Students get through AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Important Questions 11th Lesson The p-Block Elements – Group 14 which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Important Questions 11th Lesson The p-Block Elements – Group 14
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Discuss the variation of oxidation states in the group -14 elements.
Answer:
- The common oxidation states exhibited by group-14 elements are +4 and +2.
- Carbon exhibits negative oxidation states.
- Heavier elements exhibit +2 oxidation state.
- The tendency to show +2 oxidation state increases in the order Ge < Sn < Pb.
- Pb exhibits +2 oxidation state as stable state because of inert pair effect.
Question 2.
How the following compounds behave with water? (a) BCl3 (b) CCl4
Answer:
a) When BCl3 is treated with water, boric acid (H3BO3 )is formed.
BCl3 + 3 H2O → H3BO3 + 3HCl
b) When CCl4 is treated with super heated steam in the presence of iron or copper, phosgene (COCl2) is fonned.
CCl4 + H2O → COCl2 + 2 HCl
Question 3.
Are BCl3 and SiCl4 electron-deficient compounds? Explain.
Answer:
The compounds in which the central atom has incomplete octet configuration are called electron deficient compounds.
BCl3 is an electron deficient molecule because boron atom has sextet configuration (6 electrons). SiCl4 is not an electron deficient molecule, because silicon atom has octet configuration.
Question 4.
Give the hybridisation of carbon in
a) CO3-2 b) diamond c) graphite d) fullerene [AP,TS 16] [TS 18]
Answer:
a) Hybridisation of ‘C in CO-23 is sp²
b) Hybridisation of ‘C in diamond is sp³
c) Hybridisation of ‘C’ in graphite is sp²
d) Hybridisation of ‘C’ in fullerene is sp²
Question 5.
Why is CO poisonous? [AP, TS 16][AP 18]
Answer:
Carbon monoxide (CO) forms a stable complex with haemoglobin called carboxy haemoglobin. This prevents haemoglobin from carrying oxygen into the cells of the body and it ultimately results death.
![]()
Question 6.
What is allotropy? Give the crystalline allotropes of carbon. [AP 16,20][TS 22]
Answer:
The phenomenon of existence of an element in different physical forms having same chemical properties is called allotropy. Crystalline allotropes of carbon are
a) Diamond
b) Graphite.
Question 7.
Classify the following oxides as neutral, acidic, basic or amphoteric.
a) CO b) B2O3 c) SiO2 d) CO2 e) Al2O3 f) PbO2 g) Tl2O3
Answer:
Neutral oxide : CO
Acidic oxides : CO2, SiO2, B2O3
Basic oxide : Tl2O3
Amphoteric oxides : Al2O3, PbO2
Question 8.
Name any two man-made silicates. [AP 15]
Answer:
Two important man made silicates:
Glass and cement.
Question 9.
Write the outer electron configuration of group -14 elements.
Answer:
The general outer most electron configuration of group -14 elements is ns²np².
1) Carbon – [He]2s²2p²
2) Silicon – [Ne]3s²3p²
3) Germanium – [Ar]3d104s²4p²
4) Tin – [Kr]4d105s²5p²
5) Lead – [Xe]4f145d106s²6p²
Question 10.
How does Graphite function as a lubricant? [TS 15,19]
Answer:
Graphite has two -dimensional layer structure and these layers can easily slide one over the other, as they are held by weak vanderwaal forces. Hence graphite is used as a lubricant.
![]()
Question 11.
Graphite is a good conductor. Explain. [TS 19,22][AP 15,17,22]
Answer:
In Graphite, each carbon atom is in sp- hybridised state. Each carbon atom contains one electron in pure ‘p’ orbital. Due to the presence of these free electrons, graphite acts as a good conductor of electricity.
Question 12.
Explain the structure of silica.
Answer:
- Silica is a giant molecule with 3- dimensional structure.
- In Silica, eight membered rings are formed with alternative Silicon and Oxygen atoms.
- Each ‘Si’ is tetrahedrally surrounded by four oxygen atoms.
- Each Oxygen at the vertex of the tetrahedron is shared by two Silicon atoms.
- In SiO2, Silicon atom undergoes sp³ hybridisation.
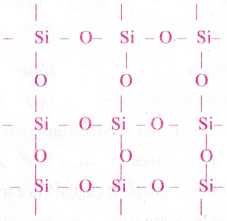
Question 13.
What is Synthesis gas? [TS 15,18][AP 20]
Answer:
The mixture of CO and H2 is known as water gas or synthesis gas or Syngas.
It is used for the synthesis of methanol and a number of hydrocarbons.
Question 14.
What is ‘producer gas’? [TS 16]
Answer:
The mixture of CO and N2 is known as Producer gas.
It is prepared by passing air over hot coke.
Question 15.
Diamond has high melting point – explain. [AP 19,22]
Answer:
In Diamond sp³ hybridisation. It has a three dimensional network involving strong C-C bonds, which are very difficult to break. Hence diamond has high melting point.
Question 16.
Give the use of CO2 in photosynthesis.
Answer:
The process of converting the atmospheric CO2 into carbohydrates by green plants is known as ‘photosynthesis’.
In photosynthesis, CO2 changes to carbohydrates such as glucose.
![]()
Question 17.
How does CO2 increase the green house effect?
Answer:
- Due to deforestation, decomposition of lime stone and burning of fossil fuels etc. CO2 concentration is increased in atmosphere.
- A blanket of CO2 gas in the atmosphere traps and reflects the infra red radiations. So atmosphere gets heated up. This is called green house effect or global warming.
![]()
Question 18.
What are silicones? [AP 15]
Answer:
Silicones:
Silicones are organo silicon polymers in which silicon is strongly linked with oxygen and carbon.
![]()
Silicones contain R2SiO as repeating unit. The structure of R2SiO unit is similar to that of ketone.
![]()
Question 19.
Give the uses of silicones.
Answer:
Silicones are used
- in the preparation of silicone rubber.
- to prepare water proof clothes and paper.
- to prepare grease and lubricants that are used in aeroplanes.
- in paints and enamels.
Question 20.
What is the effect of water on tin?
Answer:
Tin decomposes steam and liberates H2.
![]()
Question 21.
Write an account of SiCl4.
Answer:
- Silicon tetrachloridel (SiCl4) is also called as silane.
- SiCl4 can acts as Lewis acid due to availability of 3d orbital in ‘Si’.
- SiCl4 undergoes hydrolysis and forms Si(OH)4
Uses:
- SiCl4 and NH3 mixture is used to produce smoke screens.
- Ultra pure Silicon is used to make transistors.
- SiO4 prepared from SiCl4 is used in epoxy paints, resins etc.
Question 22.
SiO2 is a solid while CO2 is a gas explain.
Answer:
- SiO2 is a solid because it has giant molecule structure with strong Si-0 single bonds.
- CO2 is gas because it is made up of descrete linear O=C=O molecules with weak vander wall forces.
Question 23.
Write the use of ZSM-5. [TS 19,20]
Answer:
ZSM -5 is one type of zeolite. It is used to convert alcohols directly into gasoline.
![]()
Question 24.
What is the use of dry ice? [AP 15]
Answer:
Dry ice (Solid CO2) is used as a refrigerant for ice-cream and frozen food.
Question 25.
How is water gas prepared? [AP 18]
Answer:
The mixture of CO and H2 is called water
Water gas is prepared by passing steam over red hot coke.

Question 26.
How is producer gas prepared? [TS 19]
Answer:
The mixture of CO and N2 is call ed producer gas.
Producer gas is prepared by passing air over red hot coke.

Question 27.
C-C bond length in graphite is shorter than C-C bond length in diamond. Explain.
Answer:
- Graphite has sp² hybridisation and C-C bond involves sp² – sp² hybridized carbon.
- Diamond has sp³ – hybridisation and C-C bond involves sp³ – sp³ hybridized carbon.
- If the ‘s’ character (in sp²) in a hybridised atom increases then the size of the hybridized orbital decreases. This results in more overlapping which leads to shorter bond length.
Question 28.
Diamond is used as precious stone. Explain.
Answer:
Diamond has high refractive index. Diamonds reflect & refract the incident radiations. So diamonds glitter due to total reflection. Hence, diamonds are used as precious stones in jewellery.
Question 29.
Carbon never shows co-ordination number greater than four while other members of carbon family show coordination number as high as six-explain.
Answer:
The maximum coordination number of carbon is 4 due to absence of d-orbitals in the outermost orbit. While other members of carbon family show maximum coordination number 6 due to the presence of d-orbitals in the outer most orbit.
Question 30.
Producer gas is less efficient fuel than water gas- explain.
Answer:
At Producer gas is less fuel efficient due to presence of large proportion of non combustible nitrogen in it.
Also due to less calorific value, producer gas is less fuel efficient.
![]()
Question 31.
SiF2-6 is known while SiCl2-6 is not. Explain. [AP 16,19]
Answer:
The reasons for non-existence of SiCl2-6:
- Six large chloride ions cannot be accommodated around Si4+ due to small size.
- Interaction between lone pair of chloride ion and Si4+ is not very strong.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the difference in properties of diamond and graphite on the basis of their structure. [TS 17]
Answer:
| Diamond | Graphite |
| 1) Diamond is the hardest material. It is bad conductor of electricity due to absence of free electrons. | 1) Graphite is soft. It is good conductor of electricity due to presence of free electrons. |
| 2) Each carbon is bonded to 4 other carbon atoms tetrahedrally. | 2) Each carbon is bonded to 3 other carbon atoms to form hexagonal rings. |
| 3) It is a 3 dimensional polymer. | 3) It is a 2 dimensional polymer. |
| 4) C – C bond length is 1.54 Å and bond angle is 109°28¹. | 4) C – C bond length is 1.42 Å and bond angle is 120°. |
| 5) Carbon atoms are strongly held by covalent bonds. | 5) The hexagonal layers of carbons are held by weak Vander Waal’s forces. |
| 6) sp³ hybridisation. | 6) sp² hybridisation. |
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the following.
a) PbCl2 reacts with Cl2 to give PbCl4.
b) PbCl4 is unstable to heat.
c) Lead is not known to form Pbl4.
Answer:
a) Pb can exist in its compounds in two
different oxidation states of+2 and +4. +2 +4
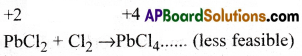
Due to inert pair effect, Pb is more stable in +2 than in +4 oxidation state.
So PbCL react with chlorine to form unstable PbCl4.
b) Pb2+ is more stable than Pb4+ due to inert pair effect. So PbCl2 is more stable than PbCl4. Thus on heating PbCl4 converts into stable PbCl2 by losing Cl2.
PbCl4 → PbCl2 + Cl2
c) PbI4 does not exist because I– ion is a powerful reducing agent. It reduces Pb4+ to stable Pb2+ion in solution. So PbI4 is not formed.
Question 3.
Explain the following:
(a) Silicon is heated with methyl chloride at high temperature in the presence of copper
(b) SiO2 is treated with HF.
(c) Graphite is a lubricant
(d) Diamond is an abrasive.
Answer:
(a) Silicon on heating with methylchloride at 300°C in the presence of copper catalyst gives dimethyl dichlorosaline.
![]()
(b)When Silica (SiO2) reacts with HF, it forms silicon tetra fluoride.
SiO2 + 4HF → SiF4 + 2H2O
(c) Graphite contains layer like structure and between two layers weak Vander waal forces of attractions are present. As a result, it is slippery in nature. Hence graphite is used as lubricant.
(d) Diamond contains three dimensional polymeric structure. Hence diamond has giant molecule structure.
Due to this giant molecular structure, diamond is very hard and having high melting point.
Hence diamond is abrasive in nature.
Question 4.
What do you understand by (a) Allotropy (b) inert pair effect (c) Catenation. [AP 19]
Answer:
(a) Allotropy:
The phenomenon of existence of an element in different physical forms having same chemical properties is called allotropy.
Crystalline allotropes of carbon are
(a) Diamond (b) Graphite
(b) lncrt pair effect:
The reluctance of’ns’ pair of electrons to take part in bond formation is known as inert pair effect. Kg; Lead exhibits +2 oxidation state as stable oxidation state due to inert pair effect (instead of +4 state).
(c) Catenation:
The phenomenon of self-linkage of atoms among themselves to form long chains (or) rings is called as catenation. [TS 18]
Carbon has highest catenation tendency due to its high bond energy (348 KJ/mole)
Question 5.
If the starting material for the manufacture of silicones is R SiCl3, write the structure of the product formed.
Answer:
When trichloro silane undergoes hydrolysis followed by polymerisation it forms cross linked silicones.
RSiCl3 + 3H2O → RSi(OH)3.
Condensation of the hydrolysed product gives three dimensional silicone.
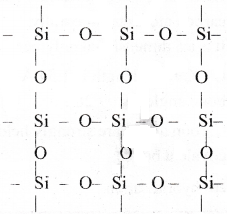
Question 6.
Write a short note on zeolites.
Answer:
- Zeolites are three dimensional alumino silicates.
- If some silicon atoms in three dimensional network silicon dioxide are replaced by aluminium atoms, then alumino silicate is formed.
- They acquire a negative charge which is balanced by cations like Na+, K-1, Ca2+ ions.
- Generally zeolites have cage like structures with cavities.
Uses:
- Zeolites acts as ion exchangers & molecular sieves.
- Used in softening of hard water.
- ZSM-5 Zeolite is used to convert alcohols directly into gasoline.
Question 7.
Write a short note on Silicates.
Answer:
Silicates :
Silicates are regarded as the metal derivatives of orthosilicic acid (H4SiO4). Most of the building materials are nothing but silicates.
Ex: Granites, slates, bricks and cement. Ceramics and glass are also silicates.
The Si-O bonds in silicates are very strong. They do not dissolve in any of the common solvents nor do they mix with other substances readily.
The silicates can be divided into six types.
(i) Orthosilicate or Nesosilicates:
Their general formula is M2(SiO4)
Ex: Willemite Zn2(SiO4)
(ii) Pyrosilicates or sorosilicates or Disil icatcs:
These contain Si2O7-6 units. Pyrosilicates are rare.
Ex: Thortvteitite Ln2(Si2O7)
(iii) Chain silicates:
They contain(SiO3)n2n- units
Ex: Spodumene LiAl (SiO3)2.
Amphiboles are one type chain silicates. Generally double chains are formed in them.
(iv) Cyclic silicates:
They are silicates having ring structures. They are formed of general formule (SiO3)n2n-. Rings containing three, four, six and eight tetrahedral units are known. But rings with three and six are the most common.
Ex: Beryl Be3Al2(Si6O18)
(v) Sheet silicates:
When SiO4 units share three comers the structure formed is an inifinite two dimensional sheet. The empirical formula is (SiO3)n2n-. These compounds appear in layer structures. They can be cleaved.
Ex: Kaolin Al2(OH)4 Si2O5.
(vi) Frame work silicates or three dimensional silicates:
Sharing all the four corners of a Si04 tetrahedron results in three dimensional lattice of formula SiO2.
Ex: Quartz, Tridymite, Cristobalite, Feldspar and ultramarine (Na8[Al6Si6O24]S2), zeolites.
![]()
Question 8.
What are silicones? How are they obtained.
Answer:
Silicones are a group of organo silicon polymers containing (R2Si-0) as repeating unit
Preparation:
First alkyl or aryl substituted chlorosilanes are prepared. These on hydrolysis followed by condensation, polymerisation gives polymeric silicones.
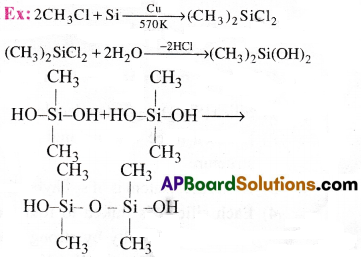
This reaction continue to give chain polymers. If water molecule is eliminated from the terminal OH groups of same chain cyclic Silicones are formed.
Question 9.
Write a short note on fuilerene.
Answer:
Fullerenes are the crystalline allotropic form of carbon with cage like structure.
Preparation:
These are formed by strong heating graphite in an electric arc, in presence of inert gases like He or Ar.
Properties of Fuilerene:
- In fuilerene, the carbon undergoes sp² hybridisation.
- C60 molecule has a shape like soccer ball and called “Buckminster fuilerene”.
- The spherical fullerenes are called bucky balls.
- It contains 20 six membered rings and 12 five membered rings. A six membered ring fused with six or five membered rings. But five membered ring can only fuse with six membered rings.
- Ball shaped fuilerene has 60 vertices and each one is occupied by one carbon atom and it is also contains both single and double bonds.

Question 10.
Why SiO2 does not dissolve in water?
Answer:
- Silica (SiO2) is giant molecule.
- It has a three dimensional polymeric structure.
- Each silicon atom is of sp³ hybridisation.
- Each silicon is linked to four oxygen atoms tetrahedrally by strong covalent bonds. So it does not dissolve in water. But at high pressures, if heated with water, it dissolves slightly.
Question 11.
Why is diamond hard? [TS 22]
Answer:
- In diamond, every carbon is in sp hybridisation. Every carbon is bonded with four other carbon atoms tetrahedrally.
- The structure extends in space and produce a rigid three dimensional network of carbon atoms.
- In this structure, directional covalent bonds are present throughout the lattice.
- To break these covalent bonds, very high energy is required. Therefore diamond is the hardest substance and thus can be used as abrasive.

Question 12.
What happens when the following are heated?
a) CaCO3 b) CaCO3 and SiO2
c) CaCO3 and excess of coke.
Answer:
a) CaCO3
CaCO3 on heating gives quick lime and liberates CO2.
![]()
b) CaCO3 and SiO2
CaCO3 on heating forms calcium silicate (CaSiO3) with SiO2
CaCO3 + SiO2 → CaSiO3 + CO2 ↑
c) CaCO3 and excess of coke
CaCO3 on heating with excess of coke forms calcium carbide(CaC2).
CaCO3 + 4C → CaC2 + 3CO
Question 13.
Why does Na2CO3 solution turn into a suspension when saturated with CO2 gas?
Answer:
By passing excess of CO2 through saturated solution of sodium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate is formed. Being sparingly soluble in water, it gets precipitated.
Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2 → 2NaHCO3
![]()
Question 14.
What happens when
a) CO2 is passed through slaked lime
b) CaC2 is heated with N2
Answer:
a) CO2 is passed through slaked lime:
When CO2 is passed through slaked lime, it turns milky due to the formation of insoluble CaCO3
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
If excess CO2 is passed, the milkyness disappears due to the conversion of insoluble CaCO3 to soluble Ca(HCO3)2.
CaCO3 + H2O + CO2 → Ca(HCO3)2
b) CaC2 is heated w ith N2:
On heating CaC2 with N2, a mixture of calcium cyanamide and graphite is fonned.

Question 15.
Write a short note on the anomalous behaviour of carbon in the group-14.
Answer:
Anomalous behaviour of carbon is due to small size, absence of d-orbitals and high nuclear charge.
Carbon differs from the other members of its group in the following respects:
- Carbon occurs in free state, whereas other elements of group-14 are almost not available in free state.
- Carbon does not contain d-orbitals in its valence shell while the other elements of its group contain d-orbitals.
- The maximum covalency of carbon is 4 whereas other elements exhibit a maximum covalency of 6.
- Carbon has a very high catenating ability.
- Carbon alone forms multiple bonds among themselves.
- Carbon forms a large number of hydrides known as hydrocarbons, which are thermally very stable. The other elements form limited number of hydrides which are thermally not very stable.
- Reducing nature of carbon is very high while the reducing nature of others is less.
- The halogen compounds of carbon are not hydrolysed, while the other halogen compounds are readily hydrolysed.
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are silicones? How are they prepared? Give one example. What are their uses?
Answer:
Silicones are organosilicon polymers, which contain -[R2 -Si -o}n as repeating unit. They are prepared in two stages.
1) In the first stage alkyl or aryl substituted chlororsilanes are prepared.
2) In the second stage, these are hydrolysed followed by condensation polymerisation.
Preparation:
When silicon is heated with alkyl or aryl halides, different methyl or aryl substituted
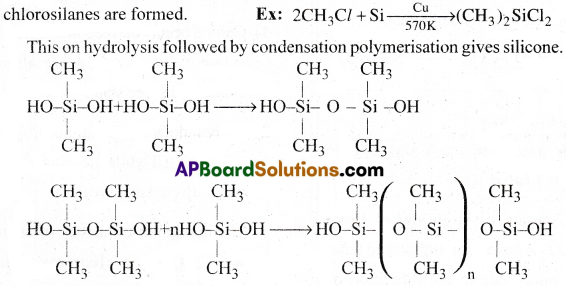
The chain length of the polymer can be controlled by adding (CH3)3 SiCl. This blocks the ends as shown below’.
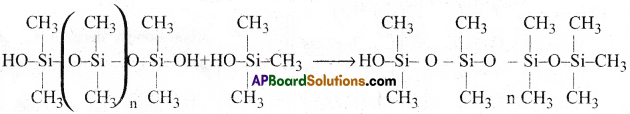
The alkyl and aryl groups present in silicones are water repelling in nature. They are thermally more stable. They have high dielectric constant. They are resistant to oxidation and chemicals.
They are used as sealants, greases, electrical insulators. They are used in making water proof fabrics. They are bio compatible. Hence they are used in surgical and cosmetic implants.
Question 2.
Explain the structure of silica. How docs it react with a) NaOH b) HF?
Answer:
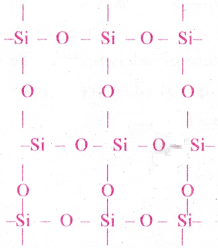
Structure of Silica:
In silica, each silicon atom is linked to four oxygen atoms by covalent bonds and they are arranged tetrahedrally around silicon atom. But each oxygen atom is surrounded by two silicon atoms only. SiO2 has a three dimensional giant Si molecular, structure
a) Reaction with NaOH:
Silica reacts with NaOH to form sodium silicate
2Na0H + SiO22 → Na2SiO3 + H2O
b) Reaction with HF:
Silica reacts with HF to form silicon tetrafluoride.
SiO2 + 4HF → SiF4 + 2H2O
Question 3.
Write a note on the allotropy of carbon.
Answer:
Allotropy:
The existence of an element in different physical forms but possessing similar chemical properties is known as allotropy.
Carbon has many allotropic forms. They are of both crystalline and amorphous. The crystalline allotropes of carbon are diamond, graphite and fullerenes.
Diamond:
In diamond, each carbon atom undergoes sp³ hybridisation and is in bond with four other carbon atoms in a tetrahedral form. This structure extends in space and produces a rigid three dimensional network of carbon atoms. These bonds are present throughout the lattice. To break all these extended bonds, large amount of energy is required. So diamonds are very hard and have high melting point. They are used as precious stones, abrasives, cutting tools etc.
Graphite:
Graphite has layered lattice structure, in which every carbon is in sp² hybridisation and in bond with three carbon atoms. The carbon atoms are arranged in sheets containing hexagonal rings. The fourth electron is in 7t bond and delocalised on all the carbon atoms in a sheet. The distance between the layers is 340 pm. They are held together by weak vander Waals forces. So they are slippery in nature. Hence graphite can be used as solid lubricant. Due to delocalised electrons graphite act as a good electrical conductor.
Fullerene:
Fullerene is a crystalline allotrope of carbon. Fullerenes are made by heating, graphite in an electric arc, in the presence of inert gas. The sooty material formed by condensation of vapour of carbon contains mainly C60 fullerene molecules. It is knowm as Buckminster fullerene. It has soccer ball shape.
C60 fullerene contains 20 six membered rings and 12 five membered rings. A six membered is fused with either six membered ring or with five membered ring. But a five membered ring is alw ays fused with six membered rings. All carbon atoms in fullerene are in sp² hybridisation and are in bond with three other carbon atoms. The fourth electron of carbon delocalises on all carbon atoms giving aromatic character to fullerene.
Question 4.
Write a short note on (a) Silicates (b) Zeolites (c) Fiilierenes
Answer:
a) Silicates :
Silicates compounds formed from the orthosilicic acid. All silicates have the basic structural unit SiO4-4 which has tetrahedral structure.
When discrete SiO4-4 unit is present in silicates they are called orthosilicates.
Different silicates are formed by joining a number of SiO4-4 units through the comers of SiO4-4 tetrahedron by sharing 1, 2, 3 or 4 oxygen atoms per silicate unit. Thus 1, 2, 3, 4 -Pyro, chain(or) ring, sheet or three dimensional silicates are formed depending on the number of oxygen atoms shared. Negative charge on the silicate is neutralised by the positive charged metal ions.
b) Zeolites :
Zeolities are three dimensional alumino silicates. If some silicon atoms in three dimensional network silicon dioxide are replaced by aluminium atoms then alumino silicate is formed. They will have some negative charge. To balance these negative charges some extra cations such as Na+, K1+, Ca2+ are present in these silicates.
Hydrated zeolites are used as ion exchangers in softening of hard water.
ZSM-5 is used as a catalyst in direct conversion of alcohols into gasoline.
c) Fiilierenes:
Fullerene is a crystalline allotrope of carbon. Fullerenes are made by heating graphite in an electrict arc in the presence of inert gas. The soot formed by condensation of vapour of carbon contains mainly C60 fullerene molecules. It is knowrn as Buckminster fullerenes. It has soccer ball shape.
C60 fullerene contains 20 six membered rings and 12 five membered rings. A six membered is fused with either six membered ring or with five membered ring. But a five membered ring is always fused with six membered rings. All carbon atoms in fullerene are in sp² hybridisation and are in bond with three other carbon atoms. The fourth electron of carbon delocalises on all carbon atoms giving aromatic character to fullerene.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Dry ice is
1) Solid NH3
2) Solid SO2
3) Solid CO2
4) Solid N2
Answer:
3) SoliclCO2
![]()
Question 2.
The correct order of atomic radii in group 13 elements is
1) B < Al < In< Ga < Tl
2) B < Al < Ga < In < Tl
3) B < Ga < Al < Tl < In
4) B < Ga < Al < In < Tl
Answer:
4) B < Ga < Al < In < Tl
Question 3.
Which one of the following elements is tinahle to form MF3-6 ion?
1) Ga
2) Al
3) B
4) In
Answer:
3) B
Question 4.
The most commonly used reducing agent is
1) AlCl3
2) PbCl2
3) SnCl4
4) SnCl2
Answer:
4) SnCl2
Question 5.
The element which exists in liquid state for a wide range of temperature and can he used tor measuring high temperature is
1) B
2) Al
3) Ga
4) In
Answer:
3) Ga
Question 6.
Ionisation enthalpy (∆i H1 kJ mol-1) for the elements of Group 13 follows the order.
1) B > Al > Ga > In > Tl
2) B < Al < Ga < In < Tl
3) B < Al > Ga < In > Tl
4) B > Al < Ga > In < Tl Answer: 4) B > Al < Ga > In < Tl
Question 7.
Which of the following oxides is acidic in nature?
1) B2O3
2) Al2O3
3) Ga2O3
4) In2O3
Answer:
1) B2O3
Question 8.
Which of the following is a Lewis acid?
1) AlCl3
2) MgCl2
3) CaCl2
4) BaCl2
Answer:
1) AlCl3
![]()
Question 9.
In the structure of diborane
1) All hydrogen atoms lie in one plane and boron atoms lie in a plane perpendicular to this plane.
2) 2 boron atoms and 4 terminal hydrogen atoms lie in the same plane and 2 bridging hydrogen atoms lie in the perpendicular plane.
3) 4 bridging hydrogen atoms and boron atoms lie in one plane and two terminal hydrogen atoms lie in a plane perpendicular to this plane.
4) All the atoms are in the same plane.
Answer:
3) 4 bridging hydrogen atoms and boron atoms lie in one plane and two terminal hydrogen atoms lie in a plane perpendicular to this plane.
Question 10.
Boric acid is an acid because its molecule
1) contains replaceable H+ ion
2) gives up a proton
3) accepts OH– from water releasing proton
4) combines with proton from water molecule
Answer:
3) accepts OH– from water releasing proton
Question 11.
BF3 is planar and electron deficient compound. Hybridization and number of electrons around the central atom, respectively are
1) sp² and 8
2) sp³ and 4
3) sp³ and 5
4) sp² and 6
Answer:
4) sp² and 6
Question 12.
Quartz is extensively used as a piezoelectric material, as it contains ______
1) Pb
2) Si
3) Ti
4) Sn
Answer:
2) Si
Question 13.
Catenation i.e., linking of similar atoms depends on size and electronic contlguration of atoms. The tendency of catenation in Group 14 elements follows the order:
1) C > Si > Ge > Sn
2) C > > Si > Ge ≈ Sn
3) Si > C > Sn > Ge
4) Ge > Sn > Si > C
Answer:
2) C > >Si > Ge ≈ Sn
Question 14.
Which of the following is incorrect statement?
1) SnF4 is ionic in nature
2) PbF4 is covalent in nature
3) SiCl4 is easily hydrolysed
4) GeX4 (X=F,Cl,Br,I) is more stable than GeX2
Answer:
2) PbF4 is covalent in nature
Question 15.
Cement, the important building material is a mixture of oxides of several elements. Besides calcium, iron and sulphur, oxides of elements of which of the group (s) are present in the mixture?
1) group 2
2) groups 2, 13 and 14
3) groups 2 and 13
4) groups 2 and 14
Answer:
2) groups 2, 13 and 14
Question 16.
Which of the following species is not stable?
1) [SiCl6]2-
2) [SiF6]2-
3) [GeCl6]2-
4) [Sn(OH)6]2-
Answer:
1) [SiCl6]2-
Question 17.
Identify the correct statements from the following:
A) CO2(g) is used as refrigerant for icecream and frozen food
B) The structure of C60 contains twelve six carbon rings and twenty five carbon rings.
C) ZSM-5 a type of zeolite, is used to convert alcohols into gasoline
D) CO is colourless and odourless gas
1) (A), (B) and (C) only
2) (A) and (C) only
3) (B) and (C) only
4) (C) and (D) only
Answer:
4) (C) and (D) only
![]()
Question 18.
Silicon has a strong tendency to form polymers like silicones. The chain length of silicone polymer can be controlled by adding
1) MeSiCl3
2) Me2SiCl2
3) Me3SiCl
4) Me4Si
Answer:
3) Me3SiCl