AP State Syllabus 9th Class Biology Solutions 5th Lesson Diversity in Living Organism
9th Class Biology 5th Lesson Diversity in Living Organism Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
Variations in organisms lead to diversity in living organisms. State reasons. (AS 1)
Answer:
- The presence of differences between organisms of the same species is called variation.
- Variation between different species is always greater than the animals within a species.
- The uniqueness of individual is the basis of the diversity that is shown by the living organisms.
- In our daily life, we see a variety of plants and animals in our locality.
- But if we go to some other places such as hills, forests or sea we entirely find different types of animals and plants.
- In fact, different parts of the world have their own typical kinds of living beings.
- Thus-we can say that variations in organisms lead to diversity in living organisms.
![]()
Question 2.
What was the basis for early classifications? (AS 1)
Answer:
- Living things are classified on the basis of their body structures.
- Living things are classified on the basis of dissimilarities and similarities.
- Charaka and Sushrut had classified plants on the basis of their medical importants.
- Parasar classified plants basing on the structure of flowers.
- Aristotle classified animals according to whether they lived on land, in water, or in the air.
Question 3.
What are the advantages of classifying organisms? (AS 1)
Answer:
Advantages of classifying organisms :
- Classification makes the study of various organisms easy.
- Classification helps to understand the inter relationships among different groups of organisms.
- Classification helps in exploring the diversity of life forms.
- Classification reveals evolution trends by showing simple body structures to complex body structures.
- Geographical distribution of plants and animals is entirely dependent on the information given by classification.
![]()
Question 4.
What is the need of classification? What questions will you ask? (AS 2)
Answer:
Need of classification :
- Classification gives better knowledge and better understanding of organisms that are studied.
- It helps to study the organisms in a proper and systematic manner.
- Classification helps to make comparison in an easier way.
- It helps in understanding relationship among the organisms and their interdependence.
- Classification makes our study more focused and helps us to handle huge population of organisms.
- Classification gives us an idea of evolution.
Questions:
1. Who made the classification?
2. What are the advantages of classification?
3. What are the recent developments being done?
Question 5.
How do monocots differ from dicots? (AS 1)
Answer:
| Monocotyledons | Dicotyledons |
| 1. In the seed embryo bears a single cotyledon. | In the seed, embryo bears two cotyledons. |
| 2. Monocots have parallel venation. | Dicots have reticulate venation. |
| 3. Monocotyledons have fibrous root system. | Dicotyledons have Tap root system. |
| 4. Examples are wheat, paddy etc. | Examples are Mango, Apple, Neem, etc. |
Question 6.
One day Kavita soaked seeds of green grams, wheat, maize, peas, and tamarind. After they became tender, she tried to split the seed. Name which would split, which would not, and identify them according to the characters. (AS 4)
Answer:
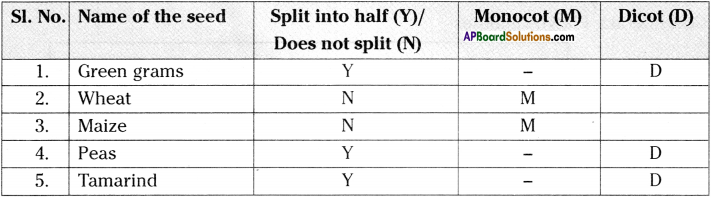
Question 7.
Make a flow chart of invertebrates in the kingdom Animalia, based upon their characteristic features. (AS 4)
Answer:
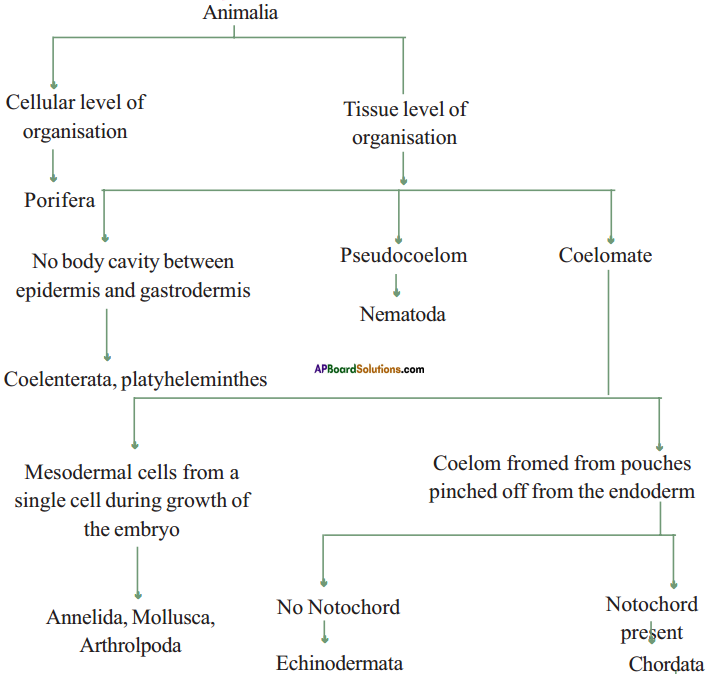
Question 8.
Write some common characters of Pisces, Reptilia, and Aves. (AS 1)
Answer:
- Pisces, Reptilia, and Aves belong to vertebrate.
- All these animals lay eggs.
- All these animals possess vertebral column.
Question 9.
Name the kingdom to which these organisms belong according to Whittaker. (AS 1)

Answer:
a) Protista
b) Animalia
c) Fungi
d) Monera
Question 10.
Explain how animals in vertebrata are classified into further subgroups. (AS 1)
Answer:
- Vertebrata can be further classified into sub groups on the basis of simple to complex body structures and their functions.
- For example, fishes have two chambered hearts, amphibians have three chambered hearts while in birds and mammals have four chambered hearts to keep the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood separate.
- The following characteristic features are considered for classifying vertebrate into the further sub groups.
| Class pisces: Characteristics: | Exoskeleton of scale, endoskeleton of bone, cartilage, breaths through gills. |
| Class Amphibia | Gills in larva, lungs in most adults, slimyskin. |
| Class Reptilia | Exoskeleton of scales, laying eggs on land only. |
| Class Aves | Exoskeleton of feathers, lay eggs outside water, flight possible. |
| Class Mammals | Exoskeleton of hair, external ears, mostly giving birth to live young ones. |
Question 11.
Platypus or Echidna is a group that forms a link between reptiles and mammals. Think and write about some characteristic features that these would have. (AS 4)
Answer:
- The platypus and echidna both belong to the group of animals known as monotremes.
- These two are characterised by the feature of egg laying mammals. Yet they are not birds or reptiles.
- Both creatures hatch their young from eggs, yet the mother of each species feeds her babies with milk from milk glands.
- These two are found in Australia and Tasmania.
- One of the characteristics of platypus is that it has an unusual duck like bill and does not have teeth an unusual characteristic for a mammal.
- Echidna, the spiny ant eater also does not have teeth. Tongue helps in feeding.
- Echidna and platypus young stay in burrow after they are hatched. Echidna develops a rudimentary pouch during breeding season.
- Both creatures have sharp claws for burrowing.
- Both the platypus and echidna like the water. Platypus hunt food in the water. Echidna regulates its temperature through swimming.
![]()
Question 12.
Sujata says Bat is not a bird but a mammal. How can you support Sujata’s statement?
Answer:
- Sujata’s statement that bat is not a bird but mammal is correct
- Like other mammals, including ourselves bats have hair or fur on their bodies.
- They are warm blooded animals.
- A baby bat that feed on its mother milk after it is born.
- Bats are the only mammals that can fly.
Question 13.
Which Phylum do I belong to? (AS 1)
a) My body is made of pores. I live in water. I do not have backbone also ……………….. .
b) I am an insect. 1 have jointed legs …………………. .
c) I am a marine living animal with spiny skin. My body is radially symmetrical ……………….. .
Answer:
a) Porifera
b) Arthropoda
c) Echinodermata
Question 14.
How can you appreciate the effort of scientists in classifying a wide range of organisms? (AS 6)
Answer:
- Classification makes the study of wide variety of organisms easy.
- It is essential to understand the inter-relationships among different groups of animals and plants.
- Classification gave us an idea of evolution of organisms from simple to complex ones.
9th Class Biology 5th Lesson Diversity in Living Organism InText Questions and Answers
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 59
Question 1.
Why do you think classification system has undergone changes over the years?
Answer:
Classification system has gone changes over the years due to the new discovered organisms, advancement in genetic science invention of powerful microscope.
![]()
Question 2.
If you were asked to classify organisms what would be your basis of classification?
Answer:
Our basis of classification would be whether the organism.
- Has a prokaryotic or eukaryotic cell
- Is unicellular or multicellular
- Is autotrophic or heterotrophic
- Mode of reproduction.
Like that, I classify the organism in an orderly manner.
9th Class Biology 5th Lesson Diversity in Living Organism Tissues Activities
Question 1.
Collect leaves from different plants, observe them carefully and fill the table.
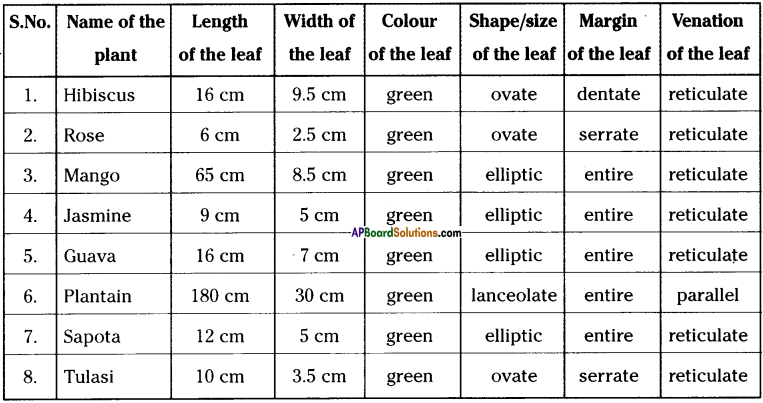
a) Could you find any two leaves which are similar with respect to any of the characters, size, shape, colour or any other as mentioned in the table?
Answer:
No. Every leaf has its size, shape and colour are same in many of the leaves.
b) Note down the differences you observed in the sample of leaves collected by you.
Write two such characters that differed most.
Answer:
1. Length and breadth of the leaves are different for each leaf.
2. Most of the leaves have reticulate venation but only in plantain parallel venation is present.
Question 2.
Collect 5 different plants from your surroundings and observe them carefully. Write your observations in the table given below.
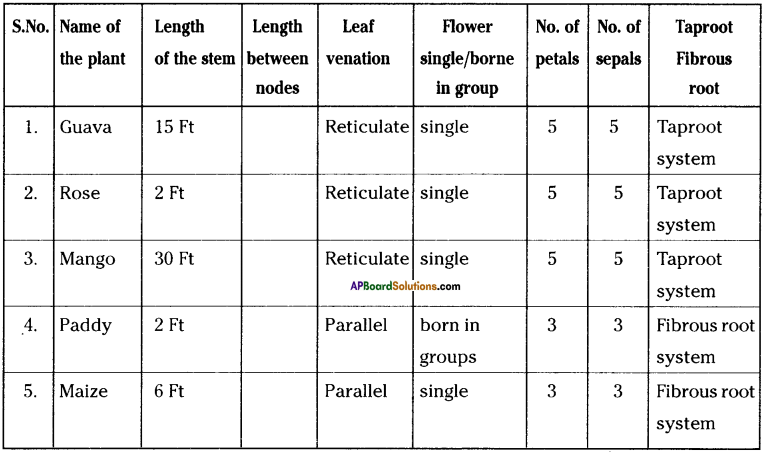
a) Which characters given above varied most?
Answer:
Length of stem, Inter nodal distance, venation in leaves, and in type of root system.
b) Select a character mentioned above which shows minimum diversity.
Answer:
Flower shows least diversity arrangement of flowers in bunches.
c) Did you find any similarities? What were they?
Answer:
Yes. Similarity in venation, number of sepals and petals, and in type of root system.
d) Did you find patterns like plants with fibrous roots had flowers borne in groups? Note the other patterns that you observed.
Answer:
Yes. The flowers are borne in groups, reticulate venation.
e) Carefully observe the plants collected by you and note down some other characters not mentioned in the table.
Answer:
Spine are present in rose plants whereas they are absent in other plants.
f) Did you notice any two plants which were alike with regard to the above characteristics? If not, note down what differences you found?
Answer:
No. Venation, root system are the differences.
![]()
Question 3.
How do you observe the number of cotyledons in different seeds? Write your findings in the table.
Answer:
Observing cotyledons in seeds :
- Collect seeds of plants from green gram, red gram, bengal gram, wheat, paddy, groundnut, maize and soak them for a day.
- Take a maize seed and press it between fingers.
- A small whitish structure come out of the maize seed.
- Whitish structure is known as embryo/baby plant.
- The portion left in our hand within the seed coat has a single cotyledon.
- Repeat the activity with soaked seeds by pressing them with fingers.
- Observe the pressed seeds with the help of a hand lens and fill the table.
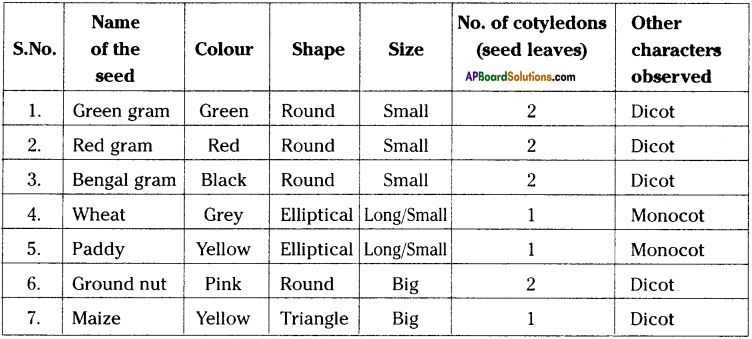
Activity – 4
Question 4.
Collect the plants or pictures of the plants to complete the following table.
Answer:
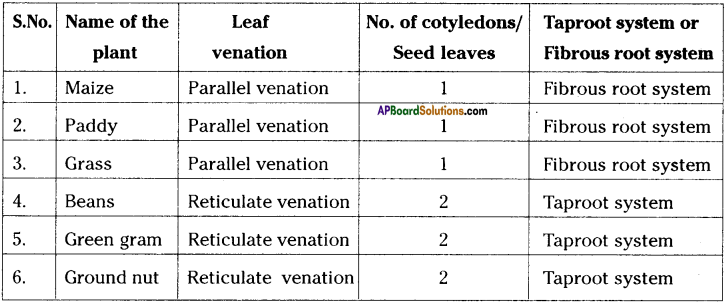
Activity – 5
Question 5.
Collect housefly, mosquito, ant, dung beetle, butterfly, moth and cockroach from your surroundings. Observe them with magnifying glass and fill the table.
Answer:
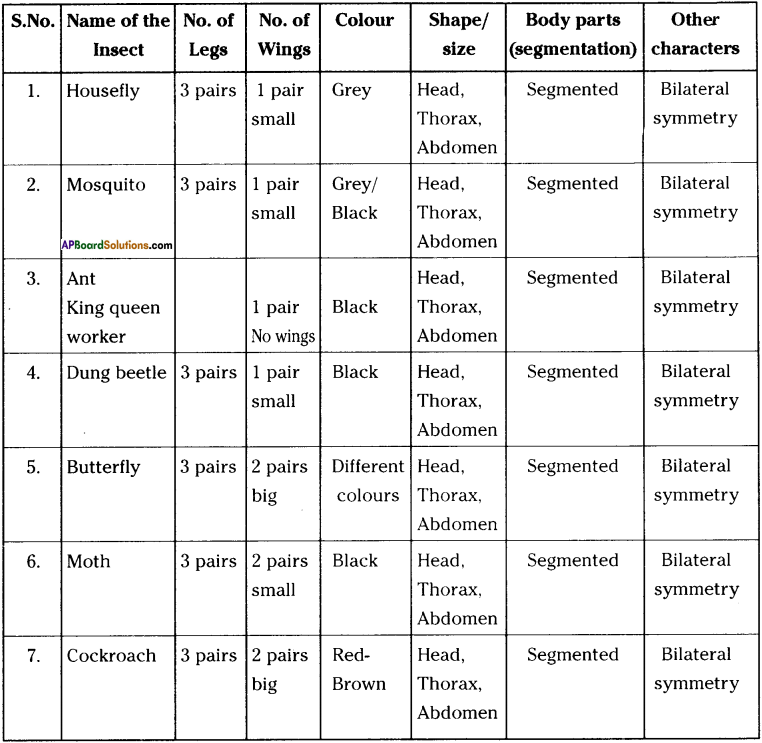
a) What differences did you observe with regard to legs?
Answer:
In some insects legs are large in size whereas in some like Cockroach, Butterfly the legs are big in size.
b) What differences did you observe with regard to wings?
Answer:
In ant, housefly, mosquito and in dungbeetle a pair of wings are present whereas in butterfly, moth and cockroach 2 pairs of legs are present. In some like ant, housefly, mosquito the wings are small whereas in others they are big in size.
c) Is there any relationship between the number of wings and legs?
Answer:
As the size of the wings increases the length of legs decreased. The number of legs in all the insects are 3 pairs whereas the wings are one or two pairs.
Activity – 6
Question 6.
In order to observe diversity in animals select 10 children from your class and fill the following table with their data.
Answer:
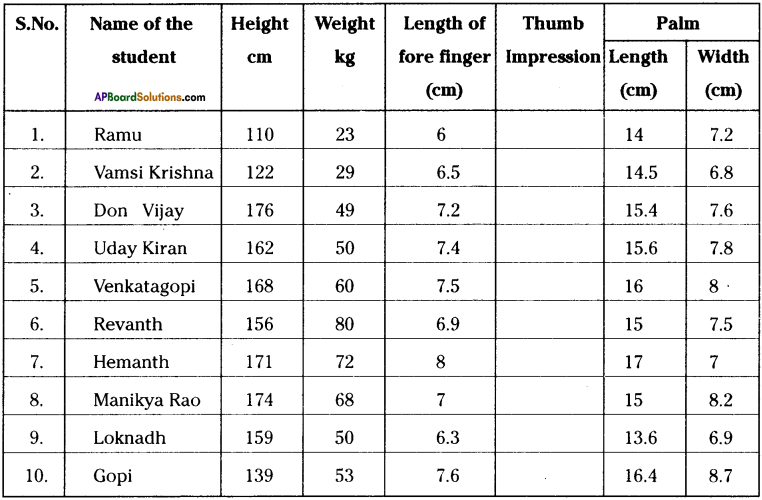
a) Which character helps you to make a group with maximum individuals?
Answer:
Height helps us to a group with maximum individuals.
b) Which character helps you to have just a single individual in a group?
Answer:
Thumb impression.
c) Compare your group table with that of other groups and note down the differences you found.
Answer:
Student’s activity.
d) Did you find same observations of any two students in your class?
Answer:
No.
Activity – 7
Question 7.
Collect two small almost equal sized neem plants from your surroundings observe them and fill the table.
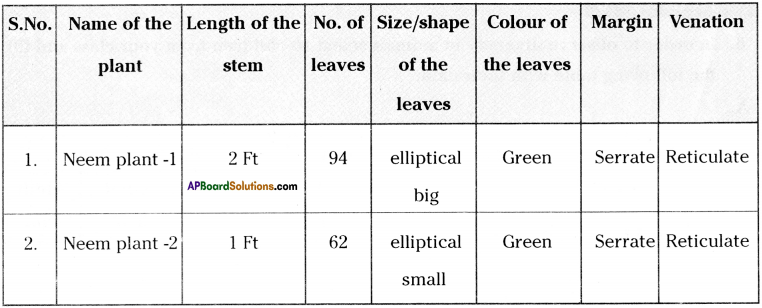
a) What differences did you find in the similar neem plants?
Answer:
The differences are in length of the stem and number of leaves.
b) Why do such differences present in nature?
Answer:
Every plant has got its own characteristics. The age of the plants also responsible for diverse characters.
Activity – 8
Question 8.
How do you observe moss plant through hand lens or dissection microscope? Draw the diagram and write the characteristics of moss plants.
Answer:
- Collect mosses from the greenish velvety growth on bricks during rainy season.
- Scrap a bit of the greenish velvety over a slide and observe under a dissection microscope.

Observations :
- The structure that are seen in moss plants are not flowers but they are spores.
- Spores are formed in Sporangium.
- Spores contain very little amount of food.
Lab Activities
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 67
Question 1.
Observe slide of Hydra under a microscope. Draw the diagram and write your finding.
Observations :

a) Is the body made of single cell or a group of cells?
Answer:
The body of Hydra is made up of number of cells.
b) Did you find any hollow structure inside the body?
Answer:
The hollow structure found inside the body is called coelom or body cavity.
c) Did you find any other characters in it?
Answer:
- The proximal or aboral end is drawn into a slender stalk on the end of which is the basal disc for attachment.
- The free distal end or oral end bears the mouth which is situated on hypostome.
- The hypostome is encircled by 6 -10 tentacles.
- Bud is present at side with a mouth or tentacles like the parent.
Question 2.
Observe slide of tape worm (Taenea Solium) under microscope and write its external characters. Draw diagram of it.
Observations :

a) How does the body look like?
Answer:
1) The body of Taenia Solium (Tape worm) is long, dorso- ventrally, flattened, narrow, ribbon like.
2) Body consists of scolex or head, neck and strobila or body segments.
b) Did you see a body cavity in it?
Answer:
There is no true internal body cavity or coelom.
c) How does the anterior and posterior look like?
Answer:
The anterior (head) is smaller than the head of a pin. The posterior (tail) is very long and bigger than head and neck.
![]()
Question 3.
Observe slide of round worm (Ascaris) and write the characters of it by drawing the figure.
Observations :
a) Does the body look like the same as in the platyhelminthes?
Answer:
The body is round and cylindrical but not flat as in tape worm.
b) What are the differences you observed between tape worm and round worm?
Answer:

Pseudocoelom is present, whereas it is absent in Tape worm. The head and tail are tapering at the ends.
Question 4.
Observe the specimen of earthworm and draw the diagram. Write its characters you have observed.
Observations :

Answer:
- The body of earthworm is bilaterally symmetrical and extensively segmented.
- The anterior end is tapering while posterior end is more less blunt.
a) Touch the skin of the earthworm and say how do you feel?
Answer:
The skin of earthworm is moist.
b) What is the colour?
Answer:
The colour of earthworm is dark brown in colour.
c) Are there any differences you observed in its body colour and among the body parts?
Answer:
The dorsal surface is darker than the ventral surface.
d) How does it move?
Answer:
Earthworm moves by alternate contractions of circular and longitudinal muscles.
e) Are there any ring like structures seen in its body?
Answer:
Ring like segments are present in earthworm.
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 68
Question 5.
Observe the specimen of Cockroach. Draw its diagram and write its characteristics.
Observations :
a) How does the skin look like? Did you observe any hard layer on the skin?
Answer:

The entire body of cockroach is covered by a hard brown Coloured chitinous exoskeleton.
b) How many parts is the body divided into?
Answer:
The body is segmented and distinctly divisible into three parts
- Head
- Thorax
- Abdomen.
c) Observe the legs and says how does it look like.
Answer:
Three pairs of legs are present. Each leg consists of five segmented. Jointed legs are present.
d) Name some more animals whose legs are jointed as seen in Cockroach.
Answer:
Prawn, scorpion, grasshopper, ant, mosquito have jointed legs.
Question 6.
Observe the snail by keeping inside a glass beaker and observe its characters.
Observations :

a) How does the outer body look like?
Answer:
The outer body is covered with shell.
b) Keep the snail unmoved for sometime and when it starts moving observe its body.
Answer:
The animal creeps by its ventral muscular foot. The movement is gliding movement.
c) Is the body soft or hard?
Answer:
The body of the snail is soft.
d) Did you find any antennae like structure in it?
Answer:
Yes, Tentacles are present.
Question 7.
Observe specimen of starfish and write your observations.
This specimen belongs to Phylum echinodermata.
Observations :
a) What do you find on the skin of the starfish?
Answer:

Spines are present on the skin of the starfish.
b) Are there any arms and ray shaped structure in it?
Answer:
Most of them are pentamemal, it means they have five fold symmetry with rays of arms in fives.
c) Do you find a small hole in the middle of the starfish?
Answer:
In the middle of starfish a small whole is present which is the mouth of it.
Question 8.
Collect a fish from a fish monger and observe its external characters.
External characters of fish :

a) Observe the skin of the fish. How does it look like?
Answer:
Body is covered with scales.
b) Write the body parts of the fish where scales are not present.
Answer:
On the head, on the tail, fins and on the lower side of the fish.
c) Open the mouth of the fish. What do you seen in it ?
Answer:
Teeth are present in the mouth. Tongue is also present.
Activity – 9
Question 9.
Try to find out the scientific names of at least 10 organisms that you see around you.
Answer:
Scientific names of plants around us :
| Name of the plant | Scientific name |
| 1. Mango | Mangifera indica |
| 2. Coconut | Cocos nucifera |
| 3. Thati | Borassus flabellifer |
| 4. Garika gaddi | Cynodon dactylon |
| 5. Paddy | Oryza sativa |
| 6. Plantain | Musa paradisica |
| 7. Banyan | Ficus bengalensis |
| 8. Indian Goose berry (Pedda Usiri) | Emblica Officinalis |
| 9. Thotakura | Amaranthus gangeticus |
| 10. Tulasi | Ocimum sanctum |
| 11. Teak | Tectona grandis |
| 12. Kanakambaram | Crossandra infundibuliformis |
| 13. Brinjal | Solanum melongena |
| 14. Sapota | Achras zapota |
| 15. Gaddi chamanthi | Tridax procumbens |
| 16. Dhaniyalu | Coriandrum sativum |
| 17. Guava | Psidium guajava |
| 18. Rose | Rosa grandiflora |
| 19. Chinta (Tamarind) | Tamarindus indica |
| 20. China rose Mandara | Hibiscus rosa-sinensis |
Scientific names of animals around us :
| Name of the animal | Scientific name |
| 1. Crow | Corvous splendens |
| 2. Sparrow | Passer domesticus |
| 3. Frog | Rana Tigrina |
| 4. Dog | Canis familiaris |
| 5. Cat | Felis domesticus |
| 6. Chimpanzee | Anthropithecus troglodytes |
| 7. Chicken | Gallus domesticus |
| 8. Pigeon | Columbialivia |
| 9. Buffalo | Bubalus bubalis |
| 10. Honey bee | Apis indica |
| 11. Earthworm | Pheretima posthuma |
| 12. Cockroach | Periplanata Americana |
| 13. Leech | Hirudinaria granulasa |
| 14. Prawn | Palaemon malcolmmsonii |
| 15. Housefly | Musca nebulo |
| 16. Snail | Pila globosa |
| 17. Owl | Bubo bubo |
| 18. Indian cobra | Naja naja |
| 19. Domestic horse | Equus cabalus |
| 20. Green parrot | Psittacula Krameri |
