Andhra Pradesh BIEAP AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Study Material 7th Lesson Formation of a Company Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Study Material 7th Lesson Formation of a Company
Essay Answer Questions
Question 1.
Discuss the procedure to form a company.
Answer:
A Joint Stock Company requires a number of legal formalities to be complied with before it is brought into existence. Formation means establishment of company by fulfilling all formalities. The important steps to be taken by the company for formation are shown in the following chart.
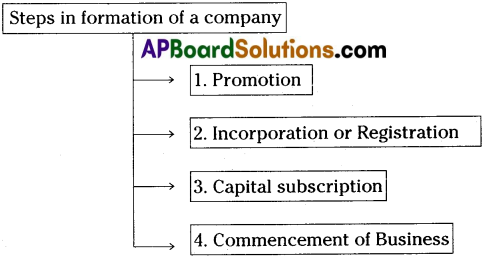
1) Promotion :
Promotion is the first stage in the formation of a company. It involves identification of business opportunity or idea, detailed investigation, assembling the requirements, and financing proposition. Promotion is the process of organization and planning the finance of business enterprise under the corporate firm.
2) Incorporation or Registration :
A company being an artificial person comes into existence only after its registration with the Registrar of Companies. It is the legal process through which an enterprise obtains recognition as a separate legal entity. Private or public limited companies must file all the necessary documents with the Registrar to obtain the Incorporation Certificate. With this certificate the company gets a separate legal entity. For this purpose a number of steps have to be taken for registration.
3) Capital subscription :
After incorporation of a company the next step will be to raise the capital. A public company cannot commence business unless the minimum subscription as stated in the prospectus is subscribed. If a company does not receive 90 percent of the issue amount from the public as subscription within 120 days, it has to refund the amount to the applicant as per the guidelines of Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines within 10 days.
4) Commencement of business:
A public company has to file the following certificates, to get the certificate of commencement.
- A declaration that a prospectus or statement in lieu of prospectus has been filed
- A declaration that directors have taken up their qualification shares and paid them.
- A declaration that minimum subscription amount has been allotted and collected.
- A statutory declaration by the Secretary of the company or a Director that all the formalities relating to commencement of business are duly complied with.
A scrutiny is made by the Registrar with all the documents and issues a “Certificate of commencement of business”. The process of company formation comes to an end with the issue of this certificate.
Question 2.
Describe various steps involved in promoting a company.
Answer:
Promotion is the first stage in the formation of a company. It involves identification of a business opprotunity or idea, analysis of its prospects, gathering the relevant information and taking steps to implement it. Promotion is considered as putting an idea into practice.
Definition:
“Promotion is the process of organizing and planning the finance of a business enterprise under the corporate form.” – L.H. Haney
“Promotion starts with the conception of the idea from which the business is to evolve and continue down to the point at which the business is fully ready to begin operation as a going concern.” – Guthmann and Dougal
To be successful the idea of business must be exposed and investigation chart given the stages of promotion.
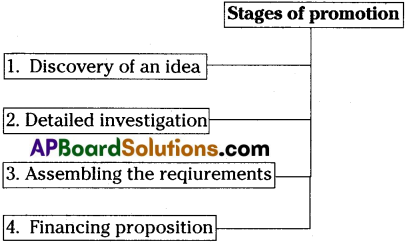
1) Discovery of an idea :
The success of business depends on the selection of a business line. The promoter has to form an idea about the type of business and its prospects. The promoter should analyse the strengths and weaknesses of the proposed idea, and develop the idea with the help of technical experts.
2) Detailed investigation :
At this stage various factors relating to the proposed unit are to be studied from the pratical point of view. To find out the strong and weak points of the idea a detailed investigation is conducted. The promoter shall estimate demand for the product, and then thinks of arranging finance and also considers the availability of workers, plant and machinery, raw materials, and cost of production. For this purpose technical experts, financial consultants, etc. are consulted.
3) Assembling requirements :
After making sure that proposed business is feasible and profitable the promoters make arrangements to assemble the requirements like directors appointment, selecting the place for unit, contacting the suppliers of raw materials purchasing of plant and machinery, etc.
4) Financing proposition :
The promoter decides about the capital structure of the company. In this process, he determines how much share capital will be issued, type of shares and debentures to be issued, and the nature of loans to be borrowed from financial institutions or banks for a long period.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the process involved in Incorporation of a company.
Answer:
A company being an artificial person comes into an existence through incorporation. A Joint Stock Company whether private or public limited must be registered with the Registrar of Companies. It is called incorporation. For that purpose the joint stock companies must file all the necessary documents with the Registrar to obtain the Incorporation Certificate. With this certificate the company gets a status of legal entity.
A number of steps have to be taken up before getting a company registered.
1) Application for approval of name :
For approval, an application is to be submitted to the Registrar of Companies of the state and obtain the approval name. A company may adopt any name which is not prohibited under the Emblems and Names Act, 1950. The Registrar is expected to approve the name within 14 days of the receipt of application.
2) Preparation of Memorandum of Association (MoA) :
MoA is the constitution of company which describes its objects, scope and the relationship with outside world. This main document must be carefully drafted, stamped and signed by seven members in case of a public company and two members in case of a private company. As per the new amendment of the Act, 1950 one member is enough to sign on MoA in case of private company.
3) Preparation of Articles of Association (AoA) :
This is the second document which contains rules and regulations relating to the internal management and also the capital structure of the business. A public limited company may not require to file its own Articles of Association. However, it may adopt model clauses prescribed in Table A, Schedule I of the Act. A private company is required to submit its articles and duly signed by the signatories.
4) Preparation of other documents :
At the time of incorporation of a company the following documents are to be prepared and submitted to the Registrar of Companies.
- Consent of the first directors
- Promoters should execute a power of attorney in favour of one of the promoters or an advocate who is to carry out the formalities required for registration.
- When the location of the registered office is finalized, prior to incorporation, the notice of it is to be filed. If not, within 30 days of its registration it is to be submitted.
- When a company by its Articles appoints any person to act as Director, Manager, Secretary their particulars have to be filed within 30 days along with MoA and AoA of the company.
5) Statutory declaration :
A declaration that all the requirement under, the Companies Act, 1950 have been complied with in Form no. 1 is to be filed with the Registrar.
6) Payment of registration fee :
If the prescribed fees has to be paid towards registration of company.
7) Incorporation certificate :
The Registrar is satisfied with all requirements under the Companies Act, 1950, issues a certificate called “Certificate of Incorporation. With the receipt of this certificate, the company gets its recognition as a corporate body.
Question 4.
What is Memorandum of Association? Explain its clauses.
Answer:
The Memorandum of Association is the most important main document of the company. It is constitution and charter of the company. It provides the foundation on which the company structure is built. It defines the scope of the company’s activities as well as its relation with the outside of the company. The contents of the MoA cannot be altered at the option of directors or even the shareholder. It is to be altered only with Government’s and court approval in many cases. The purpose of the memorandum is to enable the shareholders, creditors, and those who deal with the company to know what is the permitted range of activities of the enterprise.
The memorandum has to be divided into paragraphs consecutively numbered and has to be printed. It should be signed by seven members in case of public company and by two members in case of private company.
Memorandum of association contains the following clauses :
1) Name clause :
The name of the company should be specified in this clause. A company can choose any name it likes, however it should fulfil the following conditions.
- The proposed name should not be identical or similar to the name of existing company.
- The proposed name should not convey any connection or link with a government department or local authority.
- The name of the public company should end with the word ‘Limited’, while that of private company should contain the word ’Private limited1.
- The proposed name should not be objectionable under the provisions of Emblems and Names Act, 1950.
The name of the company must appear on the outside of every office, or place of business, in one of the local languages and on all cheques, bills, letters, notices and other official publications, etc. of the company.
2) Situation Clause :
Every company will have a registered office. This clause should specify the place and the state in which registered office is located. It is necessary to determine the legal jurisdiction and to make correspondence. If the registered office is not confirmed on the date of incorporation, it should communicate the address to the registrar within 30 days of its incorporation. The purpose of stating the registered office is that all communications, notices, circular, etc. are sent to the registered office.
3) Objects Clause:
It is the most important clause in the memorandum of association. It defines powers of the company and the scope of its activites. A company is not authorised to do any business outside the purview of the objects clause. The objects of the company must be legal and very clearly defined. It contains main objects and other objects. Great care should be taken in drafting this clause.
4) Liability Clause :
It contains the nature of liability of its members. It means that the liability of a member is limited to the nominal value of shares held by him. The sharholders are not liable for the debts of the company. A company registered with unlimited liability is not required to give this clause in memorandum.
5) Capital Clause :
It contains the capital structure of the company. The amount of capital required by the company is stated in this clause. This is called Authorised capital or Registered capital. The capital is divided into small units called ‘Shares’. The company must mention the number and kinds of shares issued and the value of each share. Company is not authorised to issue shares over and above authorised capital.
6) Subscription or Association Clause :
This clause contains the names of signatories to the memorandum. The memorandum must be signed by at least seven persons in case of public limited company and by at least two persons in case of a private limited company. Each subscriber must take at least one share in the company. The subscribers declare that they agree to incorporate the company and agree to take the shares stated against their names. The signatures of the subscribers are attested by at least one witness each.
Question 5.
What is Articles of Association and also explain its contents.
Answer:
The Articles of Association of a company are its bye-laws or rules and regulations that govern the internal management of the company and the conduct of the business. It determines the relationship between the company and its members as well as among the members themselves. Articles of Association determine the powers of the directors and officers of the company. It must be printed, divided into paragraphs, numbered consecutively and signed by each subscriber of the memorandum and filed with the Registrar.
The contents of Articles of Association:
The Articles of Association is the document which contains the rules and regulations to be followed for the purpose of internal management of the company. It generally contains the following.
- Rules and regulations.
- Rules of preliminary contracts.
- Provisions regarding use of common seal.
- Procedure of issuing share capital, number and value of shares, issue of shares, , calls on shares, lien on members’ shares, etc.
- Procedure for transfer and forfeiture’ of shares.
- Procedure for issue of debentures and stocks.
- Procedure for alteration of capital
- Provisions regarding conducting the general meetings, special meetings, voting, proxies, etc. resolutions.
- Rules regarding appointment of Directors and their remuneration.
- Provisions relating dividends and reserves.
- Preparation of Accounts and Audit, and method of appropriation of profits.
- Winding-up procedure
- Maintenance of Bank Accounts.
These bye-laws are very useful in inter management of the company.
![]()
Question 6.
What is prospectus? Explain the contents of prospectus.
Answer:
A private company can start its business immediately after receiving the Certificate of Incorporation. Whereas a public company has to raise the necessary capital from the public. In that connection the company have to invite the public to subscribe for shares in their company. This invitation to the public is known as “Prospectus”.
Definition :
As per Section 2(36) of the Companies Act, 1956, a prospectus is defined as “Any document described for issued as propectus and includes any notice, circular, advertisement or other document inviting deposits from the public or inviting offers from the public for purchase of any shares in, or debentures of a body corporate”.
Any advertisement offering shares or debentures of the company for sale to the public is called’Prospectus’.
Contents of Prospectus:
Every prospectus should disclose the matter as specified in Part -1 of Schedule-II to the Compnies Act. Some of the contents which every prospectus must include are
- Name and full address of the company.
- The particulars of the signatories to the memorandum of association and the number of shares taken up by them.
- Name, addresses, and occupations of members of the Board of Directors.
- The minimum subscription amount fixed by the promoters.
- The details of property acquired if any.
- The time of opening of the subscription list.
- The capital structure of the company, and particulars of issue.
- The amount payable on application, allotment, and calls.
- Basis for the issue price
- The particulars of preferential treatment given to any person for subscribing shares or debentures.
- The addresses of the underwriters if any.
- Particulars about reserves and surpluses.
- The amount of preliminary expenses.
- The name and address of Auditor.
- Particulars regarding voting rights at the meetings of the company.
- Management perception of risk factors.
- ‘Disclosure of investors’ grievances and redressal system.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are different types of promoters?
Answer:
The following are different types of promoters.
1) Professional promoters :
The professional promoters are specialized promoters. Specialized promotion is their whole time occupation.
2) Accidental promoters :
They are not specialists in company formation. They promote own firms as entrepreneurs.
3) Financial promoters :
These are the promoters who float new enterprises during favourable conditions in the securities market.
4) Technical promoters :
This type of promoters promote new enterprises on the basis of their specialised knowledge and training in technical fields.
5) Institutional promoters :
These are promoters who provide technical, managerial and financial assistance for the promotion of a company.
Question 2.
Discuss the differences between Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association.
Answer:
Differences between Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association :
| Memorandum of Association | Articles of Association |
| 1) Nature : Memorandum is the charter of the company. It defines the objects and scope of the company. |
It is a subsidiary document and contains the rules and regulations for the internal management of the company. |
| 2) Scope : It defines the relationship between the company and the outsiders. |
If defines the relationship between and its members and also the relationship among the members themselves. |
| 3) Contents : It contains the objects and powers of the company. |
It lays down the rules by which those objects are achieved. |
| 4) Filing : At the time of incorporation, filing of memorandum is compulsory. |
The filing of articles is optional. A public company need not file it. It can adopt rules stated in Table – A. |
| 5) Status : Memorandum is sub-ordinate to Companies Act. |
Articles of Association is subordinate to both Memorandum and Companies Act. |
| 6) Alteration : It can be altered only under special circumstances with the prior approval of and central govt, court. |
It can be altered by passing special resolution of the shareholders. In some cases only the approval of the cental govt, required. |
| 7) Legal effects: The legal effects are more harsh on memorandum. Companies Act regulated it. |
The legal effects are less on articles. The shareholders can modify the Articles and ratify it. |
Question 3.
Explain the functions of promoters. [May 17 – T.S.]
Answer:
Promoter is the person who assembles the men, money and the materials into a going concern. Promoters are those who take various steps in setting up a business organisation. Promoter is mainly concerned with the promotion of a business venture. Discovery, investigation, assembling and financing, etc. are performed by the promoter.
Functions:
- A promoter conceives an idea for the setting up of a business.
- Promoter makes preliminary investigation and ensures the future prospects of business.
- Promoter brings together various individuals who agree to associate with him and share the business responsiblities.
- He prepares various documents and gets the company incorporated.
- Promoter raises the required finances and gets the company going.
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define Promotion.
Answer:
Promotion means undertaking such a step, which would persuade a large number of people to come together for achieving a common goal through the company form of organisation. According to L.H. Haney, “Promotion may be defined as the process of organising and planning the finance of a business enterprise under the corporate form”.
![]()
Question 2.
Define MOA.
Answer:
According to Lord Cairns, “Memorandum of Association of a company is charter and defines the limitation of the powers of a company. It contains the fundamental conditions upon which alone the company is allowed to be incorporated”. The Memorandum of Association is the constitution of the company. It is the charter of the company. It provides the foundation on which the company structure is built. It defines the scope of the company’s activities as well as its relation with the outside world.
Question 3.
Minimum Subscription :
Answer:
The minimum amount of capital to be collected by a public limited company before its allotment of shares is known as “minimum subscription”. A public limited company cannot start business unless a minimum subscription as stated in the prospectus has been subscribed. It is fixed by taking into account the following requirements.
- Amount required for the purchase of property.
- Amount required for working capital.
- Amount required for payment of preliminary expenses.
- Amount required for any other expenditure for the formation of company.
Question 4.
Statement in lieu of prospectus :
Answer:
If the public company does not raise its capital by the public issue of shares, then it need not publish a prospectus. In such a company capital may be collected privately and shares may be allotted by the mutal agreement of a few people. Such public company having a share capital, and not issuing prospectus must prepare a statement in lieu of the prospectus and file it with the Registrar of Companies.
Question 5.
Criminal liability for misstatements in Prospectus:
Answer:
In case of Mis-statements or Misrepresentation in Prospectus, it gives rise to impose civil or criminal liability to pay compensation to the persons, who subscribed the shares relying on such false information in the prospectus and also criminal libaility to pay a fine up to Rs. 5000/- or imprisonment up to 2 years or both.
Question 6.
Certificate of commencement of business:
Answer:
A public limited company cannot commence its business unless it received a certificate of business commencement. This certificate is not compulsory for private limited company. It means private company can commence its business without the certificate of business commencement. The Registrar of Companies issues this certificate only when all the legal documents are submitted. Further, the registrar issues this certificate only on the confirmation of collection minimum subscription.
![]()
Question 7.
Prsopectus.
Answer:
A prospectus is a document which invites the public to promote funds to the company by way of subscribing to its shares and debentures. The history, nature, and profitability of the company is depicted in the prospectus.
