SCERT AP 7th Class Science Study Material Pdf 7th Lesson Reproduction in Plants Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 7th Class Science 7th Lesson Questions and Answers Reproduction in Plants
7th Class Science 7th Lesson Reproduction in Plants Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
I. Fill in the blanks.
1. Hibiscus propagated by _______ .
2. The male reproductive part in a flower is _______ .
3. The lower swollen part in gynoecium is _______ .
Answer:
1. stem
2. Stamens dr Androecium
3. Ovary
II. Choose the correct answer.
1. The plant which reproduces through leaves is
a) Bryophyllum
b) Rose
c) Hydrilla
d) Balsam
Answer:
a) Bryophyllum
2. The reproductive part in a plant is
a) Root
b) Stem
c) Leaf
d) Flower
Answer:
d) Flower
![]()
3. The agents of pollination are
a) Air
b) Water
c) Insects
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
III. Matching
| A) Potato | 1. Stem cuttings |
| B) Bryophyllum | 2. Seeds |
| C) Sugarcane | 3. Leaves |
| D) Neem tree | 4. Eyes |
| E) Banana | 5. Anther |
| 6. Suckers |
Answer:
| A) Potato | 4. Eyes |
| B) Bryophyllum | 3. Leaves |
| C) Sugarcane | 1. Stem cuttings |
| D) Neem tree | 2. Seeds |
| E) Banana | 6. Suckers |
IV. Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
Identify whether the sentences below are true or not. Correct the statements which are not true
a) The flowers in pumpkin are unisexual.
b) Seeds are formed in asexual reproduction.
c) Generally, roses are propagated through seeds.
Answer:
a) The flowers in pumpkin are unisexual. This statement is true.
b) Seeds are formed in asexual reproduction. This statement is false. Seeds are formed in sexual reproduction.
c) Generally, roses are propagated through seeds. This statement also false. Generally, rose plants are propagated through a vegetative propagation method called stem cuttings.
Question 2.
What do you call the transfer of pollen grains to the stigma? Explain its types with the help of labelled diagrams.
Answer:
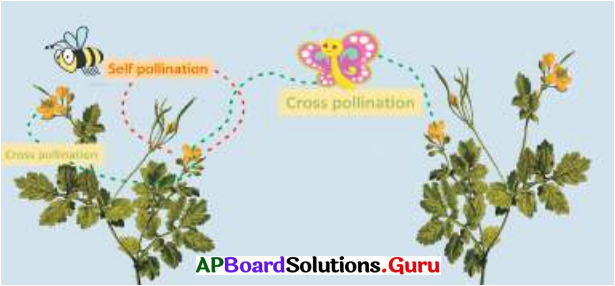
- The process of transferring pollen grains from the anther to stigma is known as POLLINATION.
- If the pollen grains are transferred from the anther of a flower to stigma of the same flower, is known as SELF POLLINATION.
- If the transfer of pollen grains takes place from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower, it is called CROSS POLLINATION.
Question 3.
Can plants produce new plants without the seeds? Explain those methods with the help of examples.
Answer:
- Yes, Some plants can produce new plants without seeds. This method of reproduction without formation of seeds is called asexual reproduction.
- In some plants asexual reproduction occurs through some vegetative parts like stem, roots and leaf. Such a propagation is called vegetative propagation.
- When the banana plants grow, a small new plant rises from the base of mother plant. Such small plants are called suckers (pilakulu). If we separate them and plant, they grow as new plants.
- If we cut the sugarcane stem into pieces with at least one node and plant it in the soil. After few days new plants will develop from the nodes.
- In Jasmine and chrysanthemum plants, small new plants arise from the underground stem of the mature parent plant. They are called layers. If these are separated from the parental plant and plant them in soil they grow into a new plants.
- If we cut the mint twigs with nodes and sow them in soil, they develops roots and give the crop.
- Potatoes have notches on them called eyes. If they are cut and plant in the suitable soil they gives rise to new potato plants.
- In addition to these natural vegetative propagation methods, some artificial vegetative propagation methods such as stem cuttings, layering and grafting are also helpful to grow new plants with out seeds.
![]()
Question 4.
What happens if the pollen of mango flower reaches the stigma of guava flower?
Answer:
- If the pollen of mango flower reaches the stigma of guava flower, fertilization does not occur.
- Fertilization occurs freely between the individuals of the same specious (type).
- But mango and guava plants belong to two different specious.
- So, there will be no fertilization and formation of new plants.
Question 5.
If all the honeybees in nature become extinct. Imagine, what will be the consequences.
Answer:
- Honeybees visit the flowers in search of nectar.
- When insects come in contact with a flower, the pollen grains stick to their legs and wings.
- Then insects visit another flower, the pollen fall on its slimy stigma.
- Thus they play key role in pollination, intern helps in fertilization and formation of seeds.
- If all the honey bees in nature become extinct, the fertilization in plants will reduce tremendously.
- This results in the extinction of several specious of plants.
- Agricultural productivity also will reduce to a great extent.
- So we should stop indiscriminate use of chemical pesticides and protect honey bees.
Question 6.
What are the materials required, procedure and precautions taken by you in the lab activity conducted to study the parts of Datura flower?
Answer:
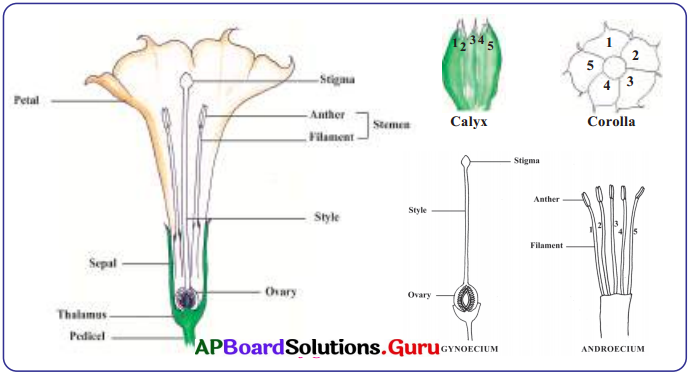
AIM: To observe the parts of a flower.
Material required:
Two datura flowers, new blade, magnifying glass, pencil. Procedure: Hold a datura flower by its stalk and observe its external features. Now draw the diagram of that flower in the box given below. Note down your observations. Now cut the second datura flower vertically into two equal parts from bottom to top. Check that all parts are cut into two equal halves. Observe and draw the internal view.
Precautions:
We should be careful while cutting the flower as the new blade is sharp and may cause injury. We should not inhale the pollen as it may cause allergy.
Question 7.
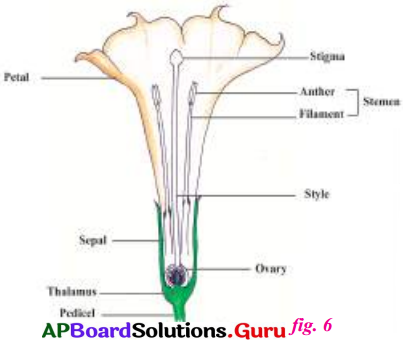
Draw the diagram of a complete flower and label the parts.
Answer:
Question 8.
Rahul goes to a field trip with his classmates, he tries to catch an insect on a flower. Do you support this?
Answer:
- No, I never support Rahul.
- Insects on the flowers helps in pollination and there by fertilization.
- Catching and killing such insects effects the fertilization.
- This leads to decrease the productivity of plants.
- This hampers the propagation of that plants also.
- All the organisms on this planet have the equal right live.
- Killing of other organisms just for fun is a cruel act Which leads to imbalance in the nature.
- “Live and let live” should be out motive.
![]()
Question 9.
Venkat, lives in a city. He maintains a roof garden at the top of his six storied building. The ridge gourd creeper bears plenty of flowers. But the flower do not grow into ridge gourds. Can you give him any suggestions to get ridge gourds?
Answer:
- Flowers should pollinate and fertilize to form fruits.
- Flowers on the ridge guard plant are unisexual flowers.
- So, self-pollination is not possible.
- For Cross pollination pollinating agents such as insects are required.
- To allow the insects, if there is any net surrounding the plants, those should be removed.
- Should not spray harmful chemicals on plants.
- Along with ridge guard, other attractive flowers having nectar should be grown in the roof garden.
- As a last trial do artificial pollination. (Transfer the pollen from male flower to the stigma of the female flower.)
Question 10.
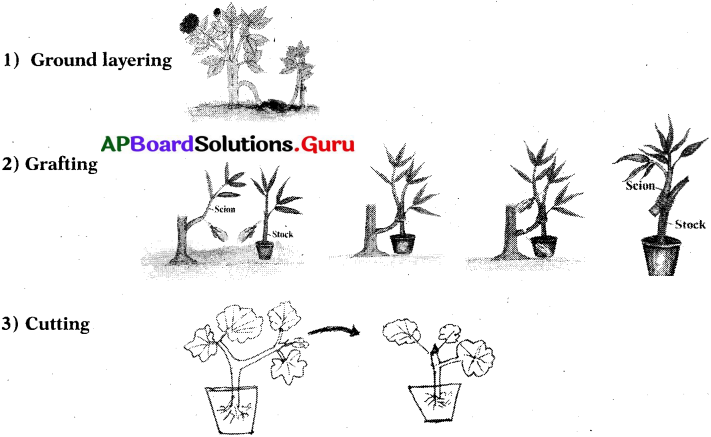
Draw the various methods of Artificial propagations on a chart and exhibit in your classroom.
Answer:
7th Class Science 7th Lesson Reproduction in Plants InText Questions and Answers
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 2
Question 1.
Can we grow all plants by planting their stems?
Answer:
No, we cannot grow all the plants by planting their stems.
Question 2.
How do new plants grow from the stems?
Answer:
New plants grow from the stems with some vegetative propagation methods.
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 3
Question 3.
Have you ever seen seeds in Banana?
Answer:
In general we never found seeds in most of the hybrid banana varities. In certain varities of banana we can find small seeds. But in the wild varities we can find large sized seeds.
Question 4.
Have you ever seen seeds in Jasmine?
Answer:
Yes, I have seen seeds in Jasmine plants. Jasmine plants give long fruits from their flowers. These fruits contain seeds.
![]()
Question 5.
Did you observe how the Hibiscus plant propagate?
Answer:
Hibiscus plant propagate by means of stem cuttings.
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 6
Question 6.
What would your mother have done to grow a basil / tulasi plant in your house?
Answer:
My mother sow the seeds of basil / tulasi in soil to grow the basil plant.
Question 7.
She might have put some seeds in the soil. Isn’t it?
Answer:
Yes. She would sow some seeds in the soil to get new plants.
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 7
Question 8.
Which part of the plant form the fruit?
Answer:
Flower form the fruit.
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 9
Question 9.
Do bitter gourd flower have whorls?
Answer:
No, bitter gourd flower has only three whorls. Either androecium or gynoecium are absent in them.
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 11
Question 10.
Do you know which part of the flower will develop into a fruit?
Answer:
- Ovary develop into fruits.
- Ovules develop into seeds.
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 12
Question 11.
Think, what changes will take place in the flower after fertilization?
Answer:
- After fertilization, the ovary ripens and turns into fruit. ’
- The remaining floral parts will fall off.
- The ovules become the seeds.
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 13
Question 12.
In which cup we observe healthy plants?
Answer:
The second cup contains healthy plants.
![]()
Question 13.
If all the seeds of a plant fall at the same place, how do the baby plants grow?
Answer:
- Baby plants will suffer from deficiency of nutrients, water and place.
- Their growth will be stunted.
Question 14.
Will they get sufficient place, nutrients, water to grow? What will happen if plants grow in such conditions?
Answer:
- Plants will not have enough space to grow freely.
- They will not get adequate amounts of nutrients and water.
- They do not obtain healthy growth.
Question 15.
Do you have any idea that how plant overcome this situation?
Answer:
- To overcome this problem, plants adopt different methods to disperse their seeds.
- Seed dispersal takes place with the help of various agents.
Think & Respond
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 12

Question 1.
Why do some plants produce small and numerous seeds?
Answer:
- All the seeds of a fruit should be able to germinate to produce new plants. Actually, it does not happen in nature.
- All the seeds don’t germinate, some will germinate but die before their maturity. Some of the seeds never germinate.
- To over come all these problems, plants produce a large number of seeds.
Question 2.
Why do some seeds have wings?
Answer:
- This type of winged seeds are dispersed by wind.
- These wings help the seeds to move easily by winds to settle in a suitable place to germinate.
Question 3.
Why are some seeds with more fibre?
Answer:
- Fibres make seeds light weight and help in floating.
- These seeds dispersed through water for longer distance.
Ex : Coconut.
![]()
Question 4.
Why do some pods of dry fruits explode?
Answer:
- Some pods of dry fruits explode is a mechanical reaction.
- In such way that they scatter the seeds all around.
- In this way they dispersal the seeds.
Question 5.
Why do some seeds have hairs?
Answer:
- Hairs help the seeds to travel in air.
- Long haired seeds are travel long distances in air.
- In that way seeds are settle at a suitable place to germinate.
Ex : Calotropis.
Question 6.
Why are many fruits sweet and fleshy?
Answer:
- Animals, birds and human beings eat these fruits and the seeds are thrown away.
- Like that way, seeds will be dispersed to different places.
- For the purpose of reproduction many fruits are sweet and fleshy,
Question 7.
Why do some seeds-have hooks?
Answer:
- Seeds have hooks and thorns, help them to stick to the animals
- So they travel one place to another place. Ex : Xanthium, urena, grass.
Question 8.
Why are some seeds heavy and round?
Answer:
- Seeds that are heavy and round are dispersal by water.
- They fall into the bottom of water
- They carried by the flow of water for long distances.
Ex : Seeds of Lotus.
Question 9.
Why are some seeds are delicate and small?
Answer:
- This type of seeds are dispersed through winds
- They are delicate, small, light in weight and hairy.
- These qualities enable them to travel with the mind and settle at a suitable place to germinate
Activities and Projects
Question 1.
Collect information from elders, internet or your school library regarding the method of vegetative propagation in Onion, Garlic, Ginger, Gladioli, Sweet potato, Bryophyllum, Begonia.

Answer:
| Plant | Method of vegetative propagation |
| 1. Onion | New plants grow from bulbs. |
| 2. Garlic | Individual garlic cloves are planted and they each produce a bulb. |
| 3. Ginger | New plants are propagated through rhizomes. |
| 4. Gladioli | New plants are propagated through corms (modified stems). |
| 5. Sweet potato | New plants grow from modified roots. |
| 6. Bryophyllum | New plants grow from the buds on the leaves (Epiphyllons buds) |
| 7. Begonia | New plants grow from buds on the leaves (Epiphyllons buds) |
Question 2.
Grow a plant using seeds and exhibit in the classroom record its growth.
Answer:
Activities
Activity – 1
Question 1.
Discuss with your friends and teachers and fill the table given below with ‘Yes’ or ‘No’ options. Answer the questions given below.
| Name of the plant | Reproduce through seeds | Reproduce without seeds |
| 1. Jasmine (malli) | Yes | Yes |
| 2. Tamarind (chinta) | Yes | No |
| 3. Curry leaf (Karivepaaku) | Yes | Yes |
| 4. Banana (Arati) | Yes | Yes |
| 5. Coriander (kottimeera) | Yes | No |
| 6. Drumsticks (munaga) | Yes | No |
i) Which plants are reproduce through seeds?
ii) Which plants are reproduce without seeds?
iii) Which plants are reproduce by both means?
Answer:
i) Tamarind, Coriander, Drumsticks plants repr oduce through seeds.
ii) Jasmine, Curry leaf, Banana plants reproduce without seeds.
iii) Jasmine, Curry leaf and some Banana plants reproduce by both means.
![]()
Activity – 2
Sheet For Lab Activity
Student Name : _____________________________________________
Date : _____________________________________________
AIM: To observe the parts of a flower.
Material required:
Two datura flowers, new blade, magnifying glass, pencil.
Procedure :
Hold a datura flower by its stalk and observe its external features. Now draw the diagram of that flower in the box given below. Note down your observations.
Parts of the flower :

External parts :
SEPALS:
Colour : Green Petal
Shape : Round tubular
Number : 5
Are they United/Separate ? United PETALS:
Colour : White
Shape v : Round tubular
Number : 5
Are they United/Separate? United
Procedure:
Cut the second datura flower vertically into two equal parts from bottom to top. Check that all parts are cut into two equal halves. Observe and draw the internal view.
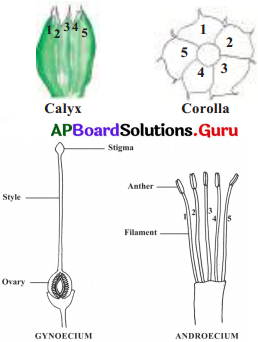
Internal parts:
ANDROECIUM:
Colour : White
Shape : Thin filamentous
Number : 5
Are they United/Separate?
Separate
GYNOECIUM: Style
Colour : Light Yellow
Shape : Long tube like
. swollen at the base Ovary
Number : 1-Ovary – style – stigma
Are they United/Separate ? Separate Gynoecium
Activity – 3
Question 3.
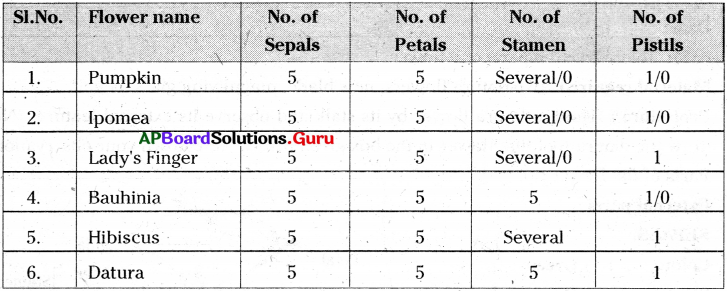
Collect different varieties of flowers from your school garden. Take each flower and count the parts in it. Record the details in the given table.
i) Which flowers have all four whorls?
ii) Mention the flowers in which one or two whorls are missing.
iii) Write the whorl \ whorls which are missing.
Answer:
i) Lady’s fingers, Hibiscus and Datura flowers have all the four whorls.
ii) In Pumpkin, Bauhinia, Ipomea flowers one or two whorls are missing.
iii) Either androecium or gynoecium are missing.
Give examples for complete flowers …………………, ………………………, ………………….
Hibiscus, Datura etc.
Give examples for incomplete flowers …………………., …………………
Pumpkin, Ridge gourd, etc.
Activity – 4
Question 4.
Collect flowers of hibiscus, papaya, ridge gourd and some other flowers. Fill the table given below by observing the androecium and gynoecium.
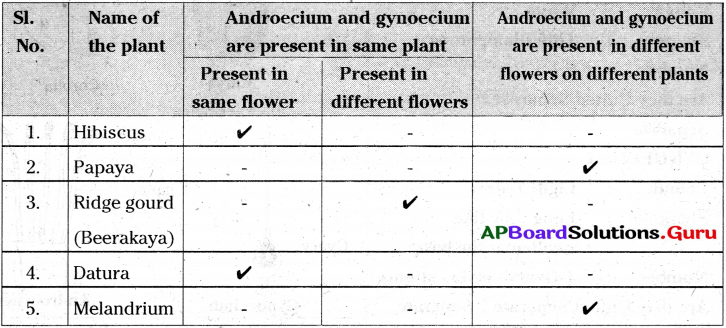
i) In which plants either androecium or gynoecium is present?
ii) In which plants both androecium and gynoecium are present in the same flower?
iii) In which plant both androecium and gynoecium are present separately in different flowers of the same plant?
iv) In which plant both androecium and gynoecium are present in different flowers of different plants?
Answer:
i) Papaya, Ridge gourd, Bitter gourd
ii) Hibiscus, Datura.
iii) Ridge gourd, Bitter gourd
iv) Papaya
Activity – 5
Question 5.
How do you prove that seed dispersal is necessary for plants?
Answer:
- Take two cups with soil.
- Take a handful of mustard seeds in the first cup and only four mustard seeds in the second cup.
- Pour equal amount of water daily and observe them regularly for 15 days.
Observations:
- Numerous plants germinated in the first cup. They do have not enough space to grow freely. They are also not getting sufficient nutrients and water to grow. The plants present in the first cup are not healthy.
- In the second cup, the four mustard seeds germinated into new plants. They have enough space, water and nutrients to grow. They are healthy.
Inference:
All the plants try to spread their seeds to distant places to increase the chances of survival and propagation. So, they adopt different methods to disperse their seeds. It occurs with the help of different agents.
![]()
PROJECT : Page No. 13
Question 6.
Now Collect information about various agents of seed dispersal from internet, your school library or by observing your surroundings. Make a Scrap book with pictures and your illustrations. And fill the below table with at least three examples each.
| Agents of dispersal | Name of the seeds/fruit |
| Wind | Calotropis. Milk weed, Dandelion, Maple |
| Water | Coconut, Lotus, Water Lily |
| Animals | Guava, Tomato, Seeds of grass plants |
| Bird | Neem, Thorn apple, Cucumber, Achyranthus |
| Man | Sugarcane, Wheat, Pulses |
| Any other | Bhendi, Mustard, Kanakambaram |
