AP State Syllabus AP Board 6th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 10 Practical Geometry Unit Exercise Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 6th Class Maths Solutions 10th Lesson Practical Geometry Unit Exercise
![]()
Question 1.
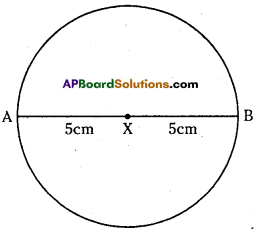
Construct a circle with centre X and diameter 10 cm. Sol. Given diameter of circle d = 10 cm
Solution:
We know that radius of circle r = \(\frac{d}{2}=\frac{10}{2}\) = 5
So, radius of the circle is 5 cm.
Now, draw a circle with radius 5 cm.
Question 2.
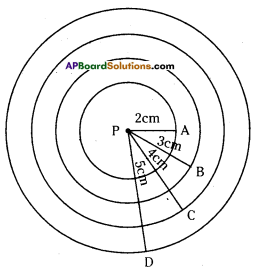
Draw four circles of radius 2 cm, 3 cm, 4 cm and 5 cm with the same centre P.
Solution:
Radii of four circles are PA = 2cm, PB = 3cm, PC = 4cm and PD = 5cm with the same centre P was constructed.
![]()
Question 3.
Draw the angles given below using a protractor.
(i) 75°
(ii) 15°
(iii) 105°
Solution:
(i) 75°
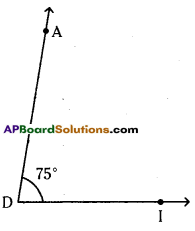
∠ADI = 75°
Steps of construction :
- Draw a ray \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{DI}}\) with vertex D.
- Place the centre point of the protractor at D and the line be aligned with DI.
- Mark a point A at 75°.
- Join DA. ∠ADI = 75° is formed.
Hence the required angle ∠ADI = 75° is constructed.
ii) 15°
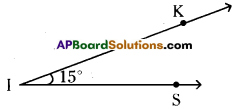
∠KIS = 15°
Steps of construction:
- Draw a ray \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{IS}}\) with vertex I.
- Place the centre point of the protractor at I and the line be aligned with \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{IS}}\).
- Mark a point K at 15°.
- Join IK.∠KIS = 15° is formed.
Hence the required angle ∠KIS = 15° is constructed.
(iii) 105°
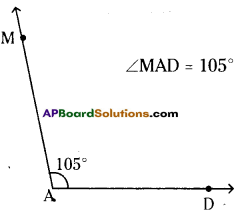
∠MAD = 105°
Steps of construction:
- Draw a ray \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AD}}\) with initial point A.
- Place the centre point of the protractor
at A and the line be aligned with \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AD}}\). - Mark a point M at 105°.
- Join AM.∠MAD = 105° is formed.
Hence the required angle∠MAD = 105° ¡s constructed.
![]()
Question 4.
Construct ∠ABC = 50° and then draw another angle ∠XYZ equal to ∠ABC without using a protractor.
Solution:
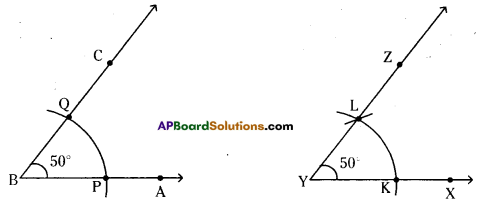
Given ∠ABC = 50° and ∠XYZ = 50°.
Steps of construction:
- Construct ∠ABC = 50°by using protractor.
- By taking any radius draw arcs from B on AB and BC at P and Q respectively.
- Draw a ray \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{YX}}\) with initial point Y.
- By taking BP as radius draw an arc on \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{YX}}\) from Y which meets at K.
- Draw arc from Y by taking PQ as radius in the ∠BAC which cuts the previous arc and mark it as L. Now draw \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{YZ}}\). So, ∠XYZ = 50° is formed.
Hence ∠XYZ = 50° is constructed which is equal to ∠ABC = 50°.
Question 5.
Construct ∠DEF = 60°. Bisect it, measure each half by using a protractor.
Solution:
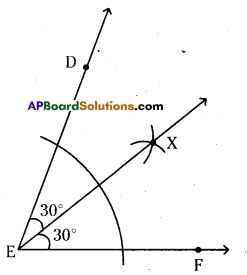
Given ∠DEF = 60°
Draw EX as the bisector of ∠DEF.
So, ∠DEX = ∠XEF = \(\frac{\angle \mathrm{DEF}}{2}=\frac{60^{\circ}}{2}\) = 30°
∴ ∠DEX = ∠XEF = 30°
