Andhra Pradesh BIEAP AP Inter 1st Year English Study Material Intermediate 1st Year English Grammar Reported Speech Questions and Answers.
AP Intermediate 1st Year English Grammar Reported Speech
Let us learn Reported Speech
What is reported speech ?
Reported speech is when you tell somebody else what you or a person said before. It is also called Indirect speech.
How do you tell others what somebody has told you ?
It can be said in two ways : Direct speech or Indirect speech.
Direct Speech
Direct speech is a kind of speech which is reported by some other person exactly in the words spoken by the speaker. This speech will be placed within inverted commas.
E.g. He said to her, “I will come”. (Direct Speech)
![]()
Indirect Speech
Indirect speech is a speech which is reported by some other person by using certain conjunctions in place of commas and making necessary changes in the verbs and the pronouns of the reported speech.
E.g. He told her that he would come. (Indirect Speech)
Parts in statement of speech
There are two parts in the statement of a narration.
1. Reporting verb
2. Reported speech
E.g. Julie said to James, ‘You are very intelligent,” (Direct Speech)
- In the above example, one that is outside the inverted commas (i.e., Julie said to James) is reporting verb and the other that is inside inverted commas (i.e., You are very intelligent) is reported speech.

- In this sentence the reporting verb and the reported speech are connected by the conjunction form ‘that’.
- The reporting verb ‘said to’ in the direct speech is changed to ‘told’ in the indirect speech.
★ If it is ‘says’ (present tense) in direct speech, then it would be ‘says that’ in the indirect speech.
E.g. Julie says, “I am an actress”.
Julie says that she is an actress.
★ If it is ‘says to’ (present tense) in direct speech, then it would be ‘tells’ in the indirect speech followed by the connecting conjunction ‘that’.
E.g. Julie says to John, “I am an actress”.
Julie tells John that she is an actress.
★ If it is ‘said’ in direct speech, then it is retained as ‘said’ followed by the connecting conjunction ‘that’.
E.g. Julie said, “I am an actress”.
Julie said that she was an actress.
★ The reporting verb said or said to is often replaced by the words like asked, requested, ordered, suggested, enquired in the indirect speech, when an order, a suggestion, a permission or a request is reported in the direct speech.
E.g. Rita said to the watchman, “Either go or wait.” (Direct Speech)
Rita asked the watchman either to go or wait. (Indirect Speech)
(this concept is discussed detail, in the coming sections)
- As the verb in the reporting verb ‘said’ is in the past tense the verb in the reported speech of indirect speech will be changed to past tense ‘was’.
- The pronoun you’ in the reporting speech refers to ‘James’ and it will be changed to ‘he’.
When reported statements are transforming you have to change.
★ Pronouns
★ Tense
★ Place and time expressions.
1-Pronoun
In reported speech, you often have to change the pronoun depending on who says what.
E.g. She says, “My mother likes oranges.” (Direct speech)
She says that her mother likes oranges. (Indirect Speech)
2-Tenses
Do not change the tense if the introductory clause is in a present tense (e.g. He says). Note, however, that you might have to change the form of the present tense verb (3rd person singular by adding -s or -es).
E.g. Jane Austen says, “I write novels.” (Direct Speech)
Jane Austen says that she writes novels. (Indirect Speech)
You must change the tense if the introductory clause is in a past tense (e.g. He said).
E.g. She said “I write novels.” (Direct speech)
She said that she wrote novels. (Indirect speech)
Examples of main changes in tense
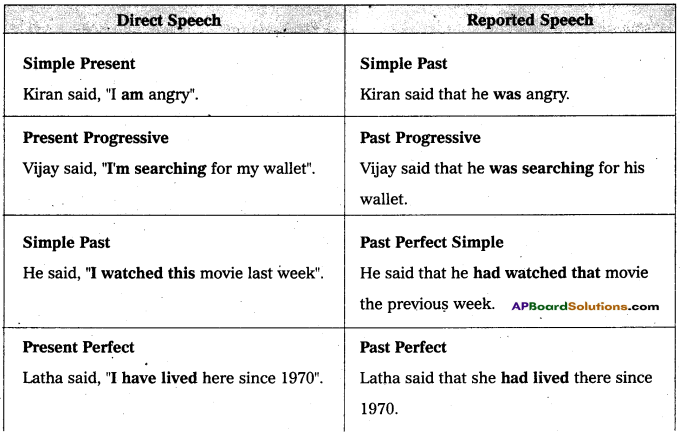

Other Modal verbs may change

The modal verbs could, should, would, might, needn’t, ought to, and used to do not normally change.
E.g.: Rajeev said, “Shyam might be correct.” (Direct Speech)
Rajeev said that Shyam might be correct. (Indirect Speech)
3 – Place, demonstratives and time expressions
Place, demonstratives and time expressions change if the context of the reported statement (i.e. the location and / or the period of time) is different from that of the direct speech.
In the following table, you will find the different changes of place; demonstratives and time expressions.
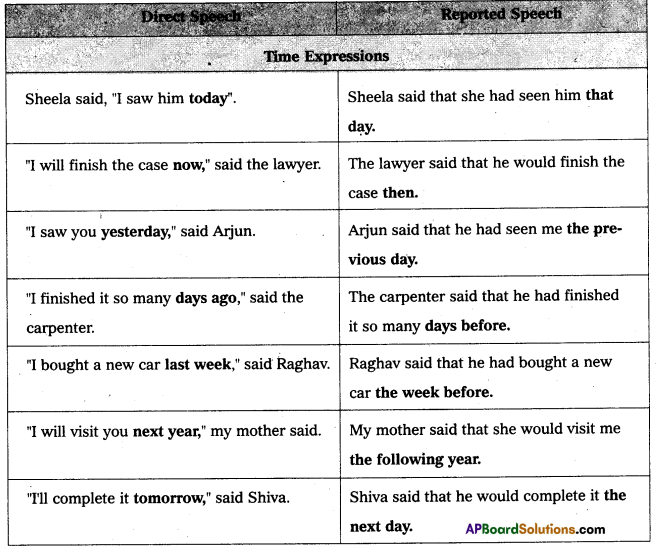

Check your understanding
What did you learn till now ?
We learnt about:
- Definition of Direct and Indirect Speech.
- Parts of the statement of a narration.
- Changes to be used in the transformation of direct speech into indirect.
- Change of pronoun
- Change of tense
- Change of place and time.
When you use reported speech, you may report by using all types of sentences
i. Assertive sentences
ii. Interrogative sentences
iii. Imperative sentences
iv. Exclamatory sentences
v. Optative sentences.
1. Assertive Sentences
Sentences denoting statements in affirmative (declaration) and negative.
E.g.: He is a good teacher.
She was not sleeping.
Assertive sentences are changed into indirect speech as follows :
E.g.: Sita said, “I am a good singer” (Direct Speech)
Sita said that she was a good singer. (Indirect Speech)
If the reporting verb is in the present or future or reported speech is a universal truth, the tense of the reported speech does not change.
E.g.: Teacher said to the students, “Mercury is a liquid metal”. (Direct Speech)
(Statement and a universal truth).
Teacher told the students that Mercury is a liquid metal. (Indirect Speech)
2. Interrogative Sentences
Sentences beginning with auxiliary verbs (yes / no type questions)
- Are you playing ?
- Was she washing ?
- Will you come tomorrow ?
Sentences beginning with question words (How, What, Where, Why, When)
- When is your exam ?
- What are you doing there ?
- How is your father ?
Interrogative sentences are changed into indirect speech as follows :
Questions can be reported in the same way as statements. When a yes-no question is reported, the reported clause is introduced by either if or whether.
Examples
- The girl asked him, “Can you dance, with me?” (Direct speech)
The girl asked him if he could dance with her. (Indirect speech) - The teacher asked the students, “Are you all going to the picnic?” (Direct speech)
The asked the students whether they were all going to the picnic or not. (Indirect speech)
We see in the above sentences that the auxiliary which is placed before the subject in direct speech is put after the subject in indirect speech. That is, when a question is reported, the indirect clause begins with if or whether and if there is any auxiliary verb, it is placed after the subject.
When the word whether is used we can continue the sentence with or not. That is, an alternative is provided with the clause beginning with whether whereas with the clause beginning with if generally an alternative is not provided.
Indirect speech: They asked him whether he went to the zoo or not.
They asked him if he want to the zoo (✓)
They asked him if he went to the zoo or not. (✗)
If the direct speech begins with who, what or which followed by the form of be as the main verb, the verb is placed at the end of the sentence.
Examples
1. Direct speech: I asked him, “Who is the doctor ?”
Indirect speech : I asked him who the doctor was.
2. Direct speech : He asked me, ‘What is your favorite food?”
Indirect speech: He asked me what my favorite food was.
When do and does are used as auxiliary verbs in direct speech, they are omitted in indirect speech.
Examples
- Direct speech : He asked me,’Where does your sister live?”
Indirect speech : He asked me where my sister lived. - Direct speech : He asked me, “Do you know French?”
Indirect speech : He asked me if I knew French. - Imperative Sentences
Sentences denoting command, request and advice are called imperative sentences.- Do not waste time.
- Please give me a glass of water.
- Let him stay here tonight.
Imperative sentences are changed into indirect speech as follows When an order, a suggestion, a permission or a request is reported, the reporting verb is followed by the word to and the bare form of the verb. The reporting verb said is often replaced by the words like asked, requested, ordered, suggested, enquired which convey the tone used in direct speech. Words like please are omitted in direct speech.
Examples
- Direct speech : He said, “Please come with me.”
Indirect speech : He requested me to go with him. - Direct speech : The teacher said, ‘You may go now.”
Indirect speech : The teacher permitted me to go then. - Direct speech : She said, “I’ll take you to the park.”
Indirect speech : She offered to take me to the park. - Direct speech : He said, “Close the window, please.”
Indirect speech : He requested me to close the window. - Direct speech : The policeman said, “Hands up!”
Indirect speech : The policeman ordered the thief to put up his hand.
* Change of ‘Let’
1. Let as a suggestion / a proposal
E.g.
- Kesav said to Komali, “Let us buy a new car.”
Kesav suggested to Komali that they should buy a new car. - Rashmi said to me, “Let us celebrate Diwali.”
Rashmi proposed to me that we should celebrate Diwali.
2. Let as a request
E.g.
- Simran said to the co-ordinator, “Let me go home.”
Simran requested the co-ordinator to let her go home. - The boys said to the gatekeeper, “Let us enter the exam hall.”
The boys requested the gatekeeper to let them enter the exam hall.
3. Let as an order
E.g. The manager said to the watchman, “Let the customers in.”
The manager ordered the watchman to let the customers in.
4. Exclamatory Sentences
Sentences expressing joy, sorrow, excitement, wonder etc.,
- What a pretty girl she is !
- Alas! All is over !
- How nice of her!
Exclamatory sentences are changed into indirect speech as follows :
Verb in the reporting verb is changed into exclaim ‘with sorrow’, exclaim with surprise’, ‘exclaim with joy’, ‘cry out’ etc.,
E.g.
- Linda said, “Hurrah! I have won the lottery.”
Linda exclaimed with excitement that she had won the lottery. - Bunty said, “Ah! My kite is high up in the air”.
Bunty exclaimed with joy that his kite was high up in the air.
5. Optative Sentences
Expressing wish and prayer etc.,
- May God bless you !
- Happy Holi, Children !
- Good bye, my dear friend !
The optative sentences are changed into indirect speech as follows :
E.g.
- The old woman said to her son, “May God bless you !”
The old woman wished / blessed her son that God might bless him. - The soldiers said, “May God save our country.”
The soldiers prayed that God might save their country.
Follow all the rules which we learned for changing the Direct to Indirect Speech in reverse for changing Indirect to Direct Speech.
Examples
- Indirect: Clinton asked Calvin to go with him.
Direct: Clinton said to Calvin, “Come with me.” - Indirect: Rani said to his father that she would be late that night.
Direct: Rani said to his father, “I will be late this night.”
Exercise-1
Convert the following sentences into direct speech. (One is done for you)
Question 1.
The Teacher says that I am a good girl.
The Teacher says, “You are a good girl.”
Answer:
The Teacher says, ‘You are a good girl.”
![]()
Question 2.
Rakesh said that the Earth moves Round the Sun.
Rakesh ______
Answer:
Rakesh said, “the Earth moves round the Sun”.
Question 3.
My mother asked me where I was going.
My mother asked me,” _________?”
Answer:
My mother asked me, “Where are you going ?”
Question 4.
Darcy asked Elizabeth whether she can dance with him or not.
Darcy asked Elizabeth, “______?”
Answer:
Darcy asked Elizabeth, “Can you dance with me or not ?”
Question 5.
Meena asked me if I could carry the bag.
Meena asked me,”______?”
Answer:
Meena asked me, “Can you carry the bag ?”
Question 6.
Leslie requested me to help her.
Leslie said to me, “Please ______.”
Answer:
Leslie said to me, “Please, help me.” ‘
Question 7.
Doctor advised Chanti to avoid unhealthy food.
Doctor said to Chanti, “______”
Answer:
Doctor said to Chanti, “avoid unhealthy food”.
Question 8.
Bella exclaimed with wonder that what a wonderful flower it was.
Bejla said, “Wow! ; ______.”
Answer:
Bella said, ‘Wow ! What a wonderful flower it is.”
Question 9.
Amar bade his friends good bye.
Amar said, “________.”
Answer:
Amar said, “Good bye friends.”
Question 10.
Sneha wished her Mom good morning.
Sneha said,” _____, Mom!”
Answer:
Sneha said, “Good morning, Mom !”.
Exercise – 2
Read the following conversation and convert the following into reported speech.
1. The manager called one of his employees into his office and told him, “Jagan, I’ve decided to make you the plant manager.”
‘Thanks, boss,” the worker replied. “What do I have to do ?” ‘
“Just water them every day,” replied the manager.
2. “Why are you late ?” asked the boss.
“Because I overslept,” replied the man.
“What?” exclaimed the boss. “Do you sleep at home as well?”
Change the following sentences from direct speech to indirect speech.
Question 1.
The traveler said, “Can you tell me the way to the railway station?”
Answer:
The traveler asked me whether I could tell him the way to the railway station.
Question 2.
Ramu said to Revanth, “Please don’t go there.”
Answer:
Ramu requested Revanth not to. go there.
Question 3.
“I’ve acted foolishly,” he said.
Answer:
He told me that I have acted foolishly.
Question 4.
“I’ve just received my progress report. Would you like to see it ?” asked my sister.
Answer:
My sister asked me if I would like to see her progress report, which she has just received.
Question 5.
Suman asked Seetha, ‘When did you arrive ?”
Answer:
Suman asked Seetha when she had arrived.
Question 6.
“Don’t go out too far in the jungle,” the villager said to the stranger.
Answer:
The villager told the stranger not to go out too far in the jungle.
![]()
Question 7.
The teacher said to me, “I want to talk to you about your son’s progress”.
Answer:
The teacher told me that he wants to talk to me about my son’s progress.
Question 8.
Seema said, ‘What a wonderful news!”
Answer:
Seema exclaimed that it was a wonderful news.
Question 9.
Meera said to me, ‘You are late. I’ve been waiting for you since 3 O’ Clock.”
Answer:
Meera told me that I was late and she had been waiting for me since 3 O’ Clock.
Question 10.
“Shut the door after you leave,” she told him curtly.
Answer:
She ordered me to shut the door after I left.
Exercise 3
Complete the sentences below in reported speech.
Question 1.
Johnny said, “I like this village.”
Johnny said ______
Answer:
Johnny said that he liked that village.
Question 2.
“Do you like Chinese dishes?” Kavya asked Suresh.
Kavya asked Suresh ____
Answer:
Kavya asked Suresh if I like Chinese dishes.
Question 3.
“I can’t drive a car,” Naveen said.
Naveen said _______
Answer:
Naveen said that he cannot drive a car.
Question 4.
“Be nice to your sister,” Mom said.
Mom asked me _____
Answer:
Mom asked me to be nice with my sister.
Question 5.
“Don’t be ridiculous,” Hema said.
Hema urged me ______
Answer:
Hema urged me not to be ridiculous.
Question 6.
“Don’t waste your time,” said the teacher.
The teacher told the boys _____
Answer:
The teacher told the boys not to waste their time.
![]()
Question 7.
“What have you decided to do with this project ?” Calvin asked Wilbur.
Calvin asked Wilbur ______
Answer:
Calvin asked Wilbur what he has decided to do with that project.
Question 8.
“I always stay up late,” Mom said.
Mom said ______
Answer:
Mom said that she always stays up late.
Question 9.
‘You should revise your syllabus,” said the professor.
The professor advised the students _____
Answer:
The professor advised the students that they should receive the syllabus.
Question 10.
“Where have you been till now?” Mom asked me.
Mom wanted to know _______
Answer:
Mom wanted to know where I had been till then.