the stress is directly proportional to the strain.
Thus, stress ∝ strain ⇒ stress = E (strain)
Proportionality limit :
The maximum stress on the wire, upto which stress is propotional to strain, and Hooke’s law is obeyed, is called “Proportionality limit”.
Permanent set :
The permanent deformation that is produced in the wire, when it is stretched beyond elastic limit, is called “Permanent set”.
Breaking stress :
The stress, for which the wire breaks, is called “Breaking stress”.
Question 2.
Define modulus of elasticity, stress, strain and Poisson’s ratio. [Imp.Q]
Answer:
Modulus of elasticity (E) :
Within the elastic limit, the ratio of stress and strain is called “Modulus of elasticity”.
Stress :
It is defined as the restoring force developed in the body per unit area.
![]()
Strain :
The ratio of change in the dimension of a body to the original dimension is called strain.
![]()
Poisson’s ratio (σ):
The ratio of lateral strain to the longitudinal strain of a body is called “poisson’s ratio”.
![]()
![]()
Question 3.
Define Young’s modulus, Bulk modulus and Shear Modulus. [Imp.Q]
Answer:
Young’s modulus (Y) :
With in the elastic limit, Young’s modulus is the ratio of longitudinal stress to the longitudinal strain.

Bulk modulus (K) :
With in the elastic limit, Bulk modulus is the ratio of volume stress to volume strain.

Shear Modulus (Rigidity modulus (η) :
With in the elastic limit, Rigidity modulus is the ratio of Tangential stress to she Shear strain
![]()
Question 4.
Define Stress and mention the types of Stress.
Answer:
Stress :
Stress is defined as the restoring force developed in the body per unit area
1) Longitudinal stress or Tensile stress :
The stress produced with in the body, when its length is changed by applying force normal to the surface of a body is Longitudinal stress.
2) Bulk stress (or) Volume stress :
The stress produced with in the body, when its volume is changed by applying force normally and uniformly all over its surfaces is called Bulk stress.
3) Shear stress (or) Tangential stress :
The stress produced with in the body, when its shape is changed by applying tangential force on its surface is called Shear stress.
Question 5.
Define strain and explain the types of strain. [AP 22; TS 16]
Answer:
Strain :
The ratio of change in the dimension of a body to the original dimension is called strain.
![]()
Different types of strain :
i) Longitudinal strain :
The ratio of the change in length of a body to the original length of the body is called longitudinal strain.
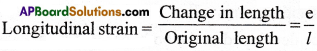
ii) Volume strain :
The ratio of the change in volume of a body to the original volume of the body is called longitudinal strain.
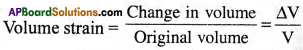
iii) Shearing strain :
Shearing strain is the ratio of the displacement of a layer to its distance from the fixed layer.
Shearing strain θ = \(\frac{x}{l}\)
Question 6.
Define strain energy and derive the equation for the same. [TS 18, 19, 19]
Answer:
Strain energy :
The energy stored in a body due to its deformation is called ‘strain energy’.
Expression for strain energy :
Consider a thin uniform wire of length / and area of cross-section A fixed at one end. Let ‘F’ be the force acting on the free end of a wire.
Work done to produce a small extension ‘de’ is dW= F de
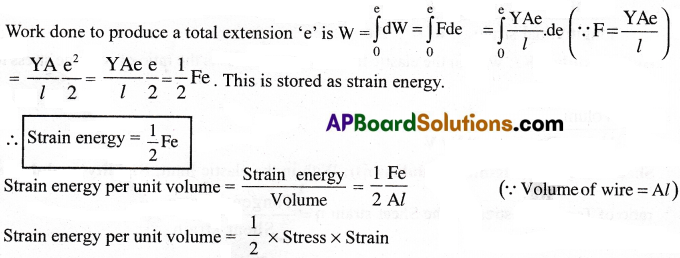
Question 7.
Explain why steel is preferred to copper, brass, aluminium in heavy-duty machines and in structural designs.
Answer:
A large force is required for steel as compared with copper, brass and aluminium wires having the same cross-sectional area to produce the same strain. It means that steel is more elastic than copper, brass and aluminium. Hence steel is preffered in heavy-duty designs.
Question 8.
Describe the behaviour of a wire under gradually increasing load. [Imp.Q][TS 20, 22; AP. TS 15, 16, 17, 18, 20]
Answer:
Consider a wire suspended from a rigid support and loaded at the other end.
Suppose the load is increased gradually until it breaks.
A graph is plotted between strain on the X-axis and the stress on the Y-axis.
The nature of graph is shown here.
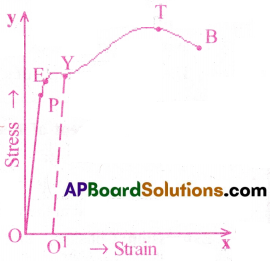
Behaviour of a wire under increasing load:
1) Proportionality limit(OP) :
The part OP is a straight line which shows that stress is proportional to strain.The wire obeys Hooke’s law upto the point P. So P is called the proportionality limit of the wire.
2) Elastic limit (PE) :
Beyond P upto E, the graph is slightly curved. When the load is removed, the wire will regain its natural length. Upto E, the wire can be deformed elastically.
3) Yielding point(Y) :
Beyond elastic limit, when the load is removed at the point Y, the wire does not regain its natural length completely. It will have a permanent increase in length. In the region EY the wire shows plastic behaviour.
4) Tensile Point(T) :
Beyond the point Y, the strain increases rapidly without any increase in the load. Even if the load is not removed, the strain increases continuously till the wire reaches the point T. The stress corresponding to T is called the tensile strength of the given material.
5) Breaking Point(B) :
Beyond the point T, the wire shows necks at few points along the length of the wire. Consequently, the wire breaks at B. This point B is called ‘breaking point’.
![]()
Question 9.
Two identical solid balls, one of ivory and the other of wet clay are dropped from the same height onto the floor. Which one will rise to a greater height after striking the floor and why?
Answer:
Ivory is more elastic than wet clay. So ivory ball shall rise to a great height as compared to a clay ball. Infact, the ball of wet clay may not rise at all.
Question 10.
While constructing buildings and bridges a pillar with distributed ends is preferred to a pillar with rounded ends. Why?
Answer:
A pillar with rounded ends supports less load than that with a distributed shape at the ends. Hence pillar with distributed ends is preferred while constructing buildings and bridges.
Question 11.
Explain why the maximum height of a mountain on earth is approximately 10 km?
Answer:
At the base of the mountain, the stress due to all the rocks on top should be less than the critical shear stress at which the rock begins to flow. This can be estimated as follows.
Let hmax be the maximum possible height of the mountain. Let ‘ρ’ be the density of the rock. If ‘A’ be the cross-sectional area of the mountain then stress at the bottom of the mountain = \(\frac{\mathrm{h}_{\max } \mathrm{A} \rho \mathrm{g}}{\mathrm{A}}\) = hmaxρg the material at the bottom of the mountain experiences this force per unit area in the vertical direction.
The elastic limit for a typical rock is 3 × 108Nm-2 and typical density of a rock, ρ = 3 × 10³kgm-3
To avoid the flow of rock hmaxρg < 3 × 108 (or) hmax ≈ 10 km
∴ The maximum height of a mountain on earth is approximately 10 km.
Question 12.
Explain the concept of Elastic potential energy in a stretched wire and hence obtain the expression for it. [AP 15, 18]
Answer:
When a wire is put under a tensile stress, work is done against the inter-atomic forces.
This work is stored in the wire in the form of elastic potential energy.
Expression :
Consider a thin uniform w ire of length l and area of cross section A fixed at one end.
Let ‘F’ be the force acting on the free end of a w ire. Work done to produce a small extension ’de’ is dW = F de

This work is stored in the wire in the form of elastic potential energy (U).
∴ Elastic potential energy = U = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × Stress × Strain × volume of the wire
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define Hooke’s law of elasticity and describe an experiment to determine the young’s modulus of the material of a wire.
Answer:
Hooke’s law :
Within elastic limit, the stress is directly proportional to strain.
Stress ∝ Strain
(or) Stress = E (Strain)
Where ‘E’ is called modulus of elasticity.
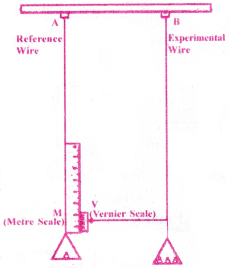
Description :
The apparatus consists of two long straight wiresA and B. They have same length and equal radius suspended side by side from a fixed rigid support.
The wire A(reference wire) carries a millimeter main scale M and a pan to place a weight. The wire B(experimental wire) of uniform cross-section carries a pan in which known weight can be placed.
A vernier scale V is attached to a pointer at the bottom of the experimental wire B and the main scale M is fixed to the reference wire A.
Procedure :
The length(l) and radius(r) of the experimental wire are measured with the help of a meter scale and screw gauge respectively. Both the reference and experimental wires are given an initial small load to keep the wires straight and the vernier reading is noted.
Now the experimental wire is gradually loaded with more weights to bring it under a tensile stress and the vernier reading is noted.
The difference between two vernier readings gives the elongation (∆l)produced in the wire. If M is the mass that produced an elongation (∆l) in the wire then the young’s modulus of the material of the experimental wire is given by
Y = \(\frac{\mathrm{g} l}{\pi \mathrm{r}^2} \times \frac{M}{\Delta l}\)
Substituting the values of \(\frac{M}{\Delta l}\), g, r and / in the above formula, Young’s modulus ot the material of the wire can be calculated.
Exercise Problems
Question 1.
A copper wire of 1 mm diameter is stretched by applying a force of ION. Find the stress in the wire.
Solution:
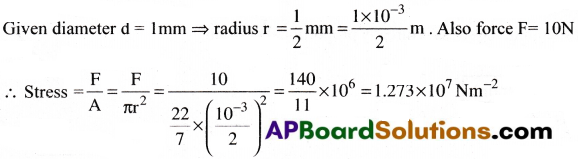
![]()
Question 2.
A Tungsten wire of length 20cm is stretched by 0.1cm. Find the Strain in the wire.
Solution:
Formula : Strain = e/l;
Given l = 20cm, e = 0.1cm
∴ Strain = \(\frac{e}{l}=\frac{0.1}{20}\) = 0.005
Question 3.
If an iron wire is stretched by 1%. What is the strain on the wire?
Solution:
Let initial length of the iron wire = l

Question 4.
A brass wire of diameter 1 mm and length 2m is stretched by applying a force of 20N. If the increase in length is 0.51 mm, Find i) the stress, ii) the strain and iii) the Young’s modulus of the wire.
Solution:
Given diameter d = 1 mm ⇒ radius r = 0.5mm = 5 × 10-4m;
Length l = 2 m; force F = 20N; ∆l = 0.51 mm = 51 × 10-5m.
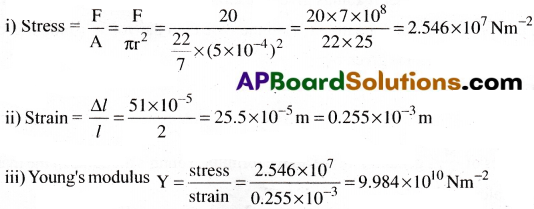
Question 5.
A copper wire and an aluminium wire have lengths in. the ratio 3:2, diameters in the ratio 2 : 3 and forces applied in the ratio 4:5. Find the ratio of increase in length of the two wires. (Ycu = 1.1 × 1011 Nm-2, YAl = 0.7 × 1011 Nm-2).
Solution:
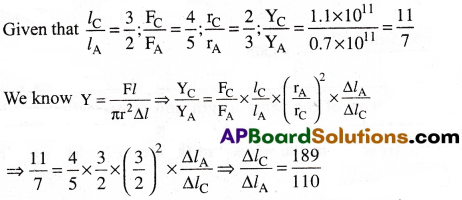
Question 6.
A brass wire of cross-sectional area 2mm² is suspended from a rigid support and a body of volume 100 cm³ is attached to its other end. If the decrease in the length of the wire is 0.11 mm, when the body is completely immersed in water, find the natural length of the wire. (Ybrass = 0.91 × 1011 Nm-2, ρwater = 10³ kg m-3).
Solution:
Given that A = 2 mm² = 2 × 10-6m²; V = 100 cm³ = 10-4 m³.
∆l = 0.11 mm = 11 × 10-5m; Yb = 0.91 × 10 11Nm-2; ρw = 10³ kg m-3.
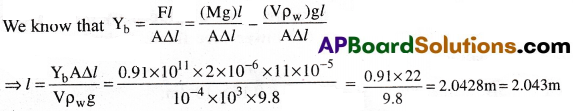
Question 7.
There are two wires of same material. Their radii and lengths are both in the ratio 1 : 2. If the extensions produced are equal what is the ratio of loads?
Solution:
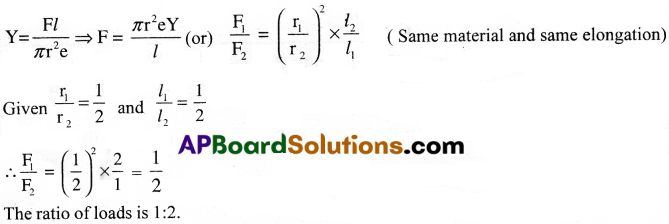
Question 8.
Two wires of different material have same lengths and areas of cross-section. What is the ratio of their increase in length when forces applied are the same?
(Y1 = 0.9 × 1011 Nm-2, Y2 = 3.6 × 1011 Nm-2)
Solution:
Here, L1 = L2 = L; A1 = A2 = A; F1 = F2 =F; Y1 = 0.90 × 1011 Nm-2; Y2 = 3.6 × 1011 Nm-2
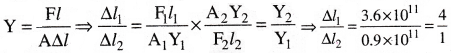
Question 9.
A metal wire of length 2.5m and area of cross section 1.5 × 10-6m² is stretched through 2mm. If its Young’s modulus is 1.25 × 1011m², find the tension in the wire.
Solution:
Given length l = 2.5m; Area A = 1.5 × 10-6m²;
∆l = 2 × 10-3m; Y = 1.25 × 1011Nm-3
![]()
Question 10.
An aluminium wire and a steel wire of the same length and cross-section are joined end-to-end. The composite wire is hung from a rigid support and a load is suspended from the free end ratio of the (i) stress in the wires and (ii) strain in the two wires.
(YAl = 0.7 × 1011Nm-2; Ysteel = 2 × 1011Nm-2)
Solution:
Here l1 = l2 = l; A1 = A2 = A; F1 = F2 = F; Y1 = 0.7 × 1011Nm-2; Y2 = 2 × 1011Nm-2

![]()
Question 11.
A 2cm cube of some substance has its upper face displaced by 0.15cm due to a tangential force of 0.3N. while keeping the lower face fixed. Calculate the rigidity modulus of the substance.
Solution:
Given force F = 0.3N; displacement ∆l = 0.15cm = 0.15 × 10-2m;
Length l = 2cm = 2 × 10-2m;
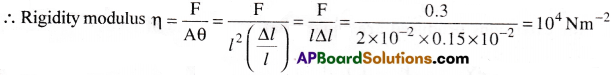
Question 12.
A spherical ball of volume 1000cm³ is subjected to a pressure of 10 atmosphere. The change in volume is 10-2cm³. If the ball is made of iron, find its bulk modulus.
(1 atmosphere = 1 × 105Nm-2).
Solution:
Given V = 1000cm³ = 10-3 m³; P = 10 atm = 10 × 105Nm-2 = 106Nm-2; ∆V = 10-2 cm³ = 10-8m³
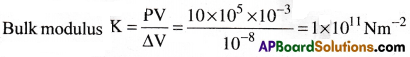
Question 13.
A copper cube of side of length 1cm is subjected to a pressure of 100 atmoshere. Find the change in its volume if the bulk modulus of copper is 1.4 × 1011Nm-2.
Solution:
Given that length l = 1m = 1 × 10-2 m ⇒ volume V = l³ = 10-6 m³; P = 100atm = 100 × 105 Nm-2; K = 1.4 × 105 Nm-2
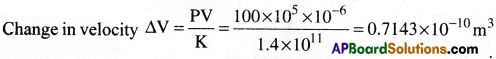
Question 14.
Determine the pressure required to reduce the given volume of water by 2%. Bulk modulus of water is 2.2 × 109 Nm-2
Solution:
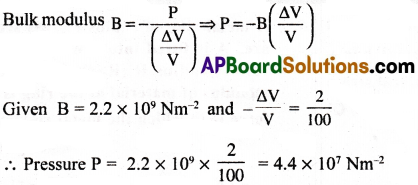
Question 15.
A steel wire of length 20em is stretched to increase its length by 0.2cm. Find the lateral strain in the wire if the Poisson’s ratio for steel is 0.19.
Solution:

Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
A wire is subjected to a longitudinal strain of 0.05. If its material has a Poisson’s ratio of 0.25, the lateral strain experienced by it is
1) 0.0125
2) 0.125
3) 0.00125
4) 12.5
Answer:
1) 0.0125
Question 2.
The Poisson’s ratio can’t “have the value
1) 0.7
2) 0.2
3) 0.1
4) 0.5
Answer:
1) 0.7
![]()
Question 3.
For a given material the Young’s modulus is 2.4 times that of rigidity modulus. Its Poisson’s ratio is
1) 2.4
2) 1.2
3) 0.4
4) 0.2
Answer:
4) 0.2
Question 4.
If for material Young’s modulus 6.6 × 1010,N/m² and bulk modulus is 11 × 1010N/m² then the Poisson’s ratio is
1) 0.4
2) 0.6
3) 1
4) infinity
Answer:
1) 0.4
Question 5.
If the ratio of lengths, radii and young’s moduli of steel and brass wires shown in figure are a,b and c respectively, the ratio between the increase in length of brass and steel would be
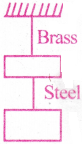
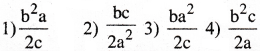
Answer:
4
Question 6.
A metal ring of radius r cross sectional area A is fitted into a wooden circular disc of radius R (R > r). If the young’s modulus of material of the ring is Y, the force with which the metal rinxpands is
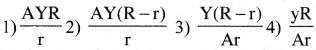
Answer:
2
Question 7.
If the work done in stretching a wire by 1 mm is 2J. The work necessary for stretching another wire of same material with double the radius of cross section and half the length by 1mm is in joule
1) 16
2) 8
3) 1
4) \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Answer:
1) 16
Question 8.
Two wires of same material and same diameter have lengths in the ratio 2:5. They are stretched by same force. The ratio of workdone in stretching them is
1) 5 : 2
2) 2 : 5
3) 1 : 3
4) 3 : 1
Answer:
2) 2 : 5
Question 9.
The length of a metal wire is /, w hen the tension in it is F, and l2 when the tension is F . Then natural length of the wire is
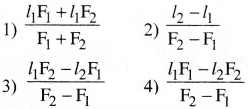
Answer:
3
![]()
Question 10.
A cube is subjected to a uniform volume compression. If the side of the cube decreases by 1% then the bulk strain is
1) 0.01
2) 0.06
3) 0.02
4) 0.03
Answer:
4) 0.03
Question 11.
Modulus of elasticity is dimensionally equivalent to
1) stress
2) surface tension
3) strain
4) coefficient ofviscosity
Answer:
1) stress
Question 12.
According to Hooke’s law of elasticity, the ratio of stress to strain
1) remains constant
2) increases
3) decreases
4) zero
Answer:
1) remains constant
Question 13.
A 60 mm cube has bulk modulus 1.25 × 1011 pascal. If the pressure is changed by 2.5 × 107 pascal, the change in volume is
1) -43.2 m³
2) -43.2 mm³
3) -43.2 cm³
4) -41.2 mm³
Answer:
2) -43.2 mm³
Question 14.
The poisson’s ratio ‘σ’ should satisfy the relation
1) -1 < σ < 0.5
2) -0.5 < σ < 0.1
3) 0.5 < σ < 1.0
4) -1.0 < σ < -0.5
Answer:
1) -1 < σ < 0.5
![]()
Question 15.
Bulk modulus of water 2 × 1011Nm-2. The pressure required to increase the; density of water by 0.1% in Nm-2 is
1) 2 × 109
2) 2 × 108
3) 2 × 106
4) 2 × 104
Answer:
3) 2 × 106
Question 16.
The increase in length of a wire on stretching is 0.025%. If its Poisson ratio is 0.4 then the percentage decrease in the diameter is
1) 0.01
2) 0.02
3) 0.03
4) 0.04
Answer:
1) 0.01
Question 17.
A material has normal density ρ and bulk modulus K. The increase in density of the material when it is subjected to external pressure P from all sides is
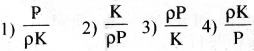
Answer:
3
Question 18.
Which of the following affects the elasticity of a substance
1) hammering and annealing
2) change in temperature
3) impurity in substance
4) all of these
Answer:
4) all of these
Question 19.
A spring of force constant 800 N/m has an extension of 5 cm. The work done in extending it from 5cm to 15 cm is
1) 16 J
2) 8 J
3) 32 J
4) 24 J
Answer:
2) 8 J
Question 20.
The breaking stress of wire depends upon
1) length of wire
2) radius of wire
3) material of wire
4) shape of cross section
Answer:
3) material of wire
Question 21.
The bulk modulus of a spherical object is ‘B’ If it is subjected to uniform pressure ‘p’, the fractional decrease in radios is
1) B/3p
2) 3p/B
3) p/3B
4) p/B
Answer:
3) p/3B
Question 22.
The following four wires are made of the same material. Which of these will have the largest extension when the same tension is applied?
1) length = 200 cm, diameter = 2 mm
2) length = 300 cm, diameter = 3 mm
3) length = 50 cm, diameter = 0.5 mm
4) length = 100 cm, diameter = 1 mm
Answer:
3) length = 50 cm, diameter = 0.5 mm
![]()
Question 23.
When a block of mass M is suspended by a long wire of length L, the length of the wire becomes (L + l). The elastic potential energy stored in the extended wire is
1) \(\frac{1}{2}\)MgL
2) Mgl
3) MgL
4) \(\frac{1}{2}\)Mgl
Answer:
4) \(\frac{1}{2}\)Mgl