These AP 9th Class Biology Important Questions 8th Lesson Challenges in Improving Agricultural Products will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Biology 8th Lesson Important Questions and Answers Challenges in Improving Agricultural Products
9th Class Biology 8th Lesson Challenges in Improving Agricultural Products 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are the three types of methods to get high yield?
Answer:
- Improving high yielding varieties.
- Using high yield management methods.
- Crop protection management.
Question 2.
What are macro nutrients? Give examples.
Answer:
Minerals that required by plants in larger quantities are called macronutrients.
E.g.: Nitrogen, Phosphorous, Potassium, Sodium.
![]()
Question 3.
What are micronutrients? Give examples.
Answer:
Minerals required in small quantities are called micro nutrients.
E.g.: Iron, Manganese, Boron, Zinc, Copper, Molybdenum, Chlorine, etc.
Question 4.
What is the major difference between short term varieties and long term varieties?
Answer:
Short term varieties produce grains more than long term varieties.
Question 5.
Give Examples of chemical fertilizers.
Answer:
NPK, Urea and Superphosphate are the examples of chemical fertilizers.
Question 6.
What is a vermi compost?
Answer:
It is the product or process of composting using worms usually earthworms is called vermi compost.
![]()
Question 7.
What is Kharif crop? Give two examples.
Answer:
Cultivation and harvesting of any domesticated plant sown in the rainy season.
Ex : Paddy, sugarcane, maize, etc.
Question 8.
What is Rabi crop? Give two examples.
Answer:
Agricultural crops sown in winter and harvested in the summer season.
Ex : Wheat, barley, sesame, etc.
Question 9.
What are mixed crops? What is the advantage of growing mixed crops?
Answer:
If more than one crop is cultivated in the same field then it is called mixed crop. Because of mixed crop cultivation, the soil becomes fertile.
![]()
Question 10.
Give a list of green manure crops.
Answer:
Crops which are grown in field and can be ploughed back into the soil for soil fertility are called green manure crops.
Ex : Sanhemp, Lobia, Green gram, Kulthi, Berseem.
Question 11.
Write two uses of biofertilizers?
Answer:
- Biofertilizers are useful to maintain soil health and productivity.
- They synthesize nutrients from environment and soil.
Question 12.
What is the benefit of crop rotation?
Answer:
Crop rotation help the farmer by adding nutrients in the place of lost nutrients.
![]()
Question 13.
What is hybridization?
Answer:
Hybridization is a process to yield high yielding variety of crops.
Question 14.
What is GMS?
Answer:
Genetically Modified Seeds are called GMS.
Question 15.
What is NPK?
Answer:
NPK is the chemical proportion of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potash. These are partially or completely synthetic in origin.
![]()
Question 16.
What are weeds?
Answer:
Unwanted plants which are grown in the crop field along with cultivated crop.
Question 17.
What are insecticides? Give one example.
Answer:
These are the poisonous chemical substances which destroy the insects in the crop field. These are sprayed on the insect affected crops.
9th Class Biology 8th Lesson Challenges in Improving Agricultural Products 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are the factors that cause increase in production of crop?
Answer:
- Production of crop depends on several factors.
- Only when there is a proper combination of several factors, the production can increase.
- Some of these factors include the kind of seeds planted, the properties of the soil, the availability and proper application of irrigation and fertilisers, the weather, con¬trolling insect attacks, the growth of seeds, and soon.
Question 2.
How to increase the food production?
Answer:
- Increasing the area of cultivated land.
- Increasing production in the existing land.
- Developing high yielding varieties.
- Alternative crops.
- Mixed crops.
- Cultivating short term crops like Rabi.
![]()
Question 3.
What is drip irrigation? What is its use?
Answer:
- Drip irrigation is a good practise in agriculture to prevent water wastage.
- In drip irrigation, water is supplied through small pipes.
- These pipes have small holes through which water passes drop by drop.
- Drip irrigation prevents wastage of water.
Question 4.
What is crop rotation? What is the benefit of crop rotation?
Answer:
- Crop rotation is the process in which one crop is followed by another crop on an agricultural field.
- When cereals are cultivated, more nutrients are utilised.
- If legumes are grown in the soil, less nutrients are utilised.
- Not only this, they synthesize some nutrients in the soil.
![]()
Question 5.
What is mixed crop? What are its uses?
Answer:
If more than one crop is cultivated in the same field then it is called mixed crop.
Uses:
- Because of mixed crop cultivation the soil becomes fertile.
- The nutrients which are used by one crop will be regained by cultivating another crop.
E.g.: Soya grown along with Pea.
Pea grown along with Green gram.
Cotton grown along with Groundnut.
Question 6.
What are Green Manure Crops? Give examples.
Answer:

- Some crops are grown so that they can be ploughed back into the soil. They are known as Green manure crops.
- Some examples are berseem, kutthi, sunhemp, lobia, green gram, etc.
Question 7.
What are the functions of soil testing centre?
Answer:
- At these centres the soil technologist collects soil samples from fields and tests the fertility levels of soil.
- They give us knowledge about the soil.
- The testing centres are situated in division and district levels.
Question 8.
What is organic farming? What are its uses?
Answer:
- To maintain soil productivity organic farming came into existence.
- In this type of farming, farmers use natural manures and natural pest controlling methods and they also practise crop rotation and mixed crop systems.
Question 9.
What are the advantages of water shed management?
Answer:
- The water shed increases the moisture in the soil and prevents soil erosion as tree roots hold the soil firmly.
- When there are many trees close by as in a forest, all of them together hold large quantities of water.
![]()
Question 10.
Write briefly about hybridization.
Answer:
- By using hybridization methods the seeds with desired characters are developed.
- Biotechnologists develop hybrid varieties by crossing between two plants which have genetically different characters and they developing new variety with useful characters.
- The hybrid varieties that are produced by hybridization techniques are high yielding, disease-resistant can thrive on less rainfall, and will grow in acidic soils also.
Question 11.
| Nutrient | Uses |
| Nitrogen | New leaves, flowers arise fast. |
| Phosphorous | Penetrates roots deep into the soil to absorb nutrients quickly. |
| Potassium | Resistance towards pests, increases the quality of smell, colour and taste of fruits. |
Now answer the following questions.
1) Name the nutrient that is responsible for formation of new fruits and leaves.
2) Name the nutrient that is responsible for increase in the quality of smell, colour, and taste of fruits.
Answer:
- Nitrogen
- Potassium
Question 12.
Write the differences between mixed cropping and intercropping.
Answer:
| Mixed cropping | Inter cropping |
| 1. Seeds : Seeds of different crops are mixed before sowing. | 1. Seeds of different crops are not mixed. |
| 2. Pattern : There is no pattern of sowing. | 2. The different crops are sown in separate rows and strips. |
| 3. Inputs : Lesser inputs of irrigation and nutrients are required. | 3. Requirement of inputs is compariti- vely more. |
Question 13.
What are the advantages of hybridisation?
Answer:
- Due to this, high yielding plants are produced.
- It makes varieties in disease resistant plants.
Question 14.
Write the differences between manure and Fertilizer.
Answer:
| Manure | Fertilizer |
| 1. It consists of organic matter. | 1. It consists of inorganic matter. |
| 2. It is eco-friendly in nature. | 2. It is not eco-friendly in nature. |
| 3. It is prepared by animal excreta and plant wastes. | 3. It is prepared commercially from chemicals. |
Question 15.
Write the uses of manures.
Answer:
Manures helps in
- improvement of soil structure
- increase in water holding capacity
- soil enrichment with nutrients
Question 16.
Why is soil replenishment essential? State one natural method of soil replefiishment.
Answer:
By growing same crop year after year in the same soil, the soil shows depletion in certain nutrients. Cropping in this field year after year leads to drop in production of crops. Crop rotation and mixed cropping are very useful in soil replenishment.
Question 17.
What are the major group activities involved for improving of crop yields?
Answer:
- Crop variety improvement programme
- Crop production improvement
- Crop protection improvement
![]()
Question 18.
How do deficiency of nutrients affect the crop?
Answer:
Deficiency of any nutrient affects physiological process in plants including reproduction, growth, and disease resistance.
Question 19.
What are the uses of crop rotation?
Answer:
- Improves fertility of the soil.
- It minimises the pest diseases.
- It controls weeds.
- It avoids depletion of a particular nutrient from soil.
Question 20.
The fields, in which legumes are grown, get enriched with nitrogen why?
Answer:
The roots of legumes have nodules on their roots which fix the atmospheric nitrogen due to which the land gets enriched with Nitrogen. Therefore, legumes are grown in a season alternating between cereal crops such as wheat and millet.
Question 21.
What is drip irrigation?
Answer:
Drip irrigation is a practice in agriculture to prevent water wastage. In this method, water is supplied through small pipes. These pipes have small holes where water pass through drop by drop.
Question 22.
Write some suggestions to improve food production.
Answer:
We should use
- High yielding seed
- Suitable irrigation system
- By using fertilizers and pesticides in a prescribed way
- Right time of sowing seeds.
9th Class Biology 8th Lesson Challenges in Improving Agricultural Products 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write a short note on organic manure.
Answer:
- The organic manure is produced by decaying the plant and animal wastes.
- The manure produced from decomposed plants and animal products has more organic material.
- This gives good nutrients to the soil. It makes the soil fertile.
- Because of humus, the natural manure, water holding capacity of soil is increased.
- Natural organic manures are generally divided into two types. One is concentrated organic manure and the other is macro organic manure.
- Groundnut, gingilli, castor, coconut, neem, jatropa seed powders are the examples of concentrated organic manures.
- Animal excreta, compost, deep hitter are the examples of macro organic manure.
- Nutrients are rich in the concentrated manures than in macro organic manures.
- Plant and animal residues in the field such as stalks and roots, cow dung, urine, etc as organic manure.
Question 2.
How is the natural manure Panchagavya is prepared?
(OR)
An Agricultural Officer who encourages Organic farming wants to demonstrate preparation of natural manure by using five main ingredients of cow products. Prepare a note on it as a lab record.
Answer:

- The main ingredients of Panchagavya are milk, curd, ghee, dung, and urine of cow.
- Mix cow dung and cow ghee.
- Settle it for four days. On the fifth day, add urine, milk, and curd of cow.
- Also add kallu, coconut water, and sugarcane juice to the mixture and then add banana paste.
- Settle it for ten days. Stir the material morning and evening.
- Then we will get panchagavya the only sprayer type of manure.
- 3% of panchagavya is helpful to grow crop with higher yielding.
- It is also used as food for hens and fish in ponds.
Question 3.
What are the uses of nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium?
Answer:
Uses of nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium :
| Nutrient | Uses |
| Nitrogen | New leaves, flowers arise fast. |
| Phosphorous | Penetrates roots deep into the soil to absorb nutrients quickly. |
| Potassium | Resistance towards pests, increases the quality of smell, colour and taste of fruits. |
Question 4.
What are bio-fertilizers? Give examples.
Answer:
Some microorganisms which are useful to synthesise nutrients from the environment or from soil to plants. These are called microbial cultures or bio-fertilizers.

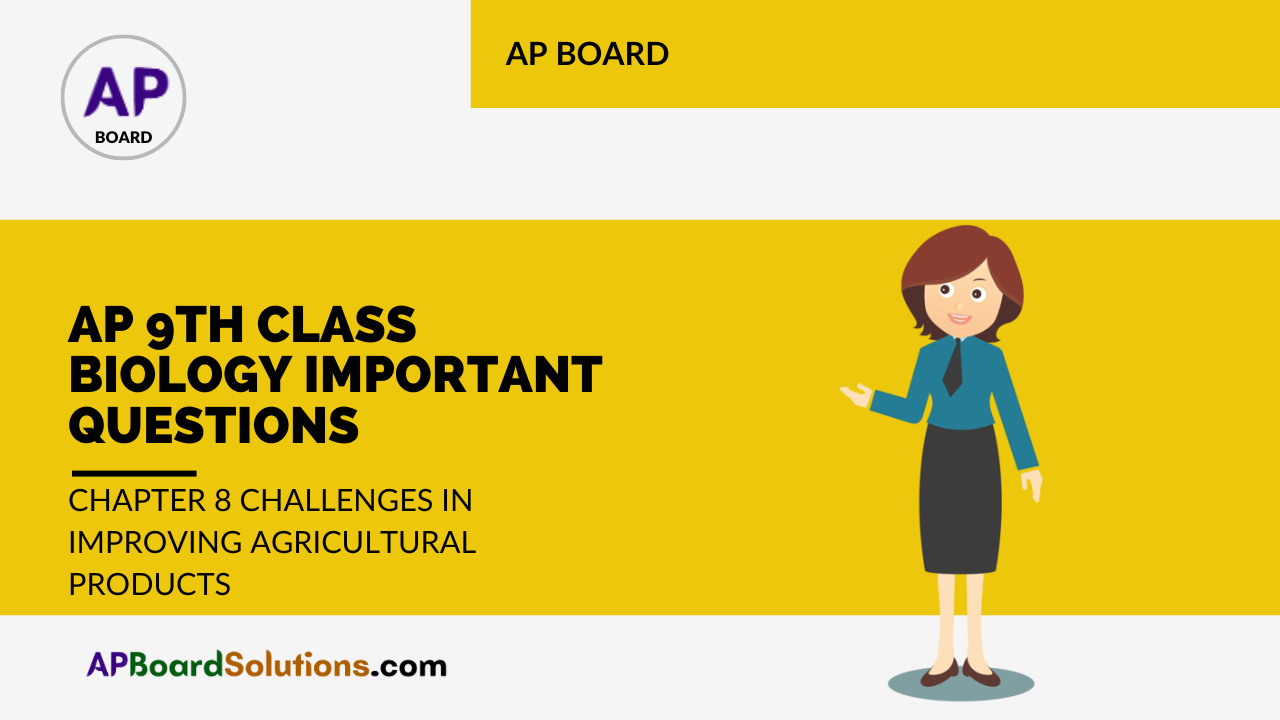
Question 5.
How vermi compost is prepared?
Answer:

- Construct 10 × 1 × ½ metres vermi compost beds in sheds which protect these beds from direct sunlight and rain.
- Collect coconut, banana, and sugarcane leaves, coconut coir, and dry black gram plants.
- Made them into 3 to 4 inches layer. This layer was wet with water.
- Collect house hold waste of dry cattle dung from the village to fill the bed.
- After two weeks of making bed, they kept thousand earth worms per square meter and covered the bed with gunny bags to maintain 30/6 to 40/6 of moisture.
- After 60 days we can collect our first manure.
- Second time, we will get the manure within 40 to 45 days.
- Every year we get the manure 6 times from these beds.
- Thus, vermi compost is prepared.
Question 6.
How Green revolution has changed the life style of farmers in India?
Answer:
- By Green revolution, the production of crops has been increased tremendously.
- Agriculture has become an industry and provides new avenues for work and fulfilment. Ecological balance may occur by the product of the green revolution.
- The soil may become fertilizer dependent. Plants are more dependent on pesticides which affect soil fertility man and animal health.
9th Class Biology 8th Lesson Challenges in Improving Agricultural Products Important Questions and Answers
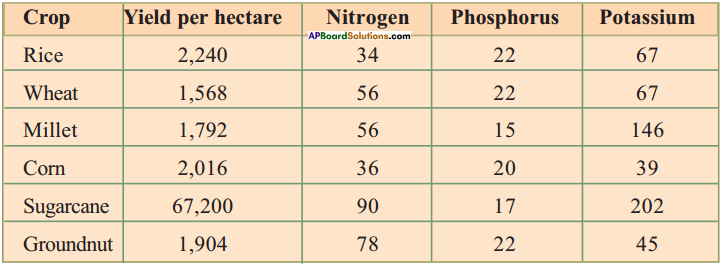
Question 1.
Absorption of salts by different crops (Units: Kg/Hectares/Season)
| Nutrient | Uses |
| Nitrogen | New leaves, flowers arise fast. |
| Phosphorous | Helps roots to penetrates deep into the soil to absorb nutrients quickly. |
| Potassium | Resistance towards pests, increases the quality of smell, colour and taste of fruits. |
a) In which crop new leaves arise fast? Why?
b) In which crop roots do not penetrate deep into soil?
c) Which crop show more resistance to pests? Why?
d) From the above table, cultivation of which crop yields more to farmer?
Answer:
- Sugarcane crop. Because it utilise nearly 90% of Nitrogen. Nitrogen is responsible for formation of new leaves.
- Millet crops.
- Sugarcane
- Sugarcane
Question 2.
How do you appreciate the role of earthworms in helping farmers?
Answer:
- Earthworms are known as “friends of farmers”.
- Earthworms make the soil loose and enables it to aerate.
- They make the soil rich with organic fertilizers and reduce the farmer’s investment on chemical fertilizers.
- They also help the farmer in improving the crop productivity and soil quality.
Question 3.
If a farmer cultivating one type of crop then what happend?
Answer:
- The crop productivity decreases.
- Soil fertility gradually decreases.
- Attack of pests on crops will increase.
![]()
Question 4.
Read the paragraph carefully and answer the questions given below.
Generally farmers use synthetic pyrethroids like pesticides, insecticides to control pests on crops. Farmers are also using so many natural pest controlling techniques.
1. Which concept in agriculture explains the above information?
2. Name some synthetic pesticides and insecticides.
3. Distinguish between synthetic insecticides and natural insecticides.
4. Write about any two natural insect control methods.
Answer:
- Crop protective methods.
- D.A.P. super phosphate, D.D.T, Heptachlore.
- Artificial pesticides are nothing but poisonous chemicals. They harm and kill the pests but also the useful friendly insects which are useful in pollination. Natural pesticides are the insects which feed on pests that destroy crops.
Ex : Dragon fly, spiders, mirids, lady bird beetle. - a) By introducing “Bacillus thuringiensis” we can protect our crops,
b) By adapting mixed crop cultivation we can reduce pests naturally.
Question 5.
The fields of Ramaiah and Somaiah are in the same area. Both cultivated the cotton crop. Ramaiah got good crop yield than Somaiah. Guess the reasons for low crop yield of Somaiah.
Answer:
- He selected high crop yield variety of cotton.
- He used better crop management methods for high yielding.
- He used better pest controlling method to get high crop yield.
- He used soil friendly fertilizers to get high yield of crop.