Students must practice these AP Inter 1st Year Economics Important Questions 7th Lesson National Income to boost their exam preparation.
AP Inter 1st Year Economics Important Questions 7th Lesson National Income
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define National Income and explain the various concepts of National Income
Answer:
In Macro Economics, National Income plays an important role. For the economic development of a country, the National Income estimates are very important.
Meaning: National Income is the total market value of all goods and services produced in a country during a given period of time.
Definition: “The labour and capital of a country acting on its natural resources, produce annually a certain net aggregate of commodities, material and immaterial including services of all kinds. This is the net annual income (or) revenue of a country.”
Concepts of National Income:
There are five main concepts of National Income. The various concepts are:
- Gross National Product (GNP) at Market Prices
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at Market Prices
- Net National Product (NNP) at Market Prices
- National Income (or) Net National Product at factor cost
- Personal Income (PI)
- Disposable Personal Income (DPI)
- Per capita Income
- Relationship between per capita income and population
1. Gross National product (GNP) at Market Prices: Gross National product at market prices is the current market value of all final goods and services produced in a country during a given period. The main components of GNP are
- The goods and services purchased by consumers; C
- Investments made by public and private sectors; I
- Government expenditure on public utility services; G
- Incomes earned through International trade; (x – m)
- Net factor incomes from abroad.
GNP at market prices = C + I + G + (x – m) + net factor income from abroad. In this concept production of goods and services must be made by the citizens of that country irrespective of where it is produced.
2. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at Market Prices: This is the part of the GNP that is produced within the country in a given period of time usually a year. In this concept, it is essential that the production of goods and services must take place within the country. Who produces it is not the criterion for computing National Income.
3. Net National Product (NNP) at Market Prices: The Country’s stock of fixed capital undergoes a certain amount of wear and tear in producing goods and services over a period of time. This user cost’ or depreciation or charges for renewals and repairs must be subtracted from the GNP to obtain Net National Product at Market Prices.
NNP at market prices = GNP at market prices – Depreciation.
4. National Income or Net National product at factor cost: It is the total income received by the four factors of production in the form of rent, wages, interest, and profits in an economy during a given period of time.
It is also the income received by persons supplying the services or resources used in production. It includes all wages earned by employees, interest paid to private individuals, net rent received by landlords and net profit of all kind of business.
The NNP is not available for distribution among the factors of production. The amount of indirect taxes are paid by the firms to the government and not to the factors Of production. Similarly, the government gives subsidies to firms for the production of certain types of goods and services and that part of the production cost is borne by the government. Hence the goods are sold in the market at a lower price than the actual cost of production. Therefore this volume of subsidies has to be added to the Net National Income.
In modern days the government sector is vastly enlarging and runs several industries and enterprises. The profits of the government do not go to the factors of production.
NI or NNP at factor cost = NNP at market prices – Indirect taxes + Subsidies – Profits of government-owned firms.
5. Personal Income (PI): It is the total income received by all persons of households in a country during a given period of time. The whole of NI earned by factors of production is not available to them. Corporate taxes have to be paid by firms before distributing them to shareholders.
Similarly, firms may prefer to keep a part of its profits for expansion or for other exigencies. This part of profits are also not distributed to its shareholders. Salaried employees make contributions for social security.
The government may provide social security allowances like pensions, unemployment allowances, scholarships, etc. These are incomes for Some sections of society even though no productive services are made by them.
Personal Income PI = NI at factor cost – Undistributed profits – Corporate taxes – Social security contributions + Transfer payments.
6. Disposable Personal Income (DPI): Disposable income is that part of personal income which is left with the individual after payment of all direct taxes like income tax, property tax, etc. generally disposable income is either spent for consumption or for savings.
DPI = PI – Personal taxes
DPI = Consumption + Savings
7. Per capita Income: Per capita income is the average income of an individual in a country. It is calculated by dividing national income by population of the country.
![]()
This concept is a good indicator of the average standard of living in a country.
7. Relationship between per capita income and population: There is a close – relationship between national income and population. These two together determine the per capita income. If rate of growth of national income is 6% and rate of growth of population is 3%, the rate of growth of per capita income will be 3% and it can be expressed as. follows.
QPC = Q – QP
QPC = rate of growth of per capita income
Q = rate of growth of national income
QP = rate of growth of population
Question 2.
Explain various methods of calculating National Income. [Mar. ’19 (TS); May, March – 2018, 2017]
Answer:
National Income is the total market value of all goods and services produced in a country during a given period of time.
Measurement of National Income:
There are three methods of measuring National Income.
- Output method or Product method
- Expenditure method and
- Income method.
Cairn Cross says “National Income can be looked in any one of the three ways, as the National Income measured by adding up everybody’s income, by adding up everybody’s output, and by adding up the value of all things that people buy and adding up their savings.
1) Output method or Product method: It is also known as the inventory method or commodity service method. In this method we are fine! the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country during a given period of time. The entire output of fined goods and services is multiplied by their respective market prices to find out the gross national product.
NI = (P1 Q1 + P2 Q2 + ……… PnQn) = Depreciation – Indirect taxes + Net Income from abroad.
where NI = National Income,
P = Price of the good or service;
Q = Quantity of good or service produced;
1, 2 n are the various goods and services produced.
The values of raw materials, intermediary goods, etc. should not be included. Only fined goods should be taken into account.
Here we find out the value added in the different sectors like agriculture, government professionals, industry and services sectors. Hence it is also called the “Value added method”.
National income based on output data is calculated by adding the sum of values added’ by each firm in each industry. Industrial activity is conventionally classified according to the standard industrial classification.
Value added is the difference between the final value of the product and the cost of the inputs of raw materials and components, i.e., it is the rise in value of the product caused by the activities of the firm itself.
2) Income method: In this method, the incomes earned by all factors of production are aggregated to arrive at the national income of a country. The four factors of production receive incomes in the form of wages, rent, interest, and profits. This is also National Income at factor cost.
NI = W + I + R + P + Net income from abroad
NI = National Income.
W = Wages,
I = Interest,
R = Rent,
P = Profits
This method gives us National Income according to distributive shares, (the most important share is that of labour)
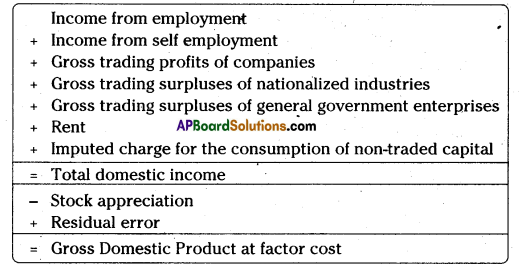
Undistributed profits of companies are included in the accounts as they have been earned in the accounting period. It makes no difference what the firm does with the profits subsequently.
Residual error refers to a sum that is added to balance the accounts. Each approach to calculating national income involves thousands of figures collected from a variety of sources. It is not surprising that the totals are not, in practice, equal. The residual error appears in the income accounts purely for the convenience of presentation.
3) Expenditure method: In this method, we add the personal consumption expenditure of households, expenditure of the firms, government purchase of goods and services, net exports plus net income from abroad.
N1 = EH + EF + EG + Net exports + Net income from abroad.
Here national income = Private final consumption expenditure + government final consumption expenditure + net domestic capital formation + net exports + net income from abroad
EH = Expenditure of Households
EF = Expenditure of Firms
EG = Expenditure of Government
Care should be taken to include spending or expenditure made on final goods and services only.
There are two different ways in which the national income of a country is estimated. They are national income at market prices and national income at constant prices.
Question 3.
Describe the components of National Income.
Answer:
In Macro Economics, national income plays an important role. For the economic development of a country, national income estimates are very important.
The toted market value of all goods and services produced in a country during a given period of time is called national income.
Definition: According to Marshall, “Labour and capital of a country, acting on its natural resources produce annually a certain net aggregate of commodities material and immaterial, including services of all kinds” is called National Income.
Components of national income: There are five main components of national income.
They are
- Consumption – C
- Gross domestic investment -1
- Government expenditure – G
- Net foreign investment – (x – m)
- Net income from abroad
a) Consumption – C: It is the total expenditure made by households on goods and services. It includes both durable and non-durable goods like food grains, clothing, medical services, etc. The level of consumption depends on the level of incomes.
b) Investment -1 : It is the expenditure by firms on goods and services which are not for current consumption. It includes expenditure on capital like machinery, roadways, bridges, etc. which will help in the production of consumer goods in the future.
c) Government expenditure (G): It is the expenditure made by the government on infrastructural facilities for the use of society. It also includes government expenditure on services like Police, Military and Judicial services.
d) Net foreign investment (x – m) : It is the income earned by a country through international trade. Every country exports a certain volume of goods produced by it and imports goods that are relatively cheaper in the international market or other countries.
The difference between the value of exports and imports (either positive or negative) has to be taken into account to estimate the national income of a country.
The net foreign investment depends on the export-import policy of the government and the comparative price level of the goods in domestic and international markets,
Y = C + I + G + (x – m)
e) Net income from abroad: Some of the nationals of a country working in other countries may be sending remittances to their country. Likewise, foreigners in one country may be sending their income abroad. Hence net income from abroad represents the difference between receipts and payments of the above type of factor incomes.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the factors that determine National Income? [Mar. 19 (TS); May. March – 2017; May 2018. 2016]
Answer:
The total market value of all goods and services produced in a country during a given period of time is called National Income.
There are many factors that influence and determine the size of national income in a country. These factors are responsible for the differences in national incomes of various countries.
a) Natural Resources: The availability of natural resources in a country, its climatic conditions, geographical features, fertility of soil, mines and fuel resources, etc. influence the size of National Income.
b) Quality and Quantity of Factors of Production: The National Income of a country is largely influenced by the Quality and Quantity of the country’s stock of factors of production.
c) State of Technology: Output and National Income are influenced by the level of technical progress achieved by the country. Advanced techniques of production help in the optimum utilization of a country’s national resources.
d) Political Will and Stability: Political will and stability in a country helps in planned economic development and for faster growth of national income.
Question 2.
What does National Income at factor cost? (National Income or Net National Product at factor cost)
Answer:
National Income at factor cost is the total income received by the four factors of production in the form of rent, wages, interest and profits in an economy during a given period of time. It is also the incomes received by persons supplying the services or resources used in production. It includes all wages earned by employees, interest paid to private individuals, net rent received by landlords and net profits of all kinds of business.
NNP is not available for distribution among the factors of production. The amount of indirect taxes are paid by the firms to the government and not to the factors of production. Similarly the government gives subsidies to firms for the production of certain types of goods and services and that part of the production cost is borne by the government.
Hence the goods are sold in the market at a lower price than the actual cost of production. Therefore, this volume of subsidies has to be added to the Net National Income.
In modern days the government sector is vastly enlarging and runs several industries and enterprises. The profits of the government do not go to the factors of production.
NI or NNP at factor cost = NNP at market prices – Indirect taxes + subsidies – profits of government-owned firms.
Question 3.
Mention any three definitions of National Income.
Answer:
Meaning: National Income is the total market value of all goods and services produced in a country during a given period of time. Several economists have defined National Income as follows:
1. Fisher’s Definition: “The National Dividend or Income consists solely of services as received by ultimate consumers, whether from their material or from their human environment.”
2. Marshall’s Definition: “The labour and capital of country acting on its natural resources, produce annually a certain net aggregate of commodities, material and immaterial including services of all kinds. This is the net annual income or revenue of a country.”
3. Kuznet Definition: According to Kuznet, “National Income is the net output of commodities and services flowing during the year from The country’s productive system into the hands of the ultimate consumers.or into the net addition to country’s capital goods”.
Question 4.
What is the relationship between per capita income and population?
Answer:
There is a close relationship between national income and population. These two together determine the per capita income. If rate of growth of material income is 6% and the rate of growth of population is 3%, the rate of growth of per capita income will be 3% and it can be expressed as follows.
QPC = Q – QP,
QPC = Rate of growth of per capita income
Q = Rate of growth of national income
QP = Rate of growth of population
A rise in the per capita income indicates a rise in the standard of living. The rise in per capita income is possible only when the rate of growth of the population is less than the rate of growth of the National Income.
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
GNP (Gross National Product).
Answer:
Gross National Product at market prices is the current market value of all final goods and services produced in a country during a given period. The main components of GNP are:
GNP at market prices = C + I- G + (x-m) + net factor income from abroad.
In this concept production of goods and services must be made by the citizens of that country irrespective of where it is produced.
Question 2.
Per capita income.
Answer:
Per capita income is the average income of an individual in a country. It is calculated by dividing national income by the population of the country.
![]()
This concept is a good indicator of the average Standard of living in a country.
Question 3.
Depreciation.
Answer:
Depreciation is a user cost of replacement cost. The consumption of fixed capital or fall in value of the capital due to wear and tear is called depreciation.
Question 4.
Disposable Income (DPI).
Answer:
Disposable income is that part of personal income which is left with the individual after payment of all direct taxes like income tax, property tax, etc. generally disposable income is either spent for consumption or for savings.
Disposable Income (DPI): Personal Income – Personal taxes (or) DPI = Consumption + Savings.
