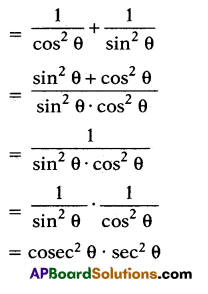These AP 10th Class Maths Chapter Wise Important Questions Chapter 11 Trigonometry will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP State Syllabus 10th Class Maths 11th Lesson Important Questions and Answers Trigonometry
Question 1.
If sin A = cos A, then find the value of A.
Solution:
If sin A = cos A
\(\frac{\sin A}{\cos A}=\frac{\cos A}{\cos A}\) = 1
⇒ tan A = 1 = tan 45° ⇒ A = 45°
(OR)
sin 45° = cos 45°
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\)
So, A = 45°
Question 2.
Find the value of x, if 2 sinx = √3
Solution:
2 sinx = √3
sin x = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
sin x = sin 60°
∴ x = 60°
![]()
Question 3.
Evaluate
(i) cos 76° – sin 14°,
(ii) \(\frac{\tan 73^{\circ}}{\cot 17^{\circ}}\)
Solution:
To find the values of the following :
i) cos 76° – sin 14°
We can write cos 76 as cos (90 – 14)
∴ cos 76 = cos (90 – 14) = sin 14
(∵ cos (90 – θ) = sin θ)
∴ cos 76° – sin 14°
= sin 14° – sin 14° = 0 ………… (1)
(ii) \(\frac{\tan 73^{\circ}}{\cot 17^{\circ}}\) = \(\frac{\tan (90-17)}{\cot 17}\)
= \(\frac{\cot 17^{\circ}}{\cot 17^{\circ}}\) = 1
(∵ tan (90 – θ) = cot θ
Question 4.
Find the value of tan245° + cot2 30°.
Solution:
tan2 45° + cot230°
= (1)2 + (√3)2
= 1 + 3 = 4
Question 5.
Find the value of sin2 30° + cos2 60°.
sin 30° = \(\frac{1}{2}\),cos 60° = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
sin2 30° + cos2 60° = (\(\frac{1}{2}\))2 + (\(\frac{1}{2}\))2
= \(\frac{1}{4}\) + \(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{2}{4}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
∴ sin2 30° + cos2 60° = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 6.
If sin (A + B) = 1 and cos B = \(\frac{1}{2}\), then find ∠A and ∠B. (0° < A + B ≤ 90°)
Solution:
sin (A + B) = 1
sin (A + B) = sin 90°
A + B = 90°
cos B = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
cos B – cos 60°
∴ ∠B = 60°
∴ ∠A = 90° – 60° = 30°
Question 7.
Simplify cot2θ – \(\frac{1}{\sin ^{2} \theta}\)
Solution:
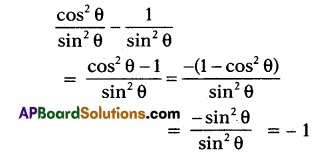
Question 8.
Does sinθ \(\frac{5}{3}\) exist for an acute angle θ?
Give reason.
Solution:
Given ‘θ’ is acute => 0° < θ < 90°
So sin 0° = 0 and sin 90° = 1
So for 0° < θ < 90°,
sin θ value lies in between zero and one.
So sin θ value cannot be greater than 1.
So sinθ = \(\frac{5}{3}\) does not exist.
![]()
Question 9.
If sin x = \(\frac{3}{4}\), then what is the value of cosec x?
Solution:
If sin x = \(\frac{3}{4}\)
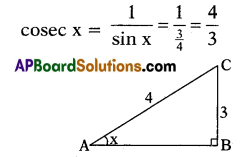
Question 10.
Among sin 90°, cos 90°, tan 90°, cot 90°, sec 90° and cosec 90°; which is/are not defined ?
Solution:
sin 90° =1
cos 90° = 0
tan 90° = not defined
cot 90° = 0
sec 90° = not defined
cosec 90° = 1
∴ tan 90°, sec 90° are not defined.
Question 11.
Express (sec2 x – 1) (cot2 x).
Solution:
(sec2 x – 1) (cot2 x)
= (tan2 x) (cot2 x) [∵ sec2A – tan2A = 1 sec2 A – 1 = tan2 A]
= \(\frac{\sin ^{2} x}{\cos ^{2} x} \cdot \frac{\cos ^{2} x}{\sin ^{2} x}\) [∵ tan A = \(\frac{\sin \mathrm{A}}{\cos \mathrm{A}}\) cot A = \(\frac{\cos \mathrm{A}}{\sin \mathrm{A}}\)]
= 1
Question 12.
Find ∠B, if tan (A – B) = \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) and sinA = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\). Also find cos B. (A, B < 90°)
Solution:
tan (A – B) = \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\)
∴ tan (A – B) = tan 30°
∴ A – B = 30°
sin A = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
sin A = sin 60°
∴ A = 60°
substituting A – B = 30°
60° – B = 30°
B = 30°
Question 13.
If tan A = \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) and tan B = √3 , then find sin A. cos B + cos A . sin B.
(A, B < 90°).
Solution:
Given, tan A = \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) = and tan B = √3
Given A, B < 90°
We know \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) = tan 30°
so tan A = \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) = tan 30°
⇒ A = 30° …………….. (1)
and tan B = √3 = tan 60°
⇒ B = 30° …………….. (2)
then
sin A cos B + cos A sin B
= sin 30° cos 60° + cos 30° sin 60°
Which can be written as
sin (A + B) = sin (30+60) = sin 90 = 1
∴ sin A cos B + cos A sin B = 1
(or)
sin 30 . cos 60 + cos 30 . sin 60
= \(\frac{1}{2} \cdot \frac{1}{2}+\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \cdot \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}+\frac{3}{4}=\frac{4}{4}\) = 1
Question 14.
Prove that
tan2A – sin2A = tan2A . sin2A.
Solution:
tan2A – sin2A
= \(\frac{\sin ^{2} A}{\cos ^{2} A}\) – sin2A
sin2A (\(\frac{1}{\cos ^{2} A}\) – 1 )
= sin2A (sec2A – 1)
= sin2A. tan2A
![]()
Question 15.
If cos A = \(\frac{7}{25}\), then find sin A and cosec A. What do you observe?
Solution:
Given that cos A = 7/25
sin2 A = 1 – cos2 A
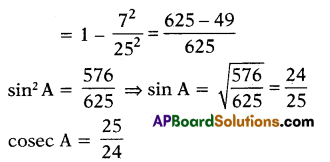
I observed that sin A . cosec A = 1.
Question 16.
If tan 2A = cot (A – 18°), where 2A is an acute angle. Find the value of A.
Solution:
tan 2A = cot(A – 18°)
= cot[90 – [90 – (A – 18°)]]
tan 2A = tan [90 – (A – 18°)]
2A = 90-(A – 18°) = 90 – A + 18°
⇒ 3A = 108°
∴ A = 36°
Question 17.
If 4 tan θ = 3, then find the value of sec θ and cosec θ.
Solution:
4 tan θ = 3 ⇒ tan θ = \(\frac{3}{4}\)
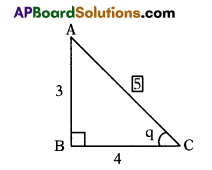
AC = \(\sqrt{\mathrm{BC}^{2}+\mathrm{AB}^{2}}\) = \(\sqrt{4^{2}+3^{2}}\) = 5
sec θ = \(\frac{5}{4}\); cosec θ = \(\frac{5}{3}\)
Question 18.
If tan 2A = cot (A – 27), where 2A is an acute angle, find the value of A.
Solution:
Given that 2A is an acute angle.
We know if tan = α = cot β (α, β acute) then α + β = 90°
(∵ tan (90 – θ) = cot θ)
So from given
tan 2A = cot (A – 27)
⇒ 2A + A – 27 = 90
⇒ 2A + A = 90 + 27
⇒ 3 A = 117 ⇒ A = \(\frac{117}{3}\) = 39
∴ A = 39°
Question 19.
Prove that
\(\sqrt{\frac{1+\sin A}{1-\sin A}}\) = sec A + tan A
Solution:

Question 20.
Evaluate (sin x – cos x)2 + (sin x + cos x)2.
Solution:
(sin x – cos x)2 + (sin x + cos x)2
= sin2 x + cos2 x – 2 sin x cos x + sin2 x + cos2 x + 2 sin x cos x
= 2(sin2x + cos2x) = 2(1) = 2
![]()
Question 21.
cos A = \(\frac{12}{13}\), then, find sin A and tan A
Solution:
Given, cos A = \(\frac{12}{13}\)
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
132 = 122 + x22
169 = 144 + x2
x2 = 25 ⇒ x = 5
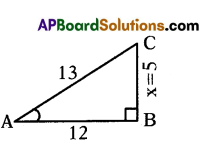
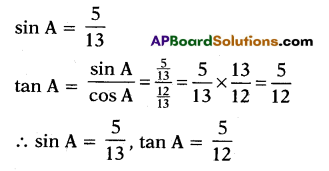
Question 22.
If 4 sin2 θ – 1 = 0 then find θ’ (θ < 90) also, find the value of θ and the value of cos2 θ + tan2 θ
Solution:
Given 4 2 θ – 1 = 0 ⇒ 4 2 θ = 1
2 θ = \(\frac{1}{4}\) ⇒ sin θ = ± \(\sqrt{\frac{1}{4}=} \pm \frac{1}{2}\)
Given θ is less than 90°
sin θ = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
sin θ = sin30° ⇒ θ = 30°
cos θ = cos = 30° \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
tan θ = tan 30° = \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\)
cos2 θ + tan2 θ = cos2 30° + tan2 30°
= (\(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\))2 + (\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\))2
= \(\frac{3}{4}+\frac{1}{3}\) = \(\frac{9+4}{12}\) = \(\frac{13}{12}\)
Question 23.
Prove that: (sin θ – cosec θ)2 + (cos θ – sec θ)2 = cot2 θ + tan2 θ – 1
Solution:
(sin θ – cosec θ)2 + (cos θ – sec θ)2
= sin2θ + cosec2θ – 2 sinθ . cosecθ . + cos2θ + sec2θ – 2 cosθ . sec θ
= (sin2θ + cos2θ) + cosec2θ + sec2θ – 2 – 2
= 1 + (1 + cot2θ) + (1 + tan2θ) – 2 – 2
= cot2θ + tan2θ + 3 – 4
= cot2θ + tan2θ – 1
Question 24.
If cosec θ + cot θ = p, show that \(\frac{p^{2}+1}{p^{2}-1}\) = sec θ.
Solution:
cosec θ – cot θ = p
∴ cosec θ – cot θ = \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{p}}\) ……………….(1)
cosec θ + cot θ = p …………..(2)
(1) + (2), We get
2 cosec θ = p + \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{p}}\) = \(\frac{p^{2}+1}{p}\) …………..(3)
cosec θ – cot θ = p
cosec θ – cot θ = \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{p}}\)
(1) – (2), We get
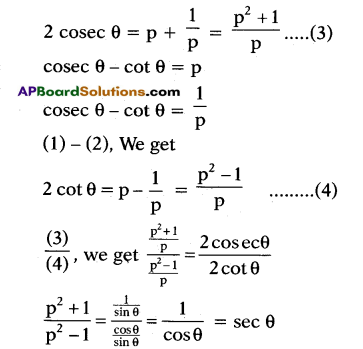
Hence proved.
Question 25.
Prove that (1 + tan2θ) + (1 + \(\frac{1}{\tan ^{2} \theta}\)) = \(\frac{1}{\sin ^{2} \theta-\sin ^{4} \theta}\)
Solution:
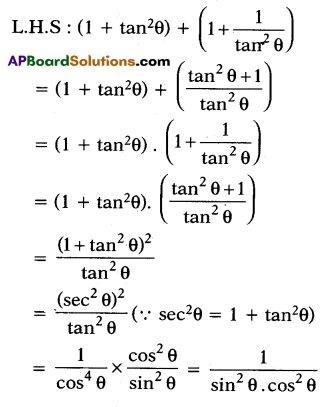
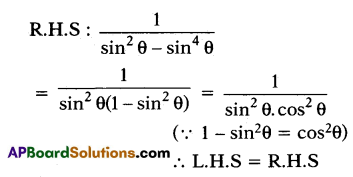
Question 26.
If sec θ + tan θ = p, then prove that sin θ = \(\frac{\mathbf{p}^{2}-1}{\mathbf{p}^{2}+1}\)
Solution:
sec θ + tan θ = p
sec2 θ – tan2 θ = 1
(sec θ + tan θ) (sec θ – tan θ) = 1
p. (sec θ – tan θ) = 1
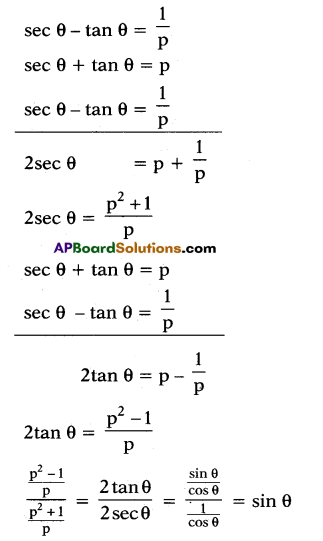
![]()
Question 27.
If cot θ = \(\frac{7}{8}\) then,
Evaluate :
i) \(\frac{(1+\sin \theta)(1-\sin \theta)}{(1+\cos \theta)(1-\cos \theta)}\)
ii) \(\frac{1+\cos \theta}{\sin \theta}\)
Solution:
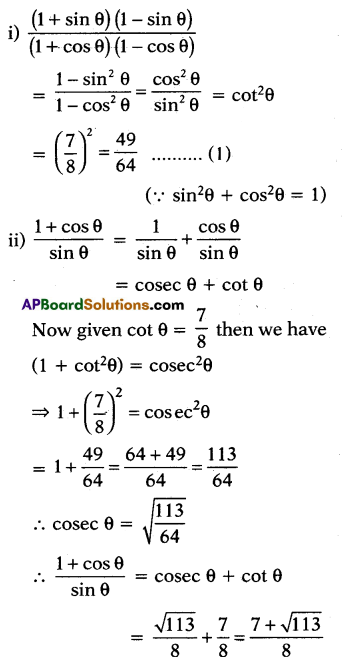
Question 28.
Show that
sec2 θ + cosec2 θ = sec2 θ . cosec2 θ.
Solution:
sec2 θ + cosec2 θ